On this page:
Parthenon Frieze Slideshow
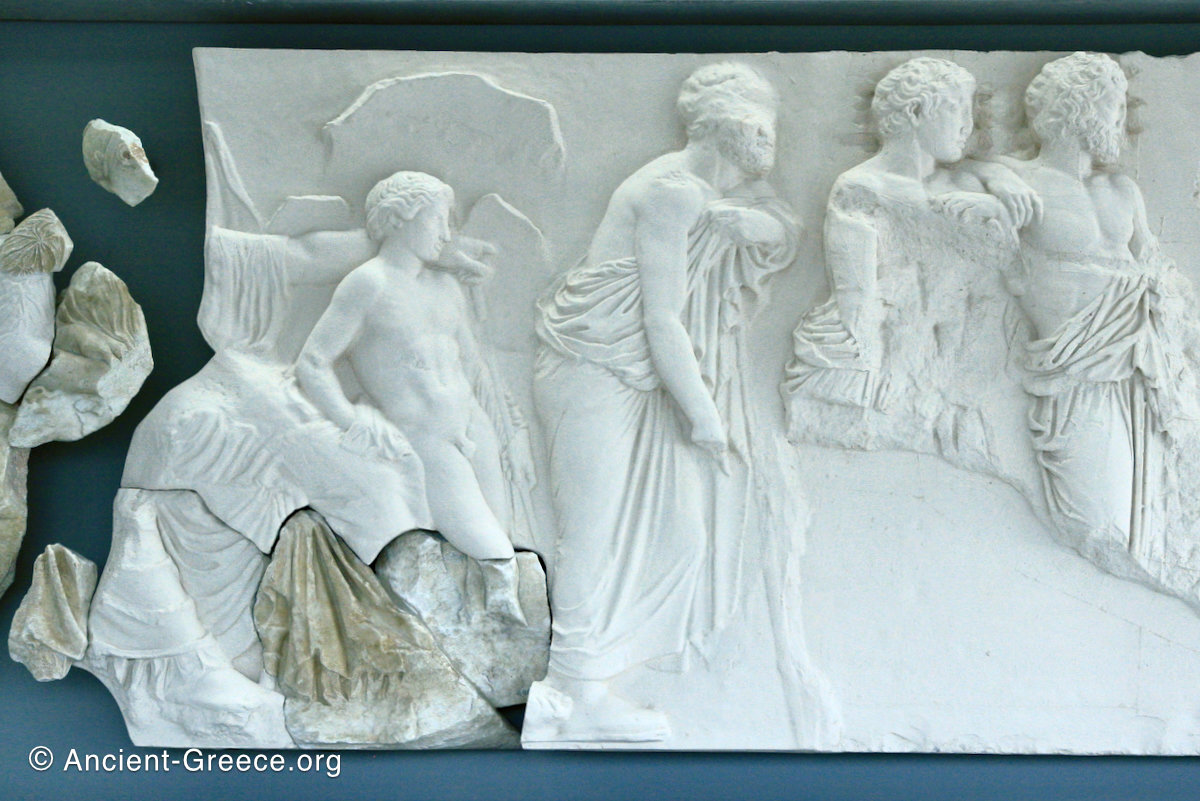
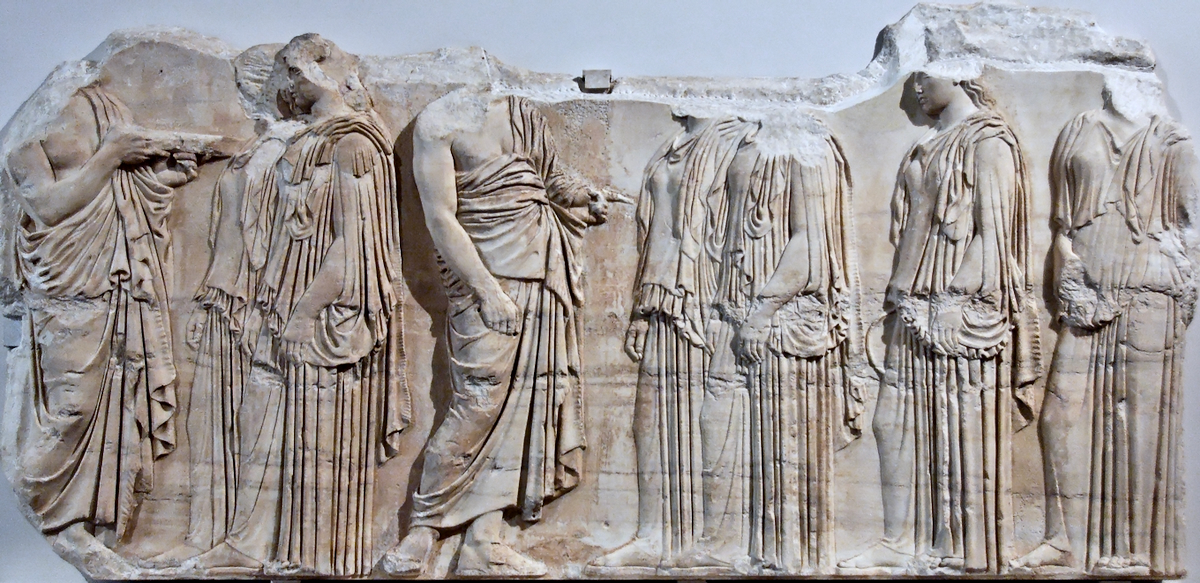
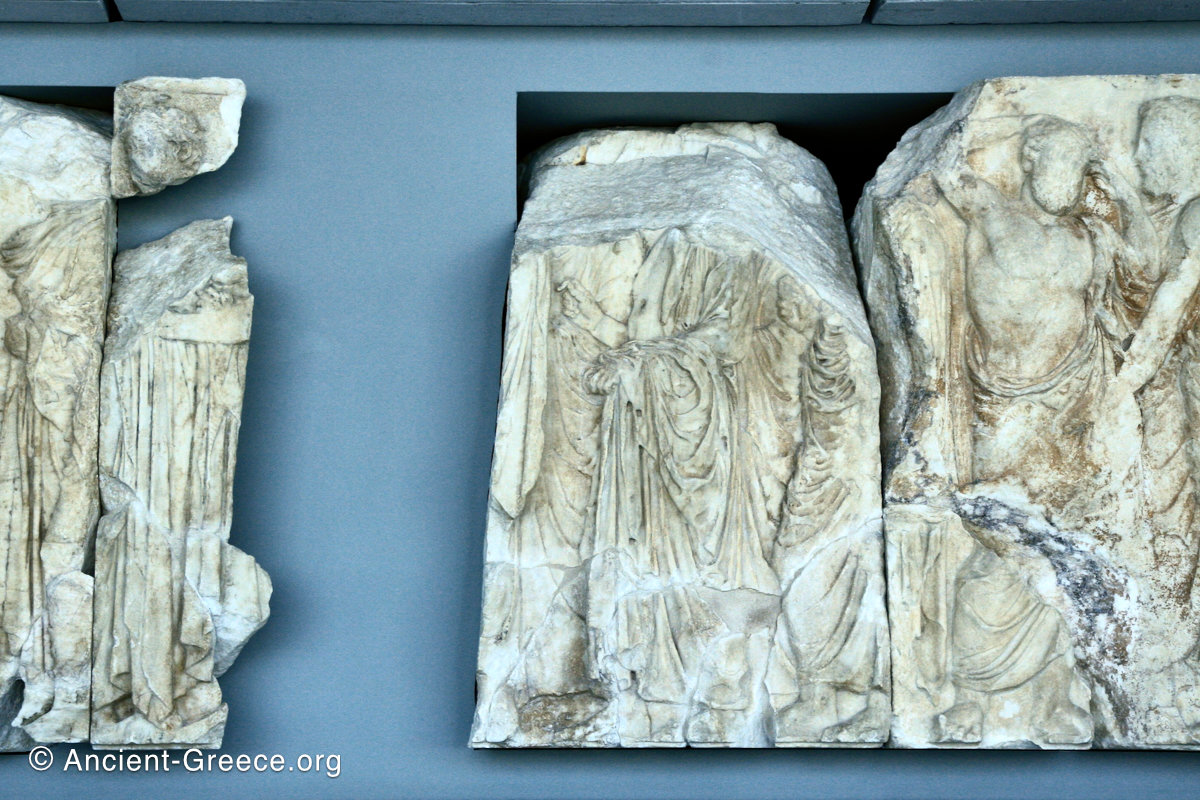
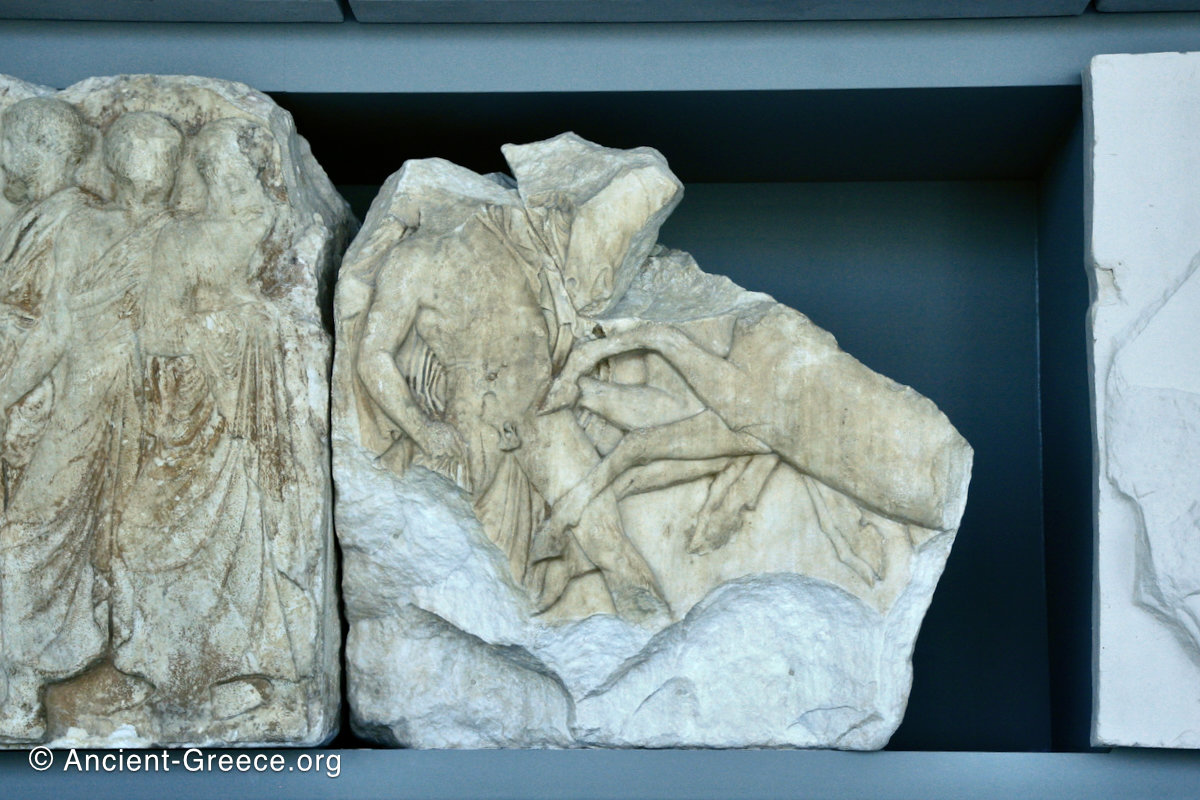
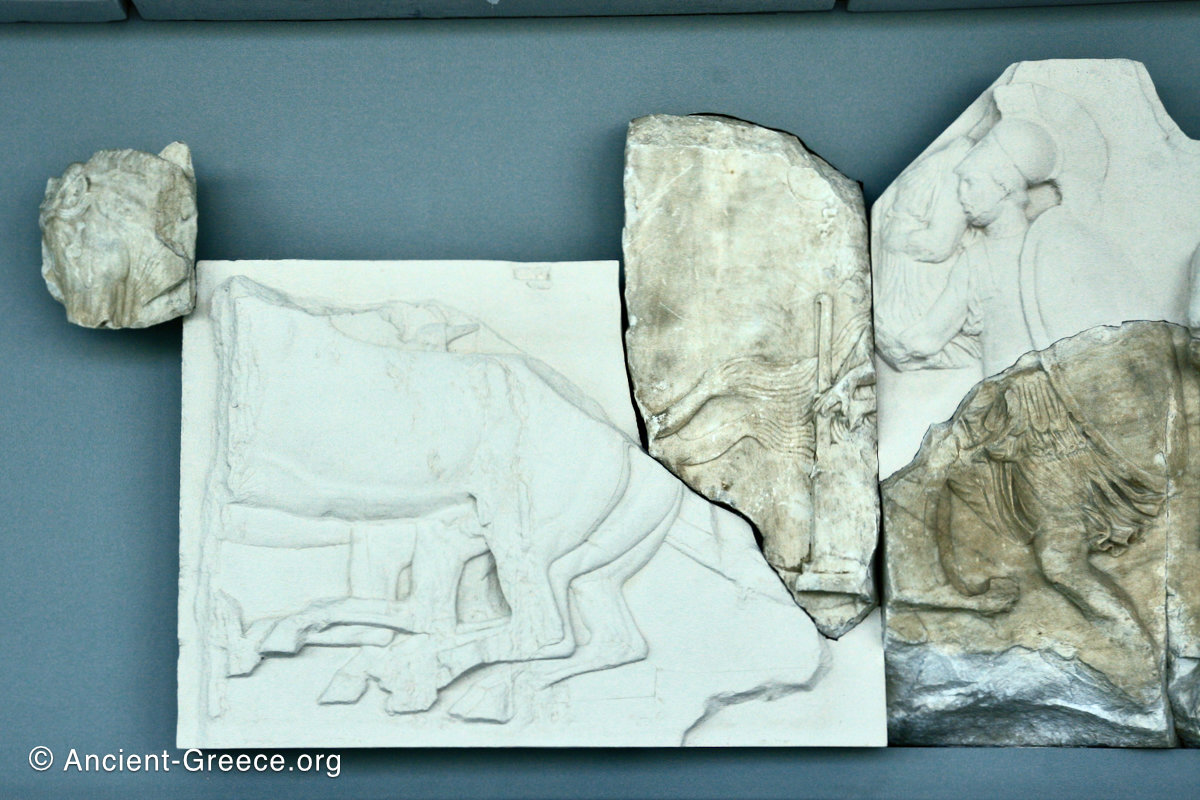
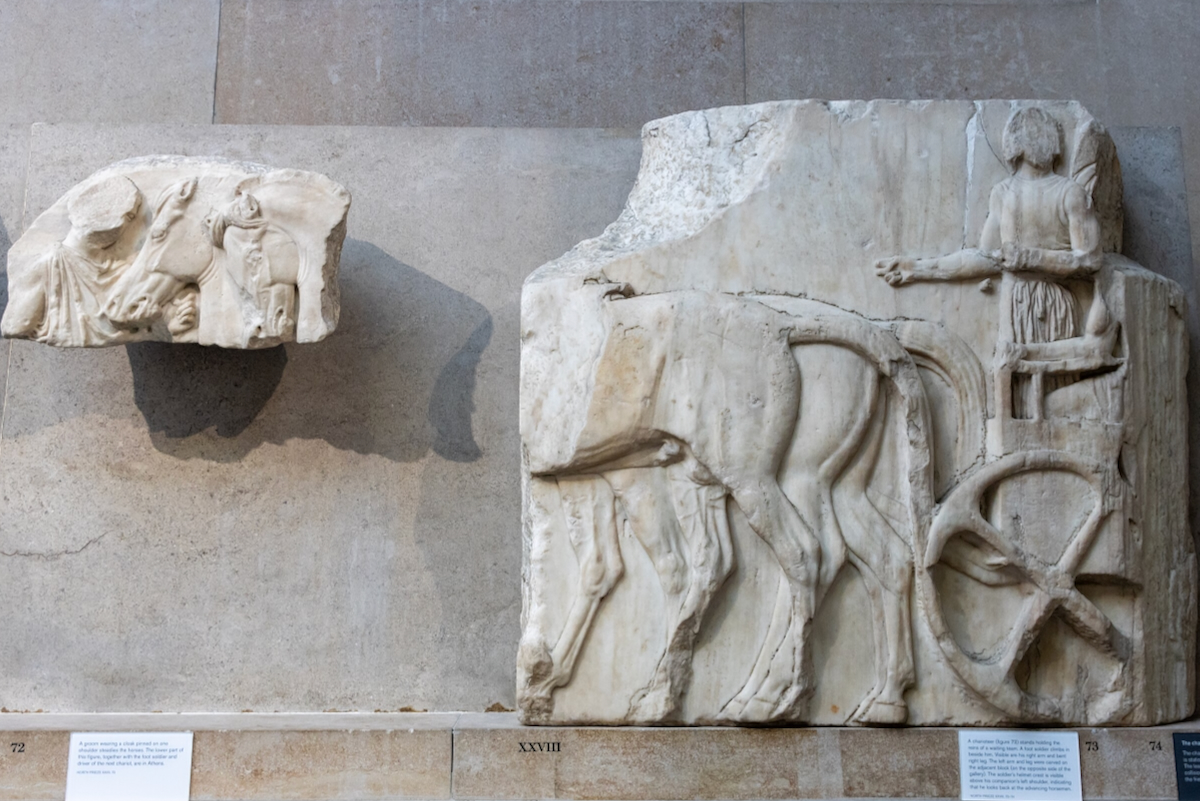
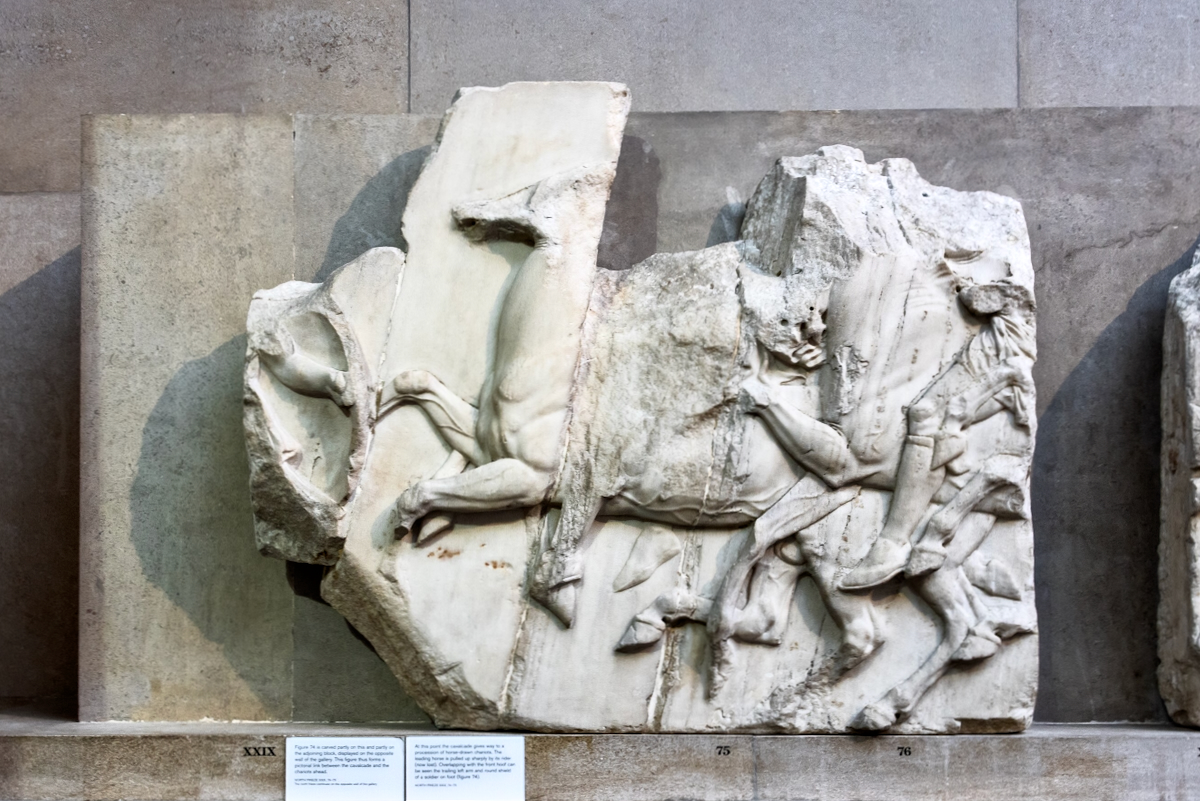
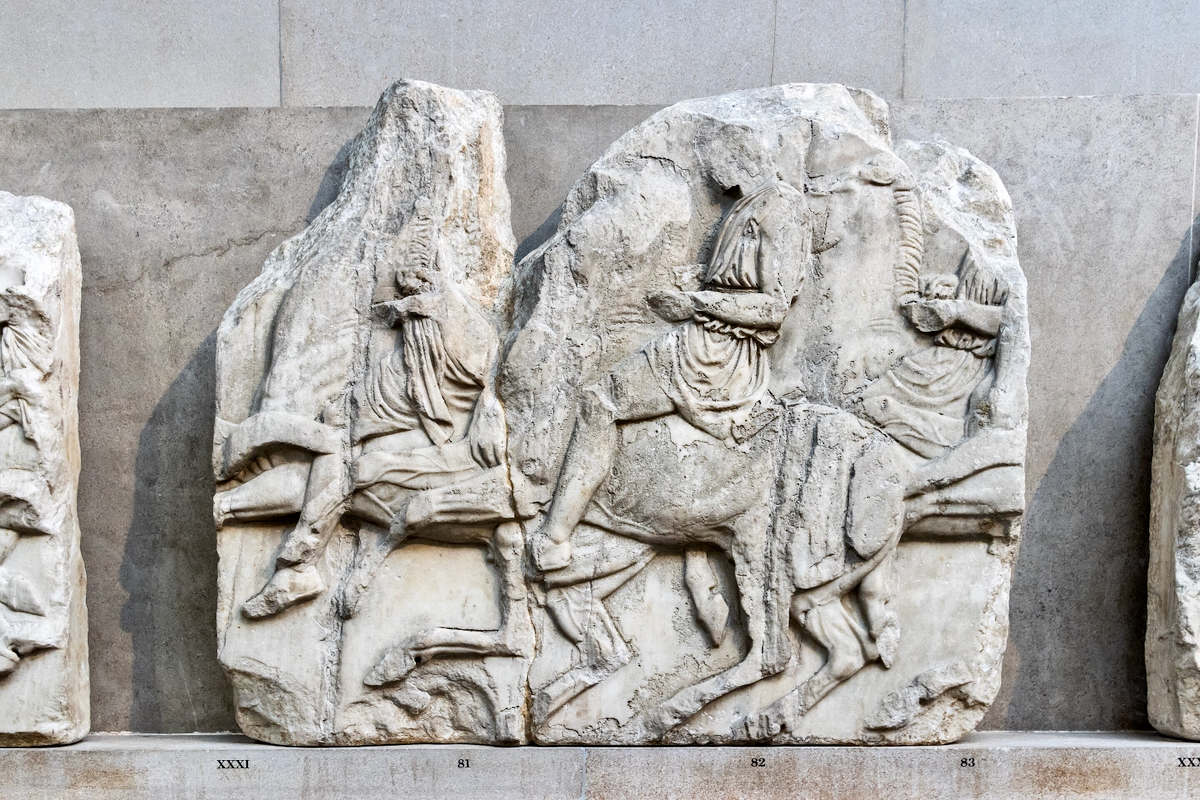
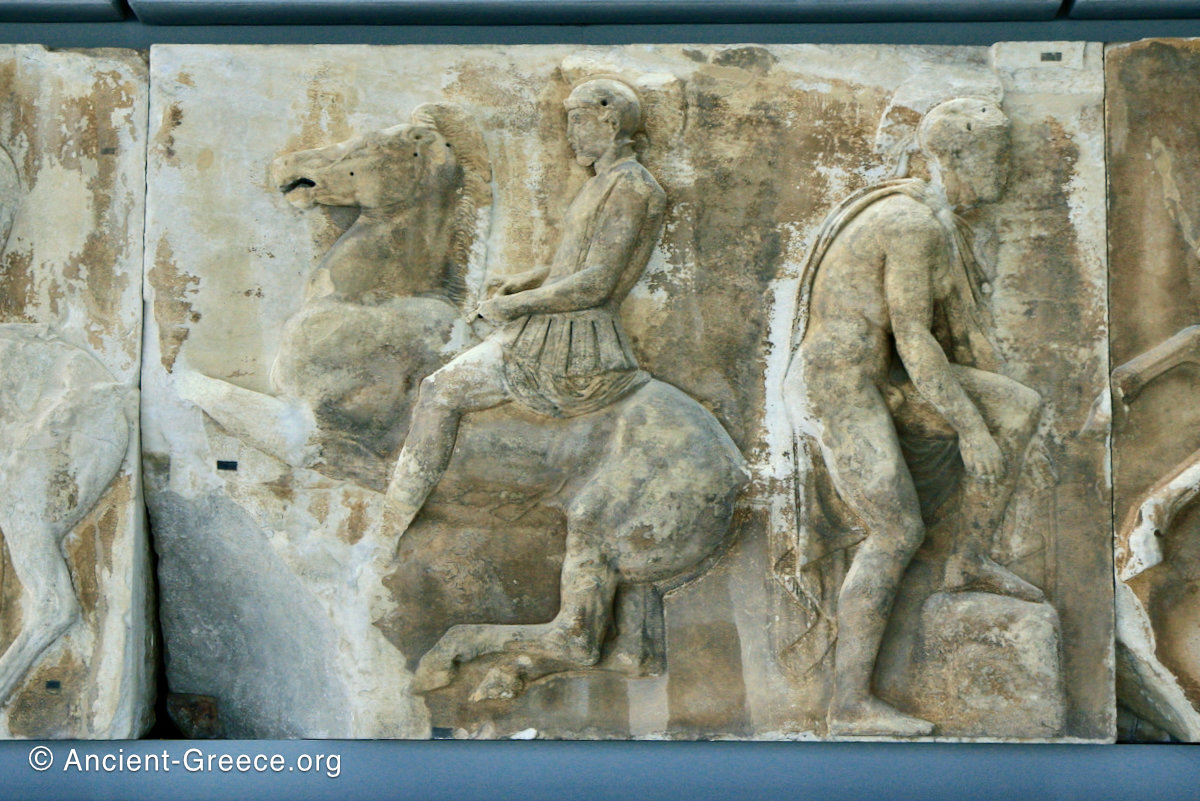
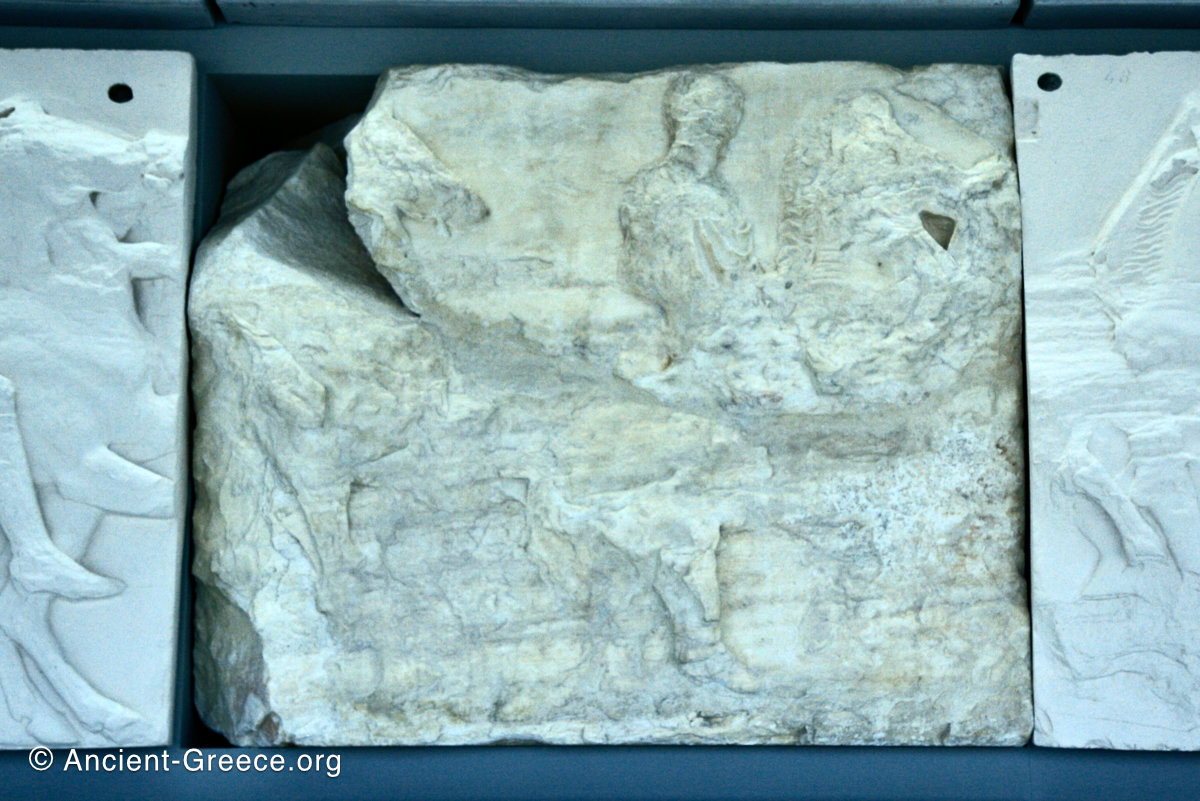
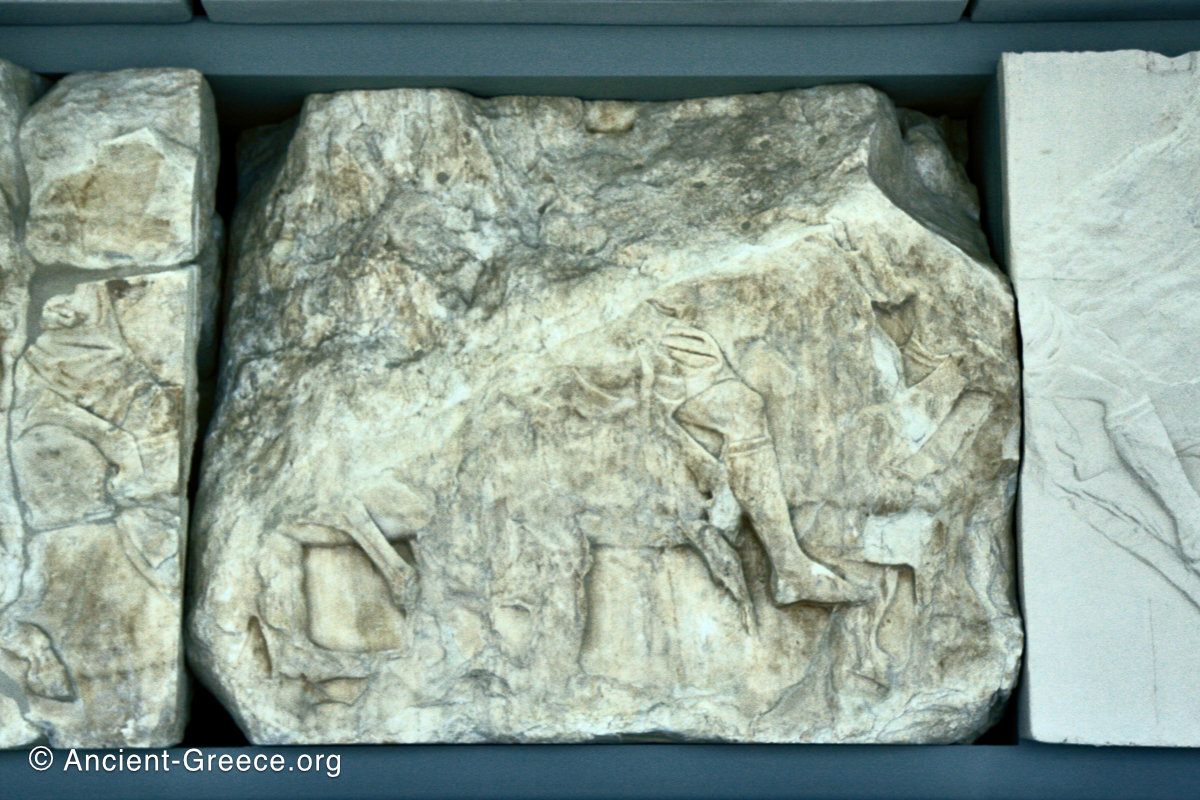
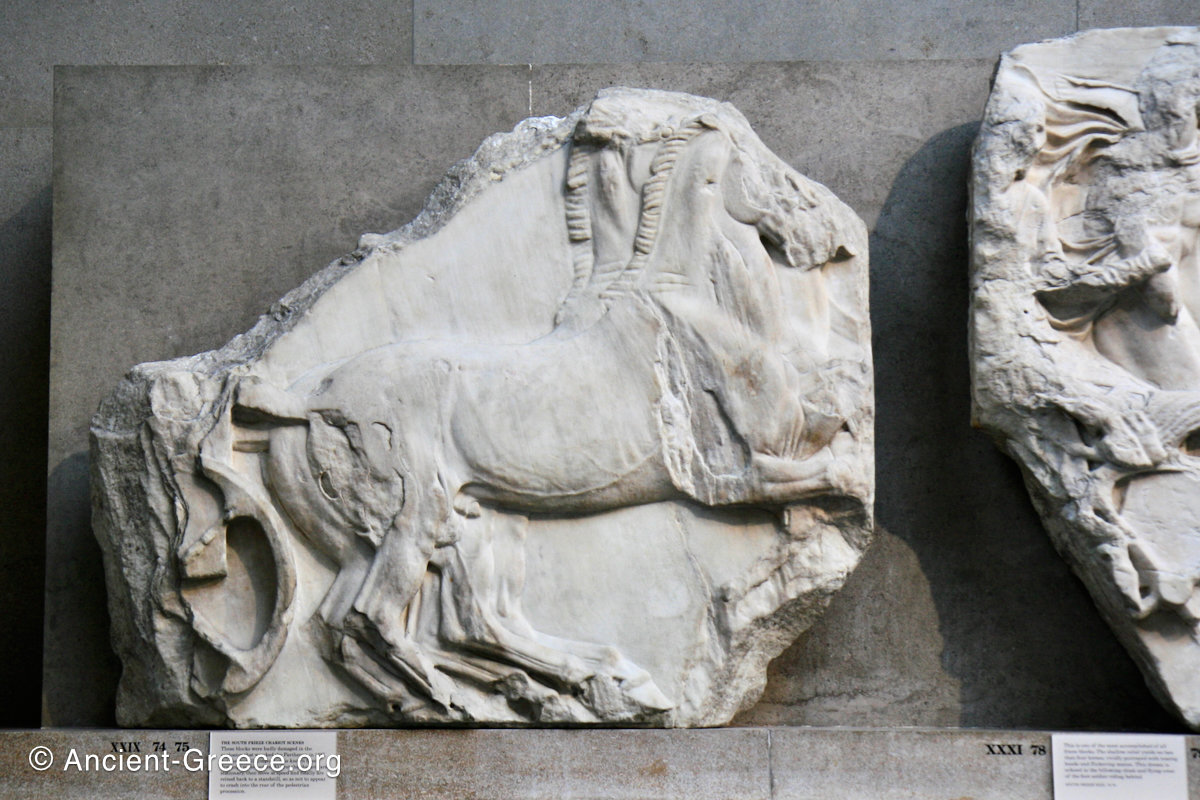
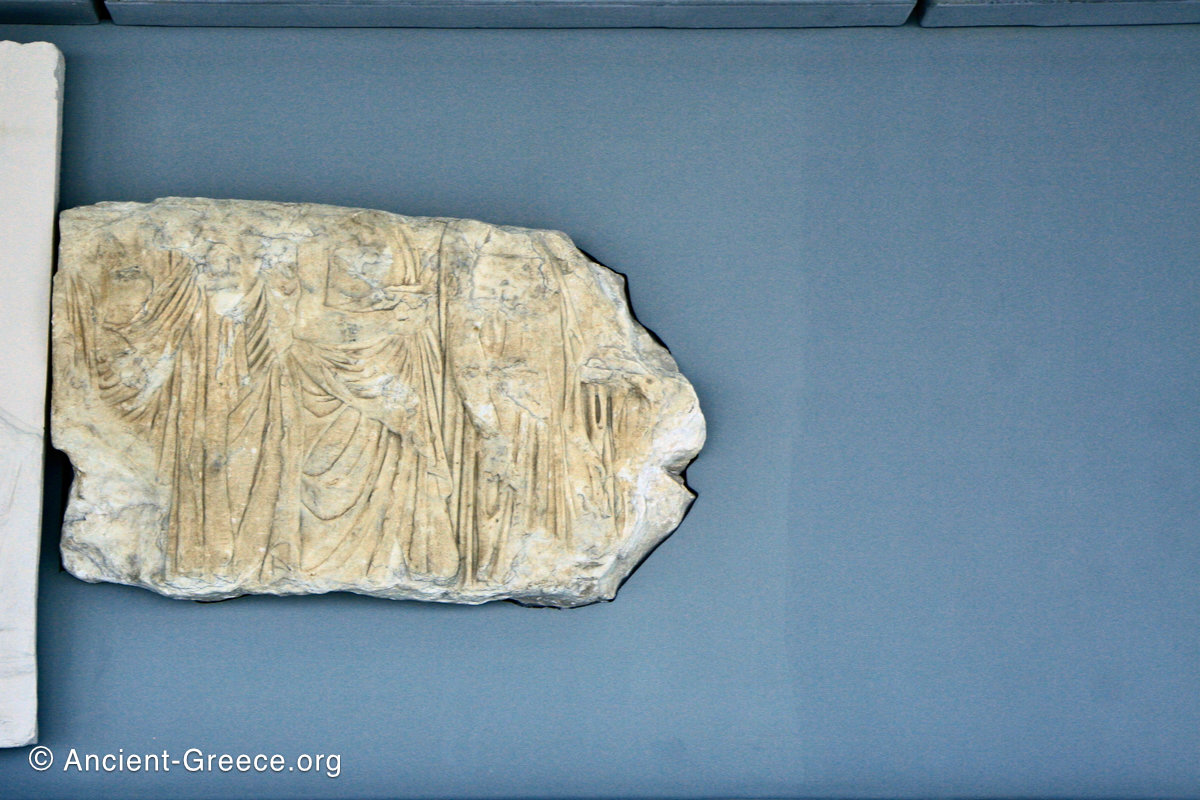
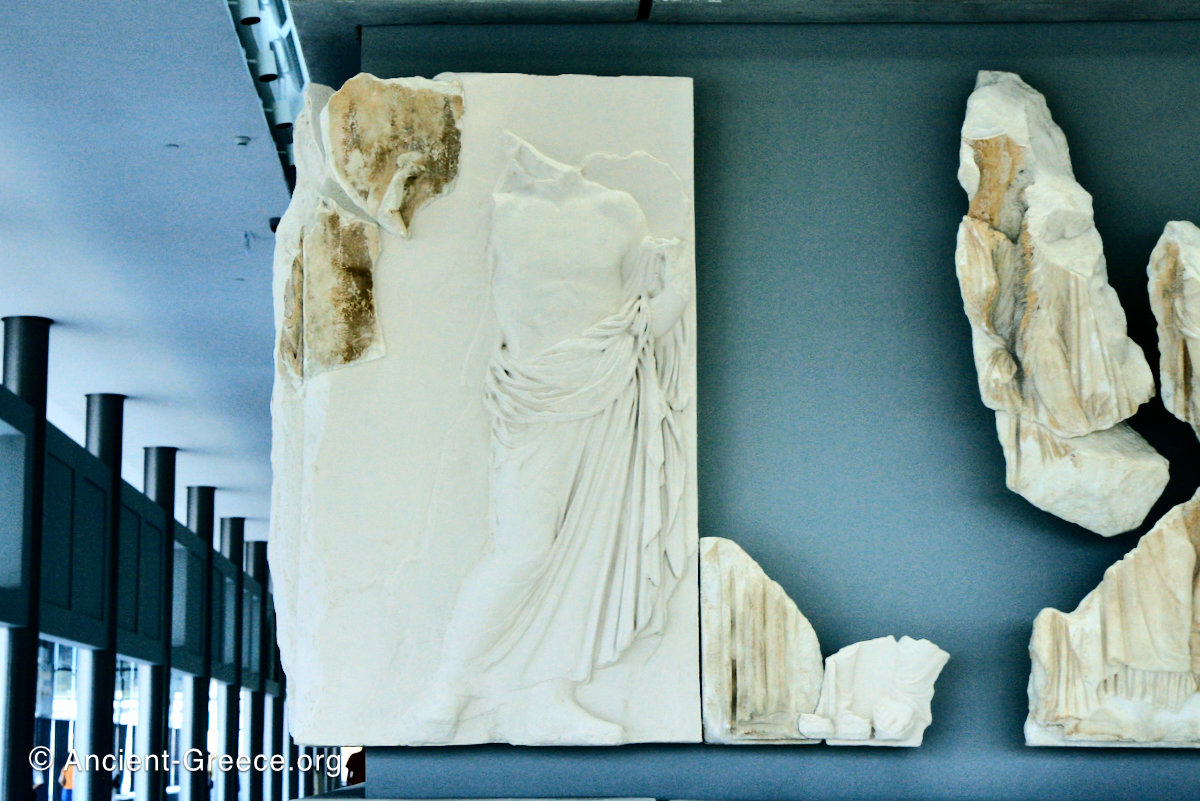
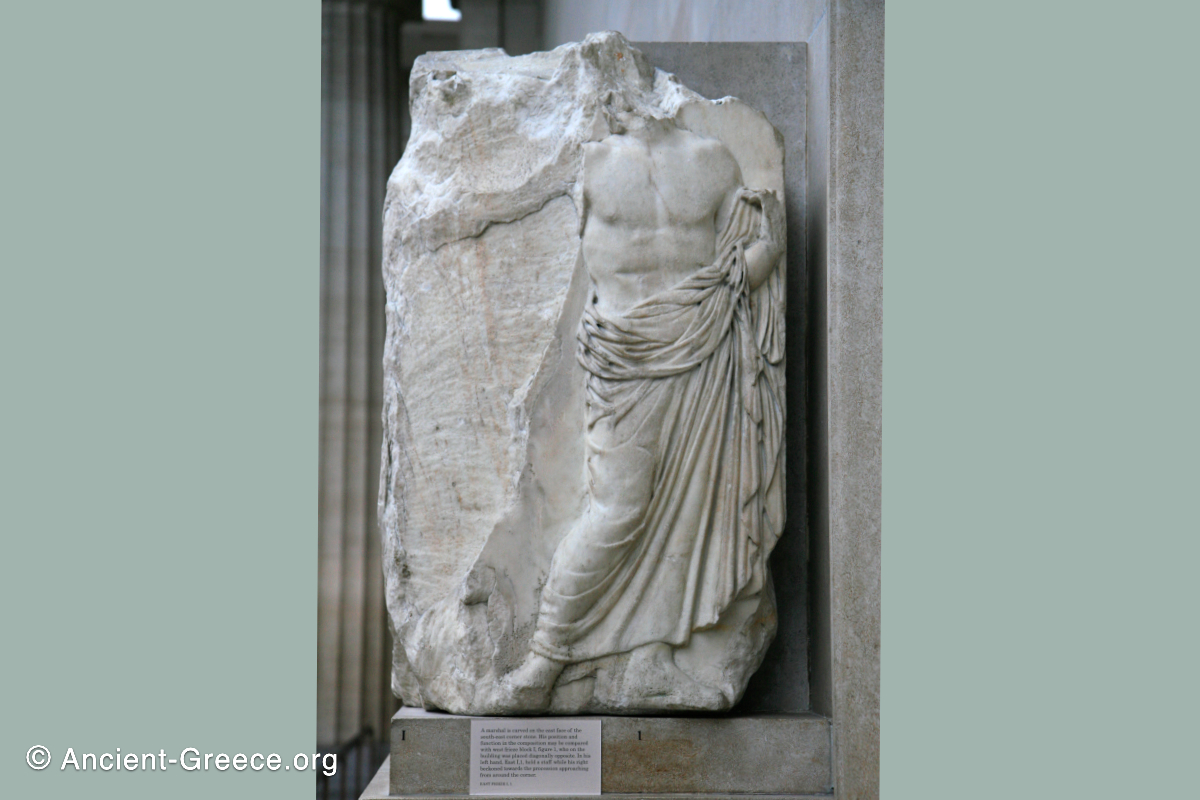
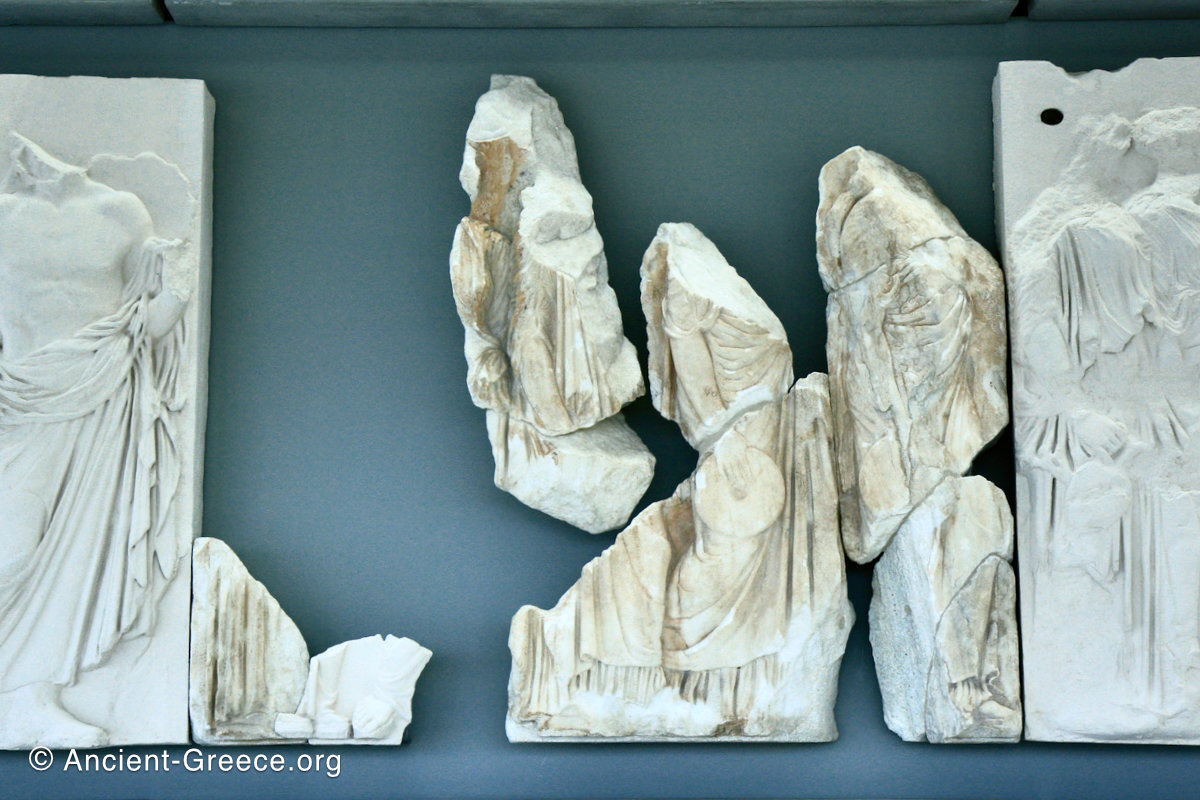
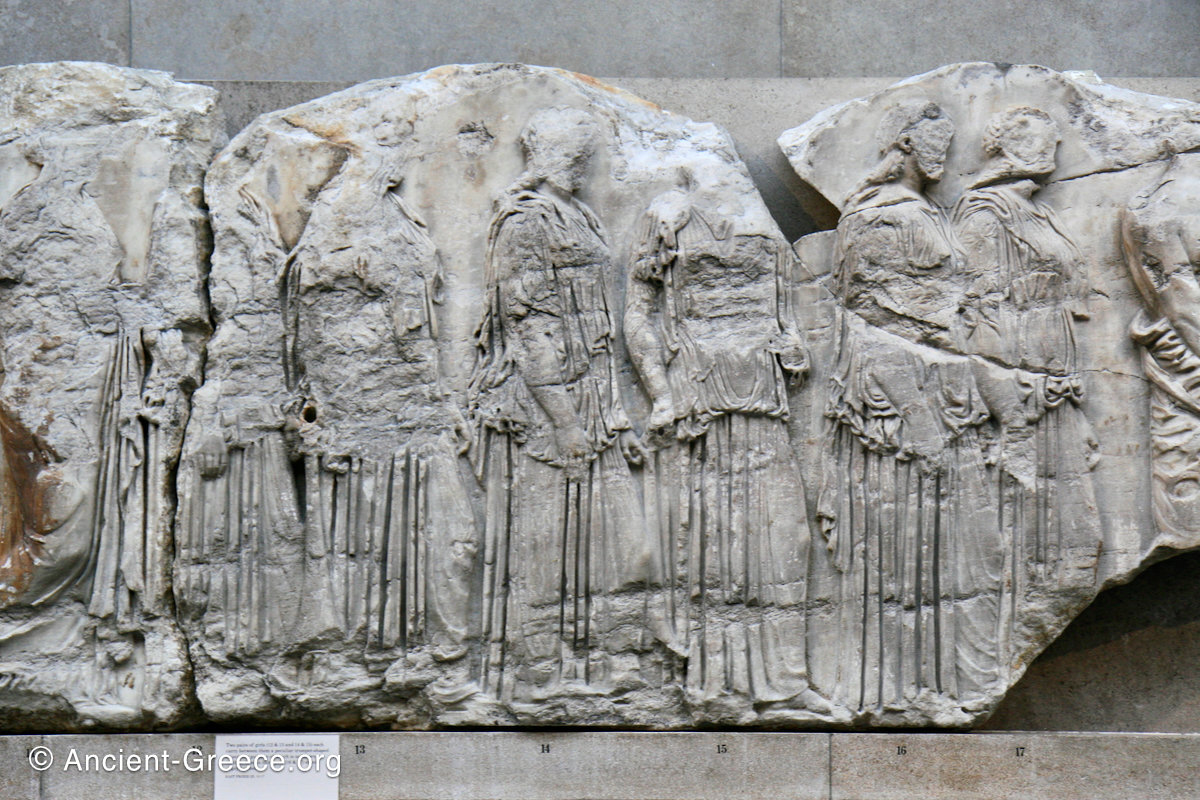
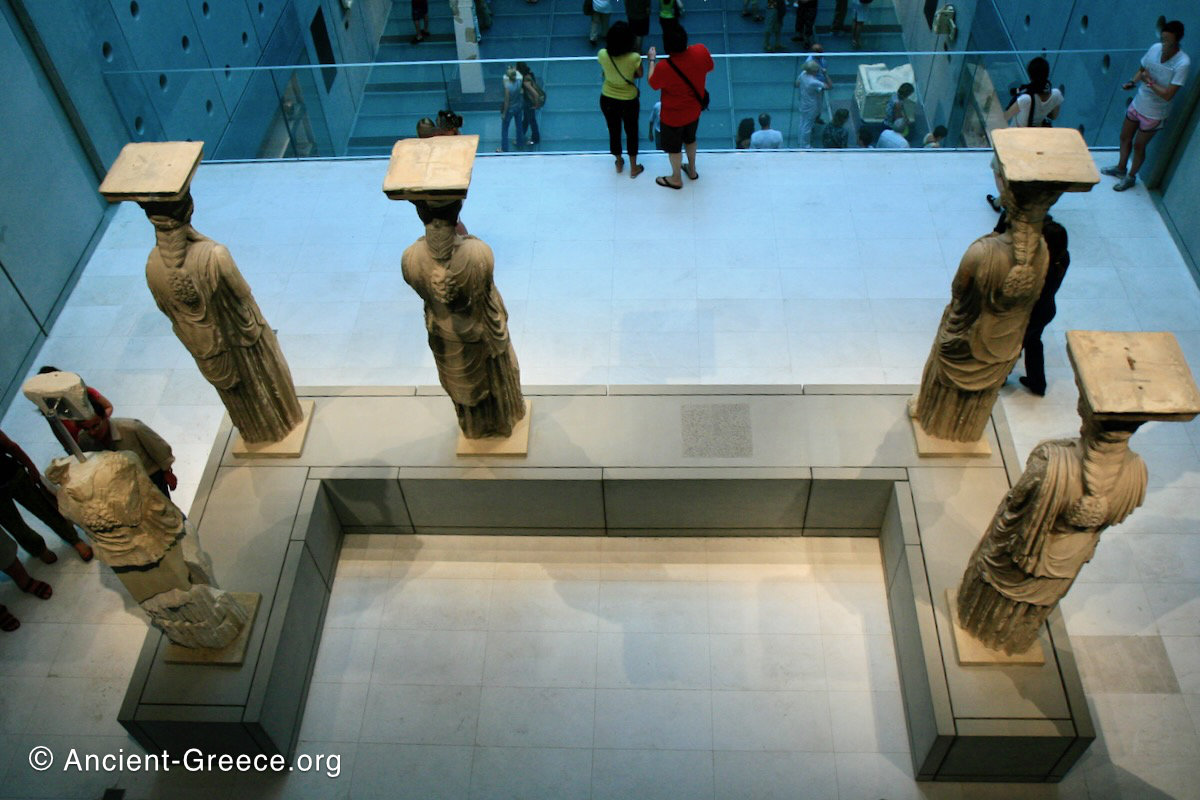
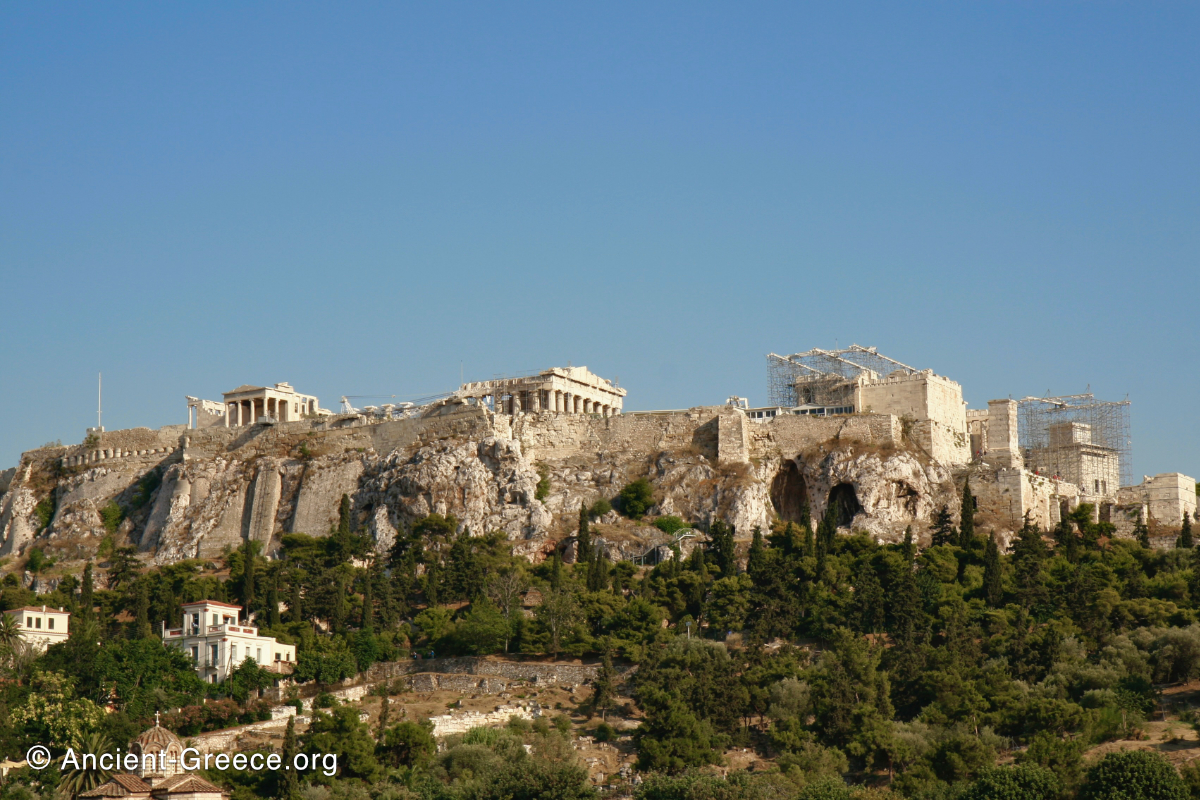
The Parthenon frieze is a continuous 1 meter high, 160 meters long, and 6 centimeters deep band of relief sculptures, created specifically to crown the entirety of the temple’s exterior wall.
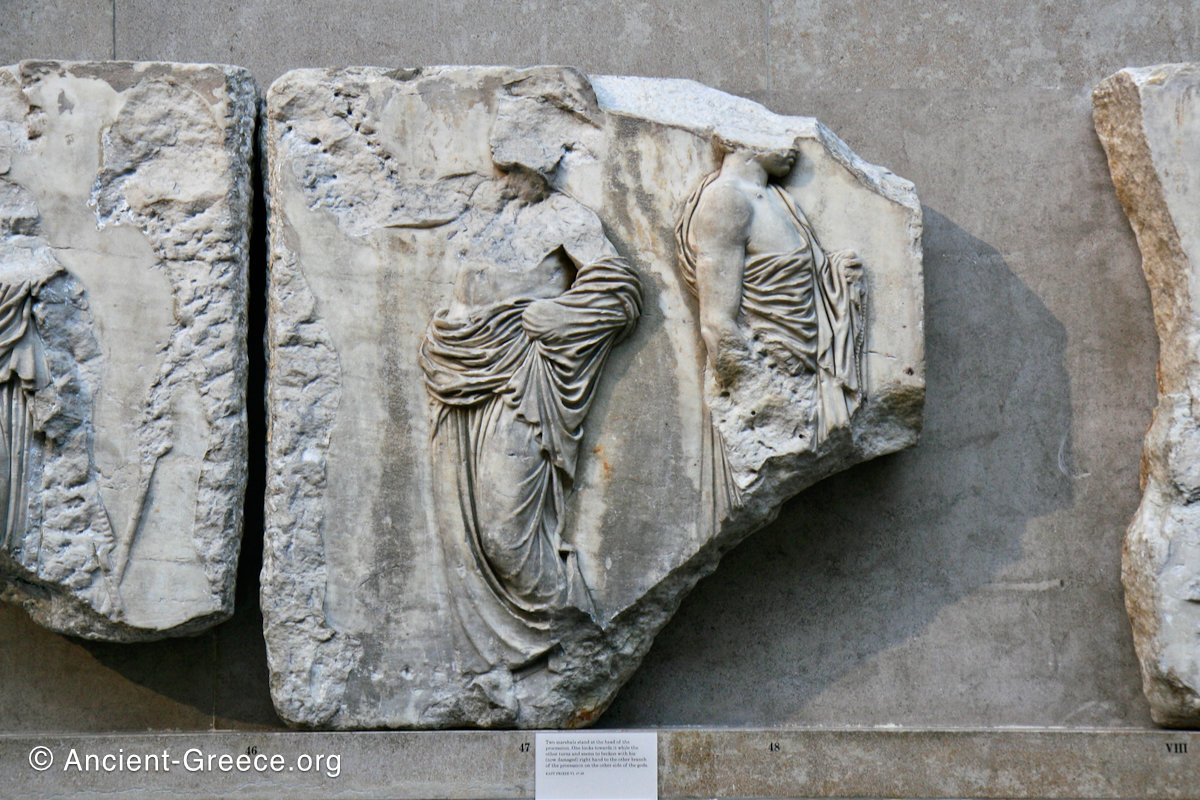
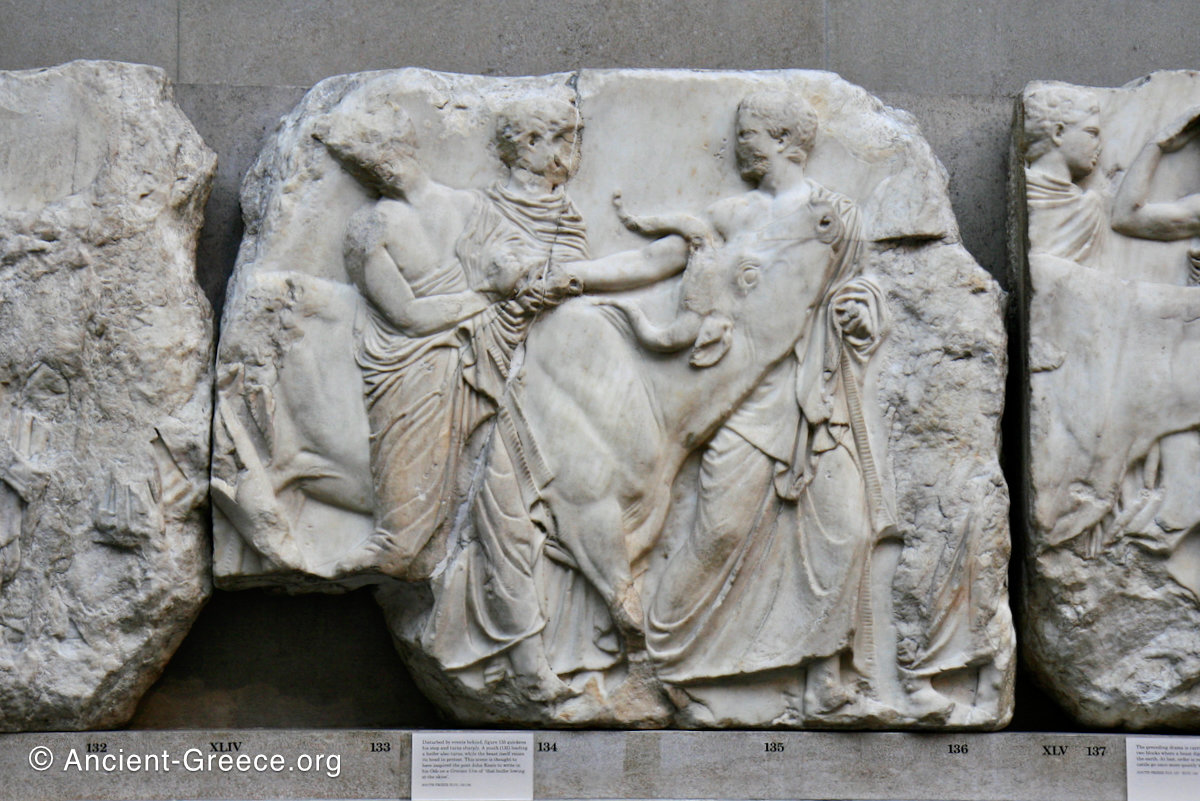
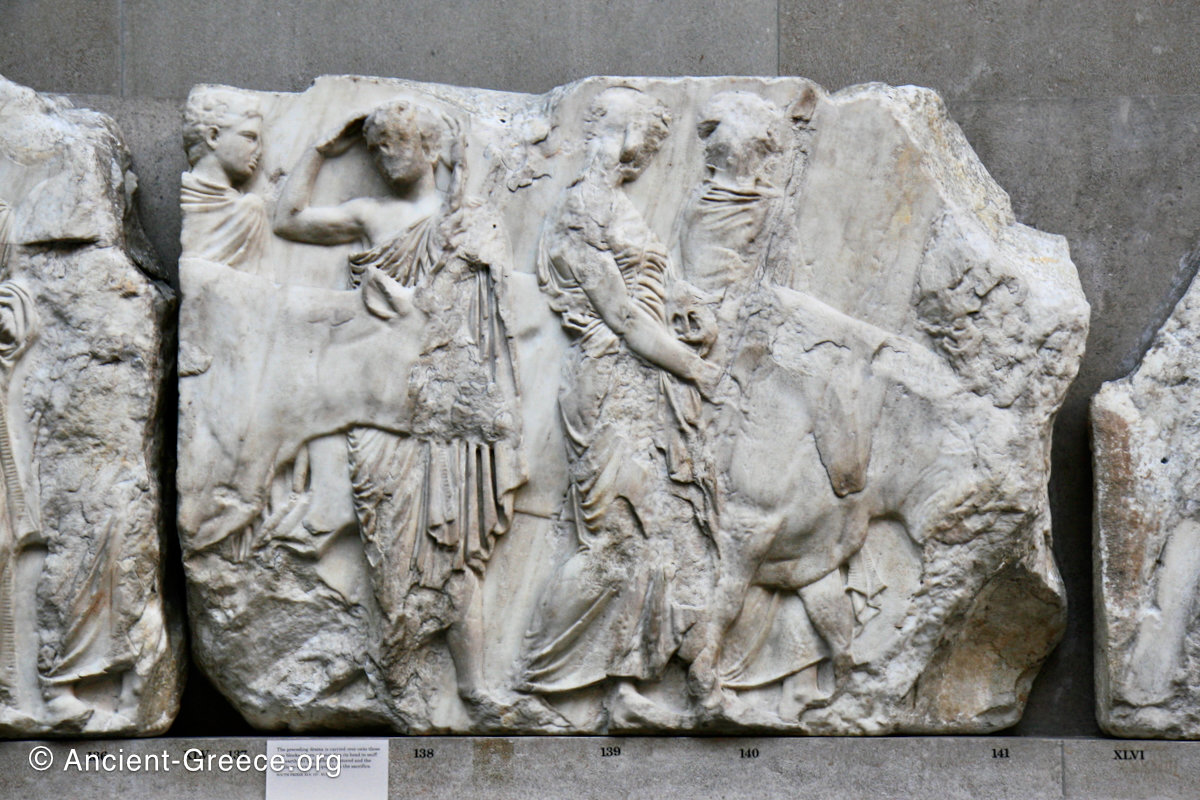
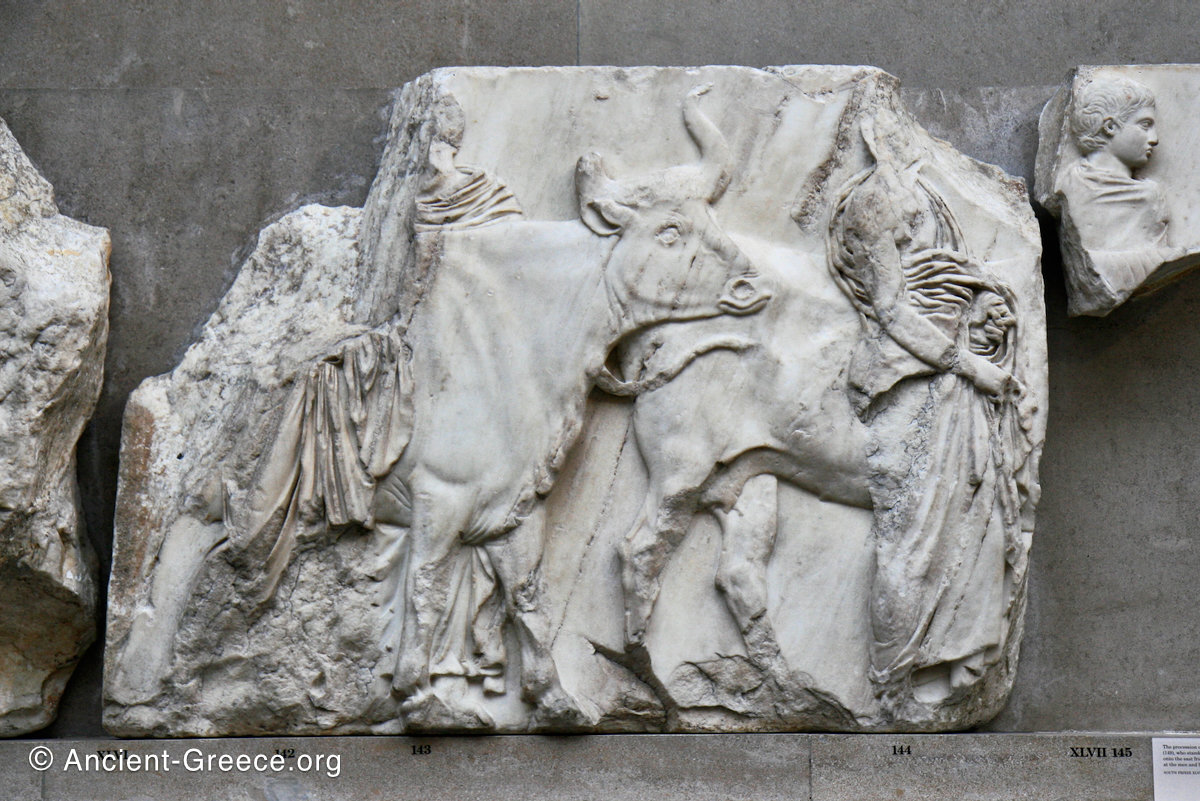
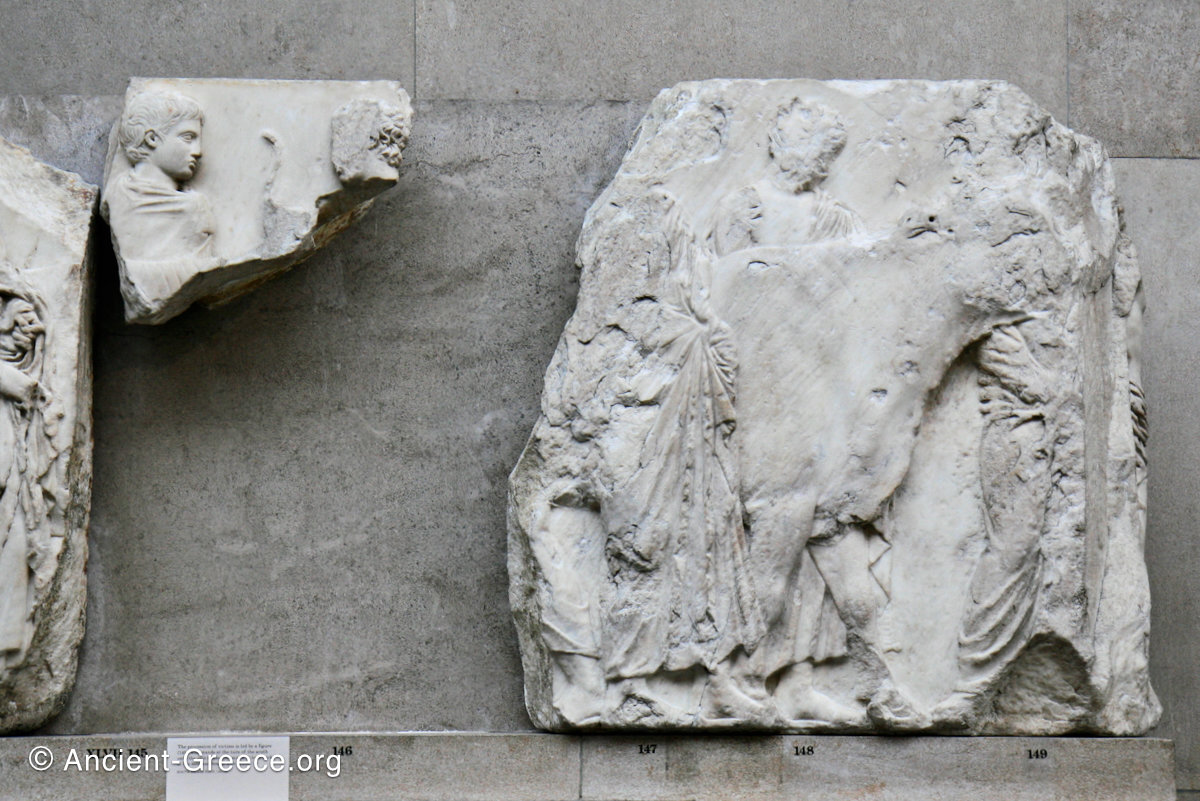
The sculptures are executed in low relief and depict the people of Athens in two processions that begin at the southwest corner and parade in opposite directions until they converge over the door of the cella at the east end of the Parthenon.
In ancient times all the sculptures as well as the buildings were vividly painted and were embellished with metal attachments in the form of spears, swords, horse reins and other appropriate accessories. In its original state, the frieze must have been dazzling with its an array of bronze accessories and colored surfaces high on the temple’s exterior wall, where it was deprived of direct sunlight until the temple’s roof collapse in the destructive fire during the Herulian invasion in 267 CE.
In the 6th century CE, the Parthenon was converted into a church with its roof covering only the ancient cella (the main interior of the ancient temple), leaving the pteroma (the long corridors between the colonnade and the exterior wall of the cella) exposed to the sky. Sections of the frieze were removed at that time to make openings for windows.
In 1180 CE, Church renovations removed the central section of the entablature, including the central scene of the east frieze and the pediment to create an enlarged apse.
Today, fragments of the Parthenon frieze are found in the Acropolis Museum in Athens, the British Museum in London, in Paris, Copenhagen, Munich, Vienna and Würzburg.
Main Theme
The majority of scholars agree that the Parthenon frieze represents the Panathenaic procession, which was a central festival in Athens during Classical times.
The iconography of the frieze and context makes this interpretation highly probable. A small controversy remains with some scholars debating whether it represents an ideal or a specific Panathenaic procession.
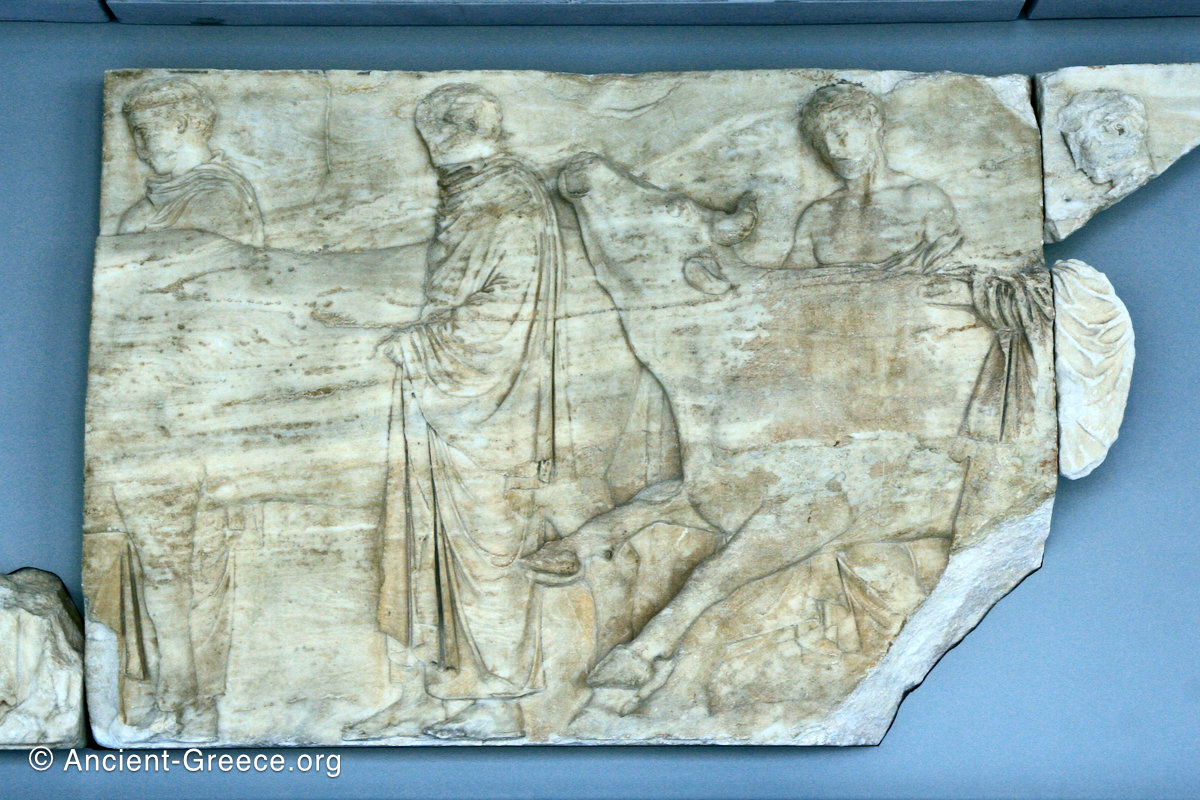
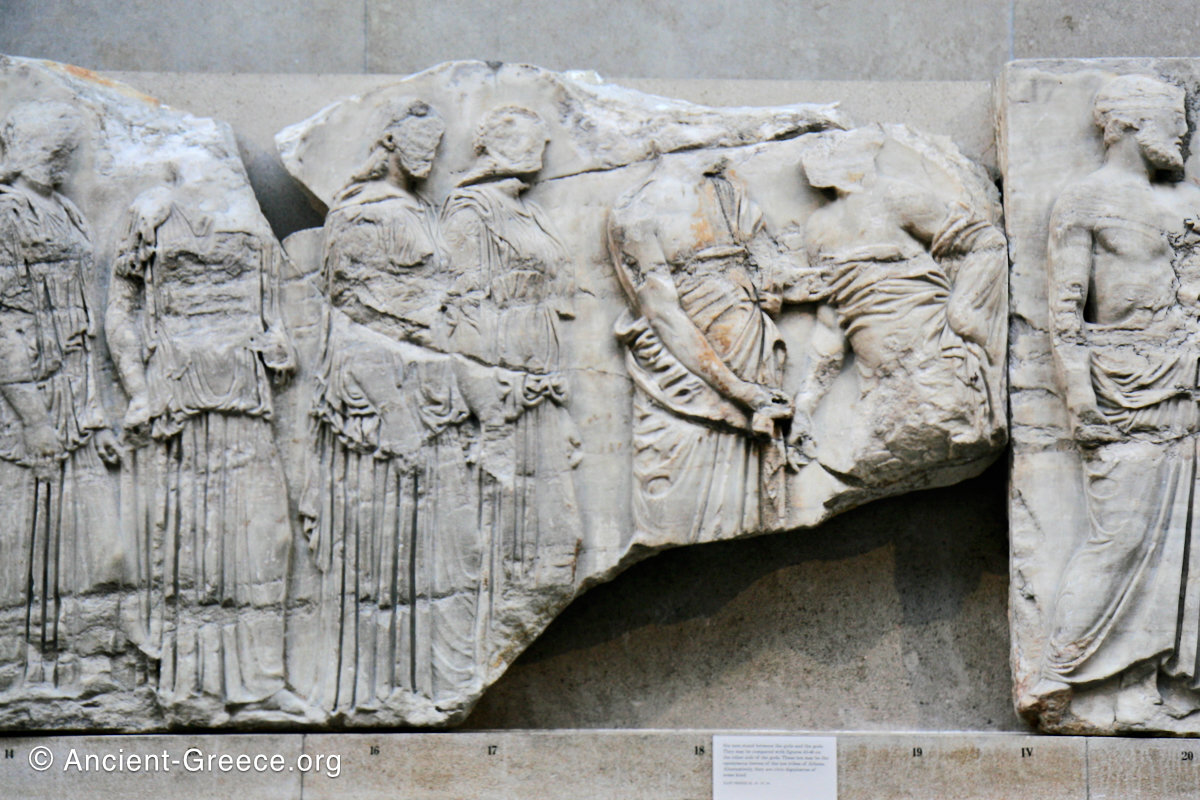
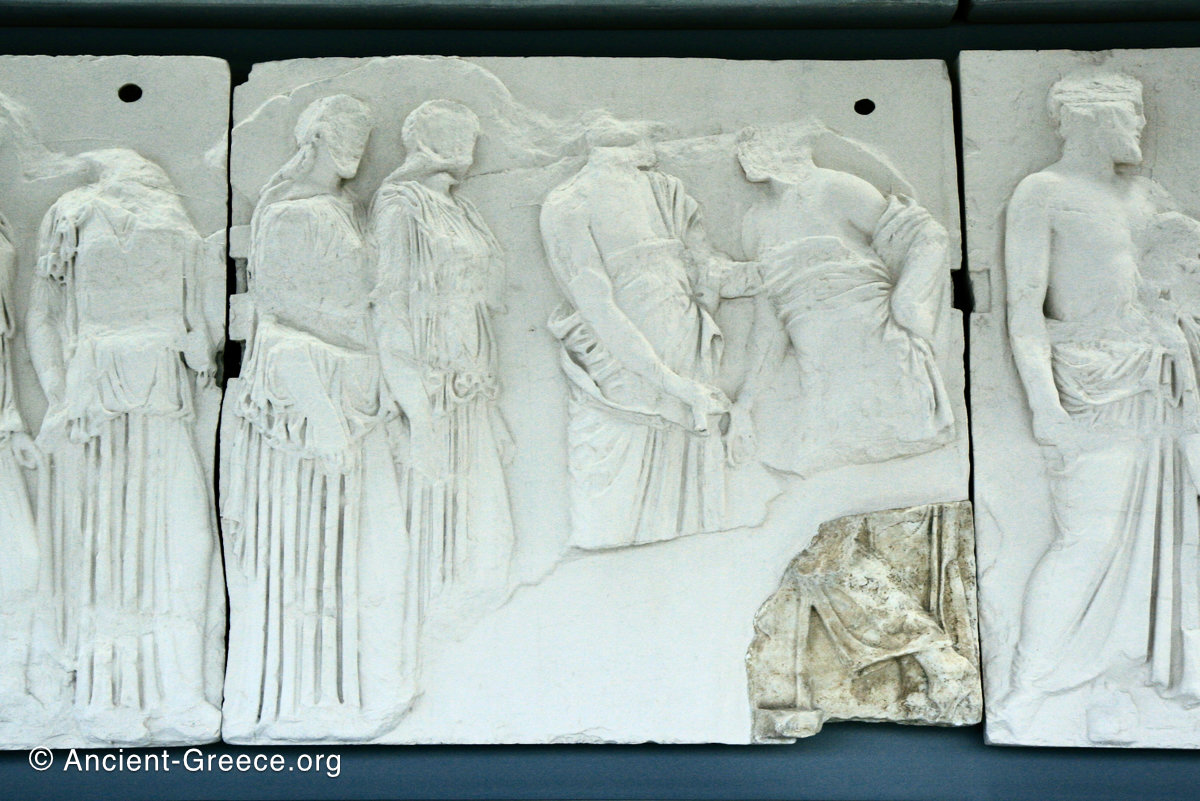
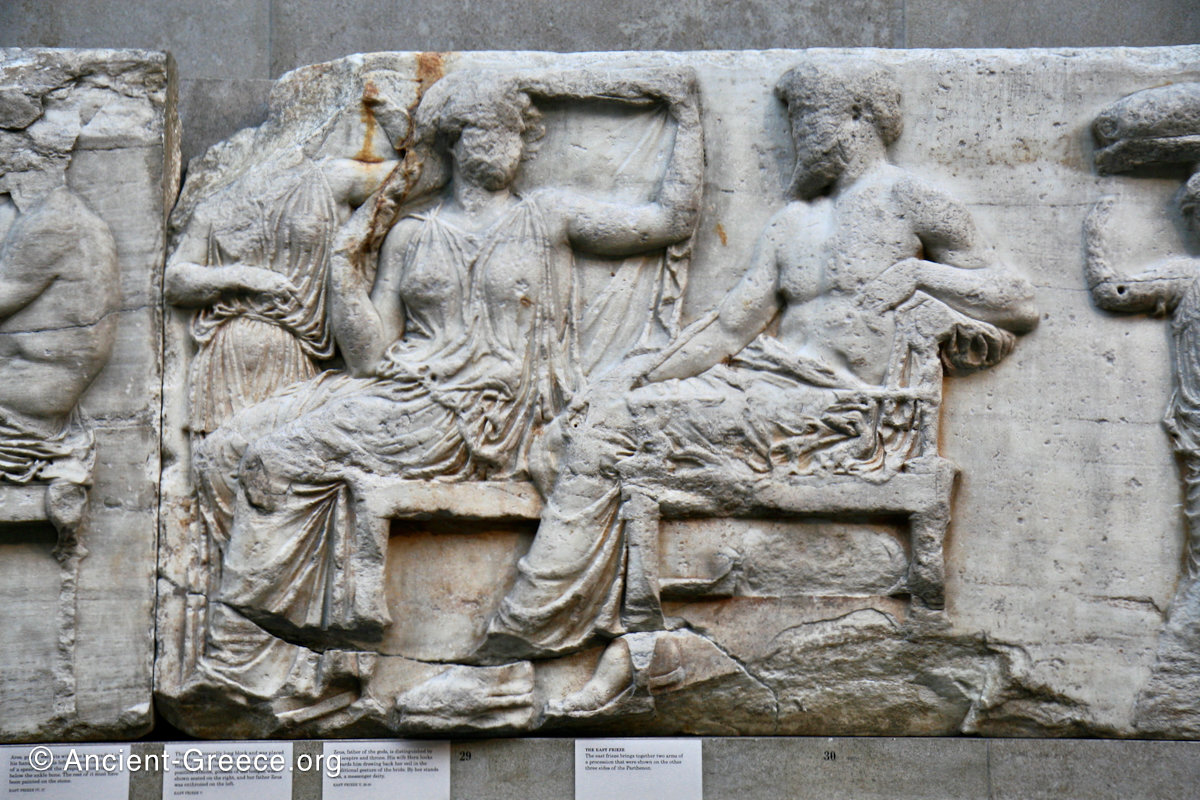
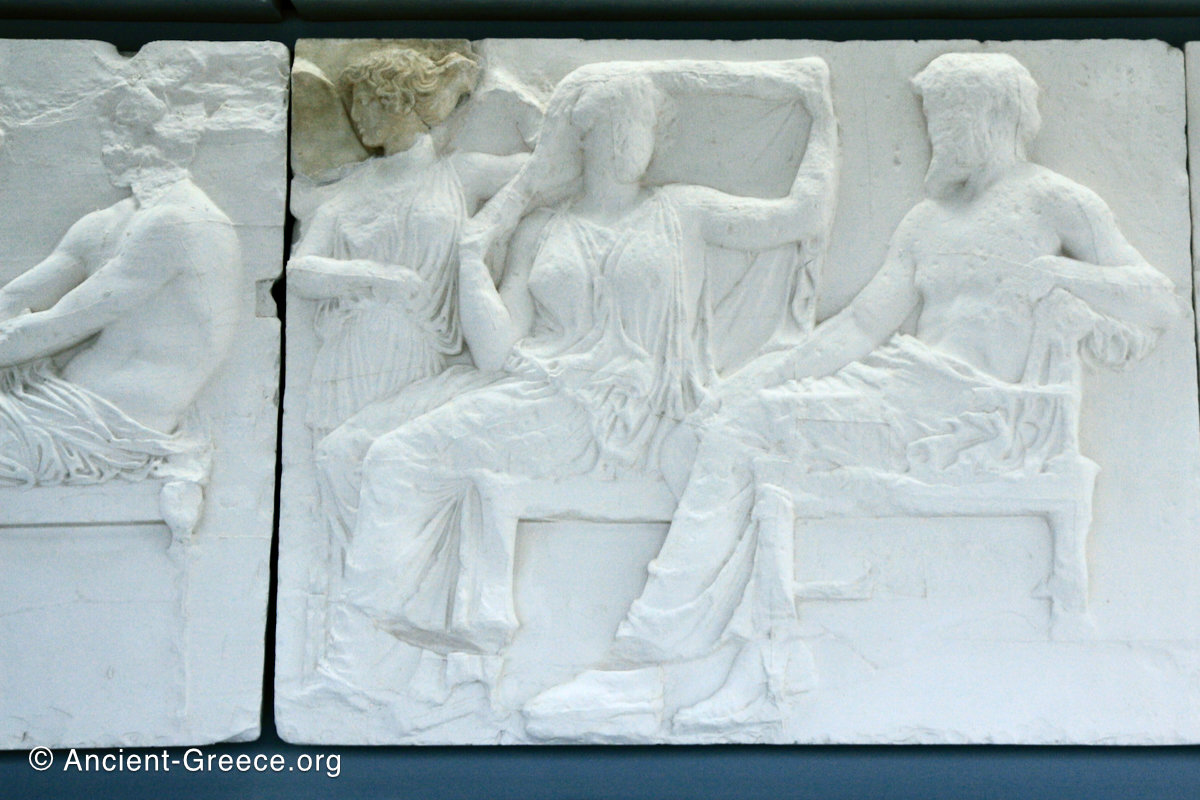
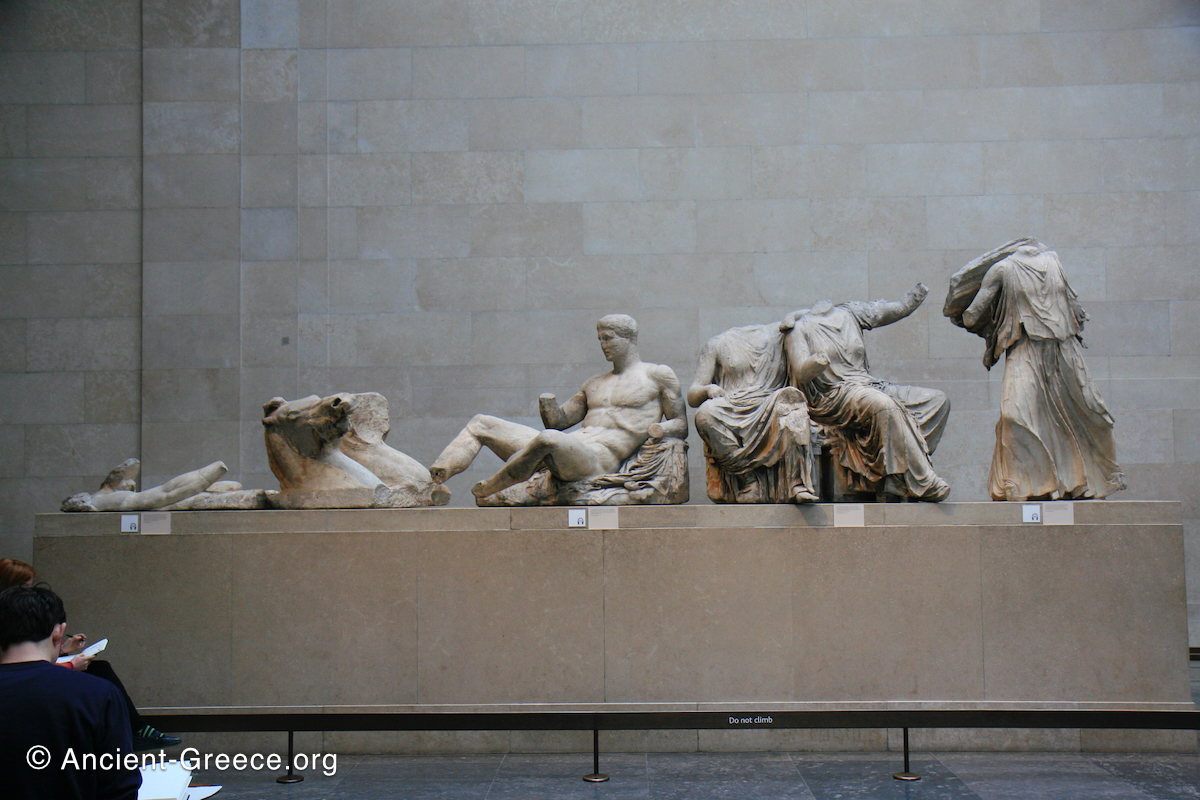
East Frieze: The Central Scene
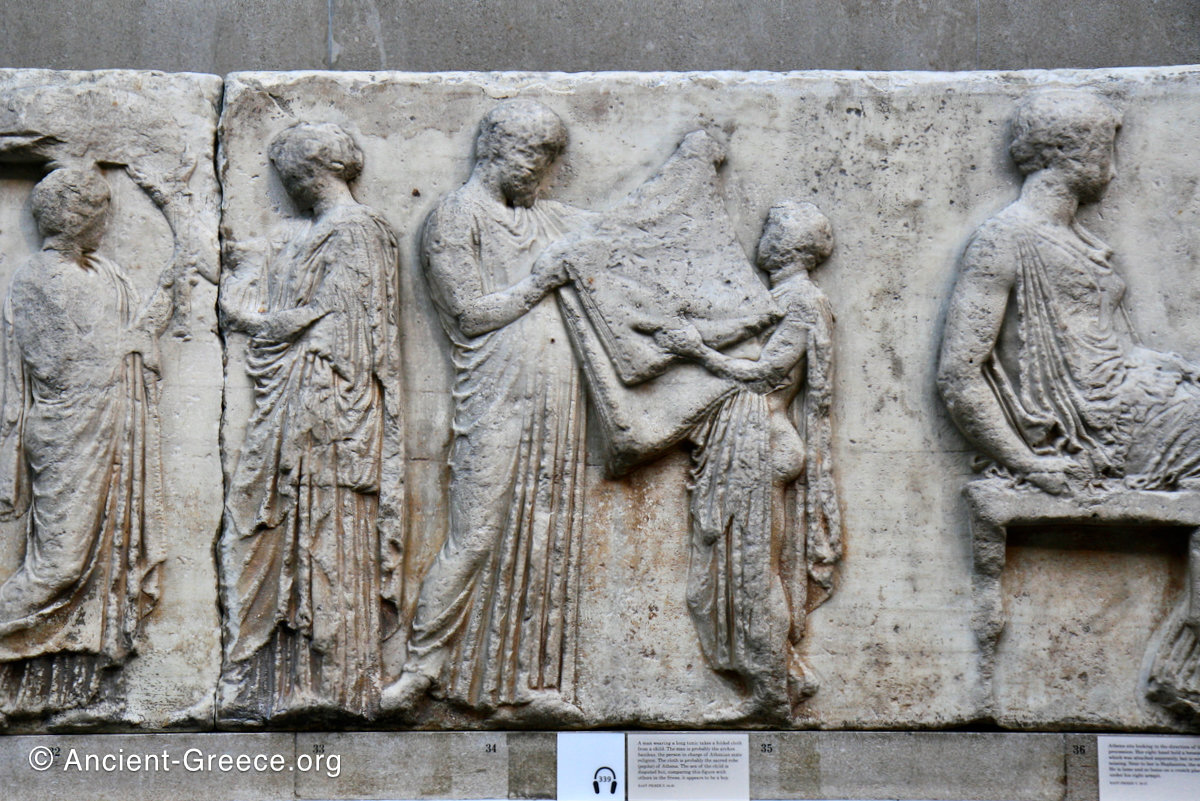
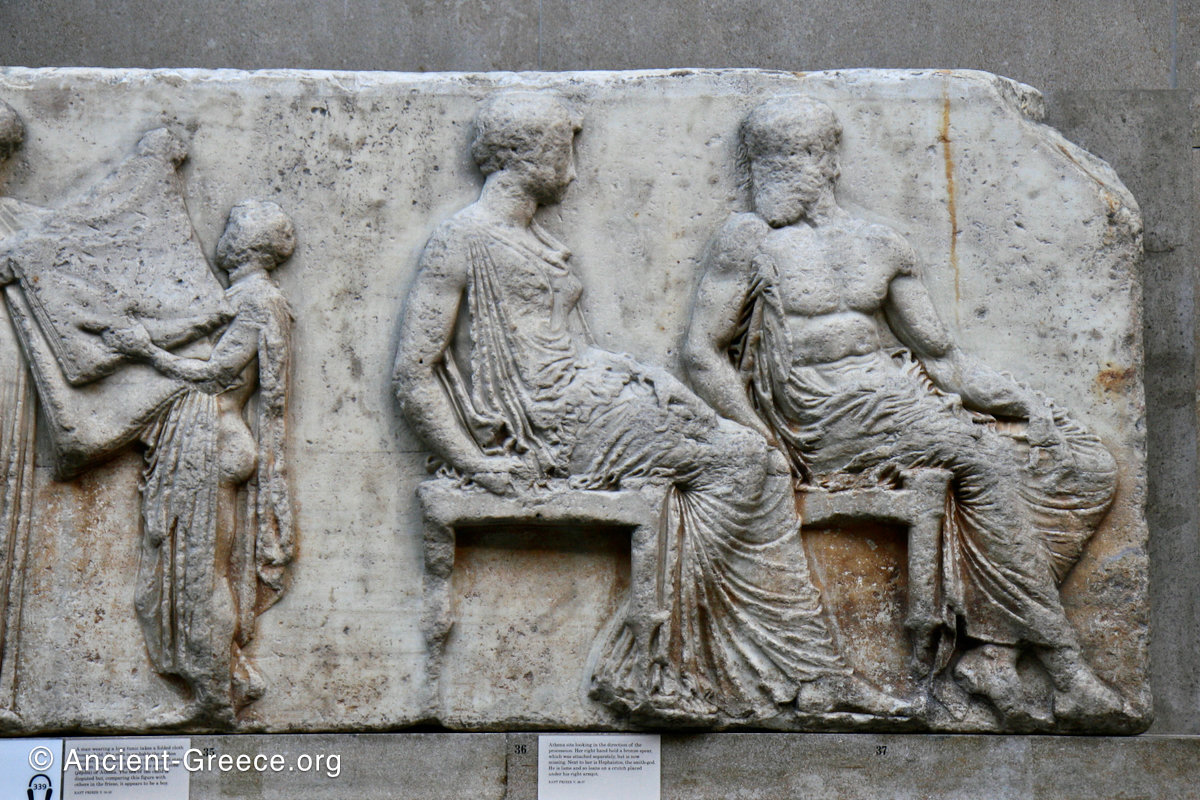
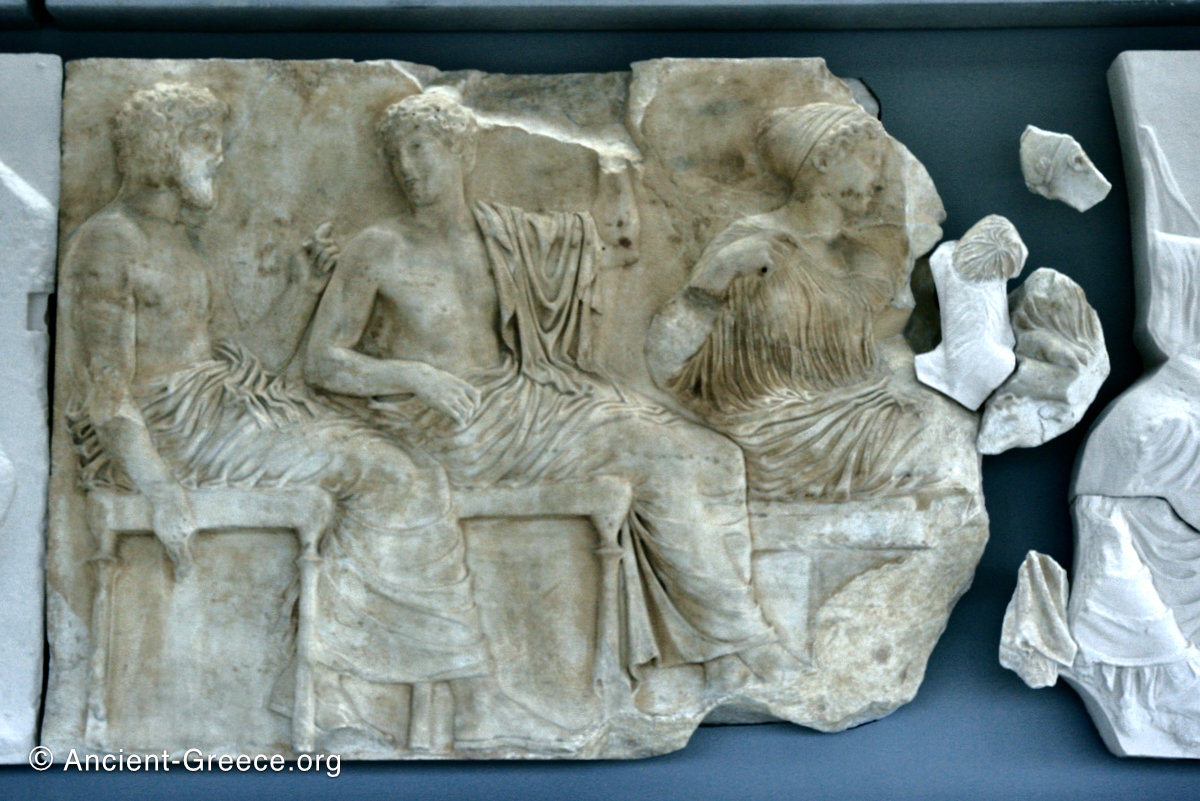
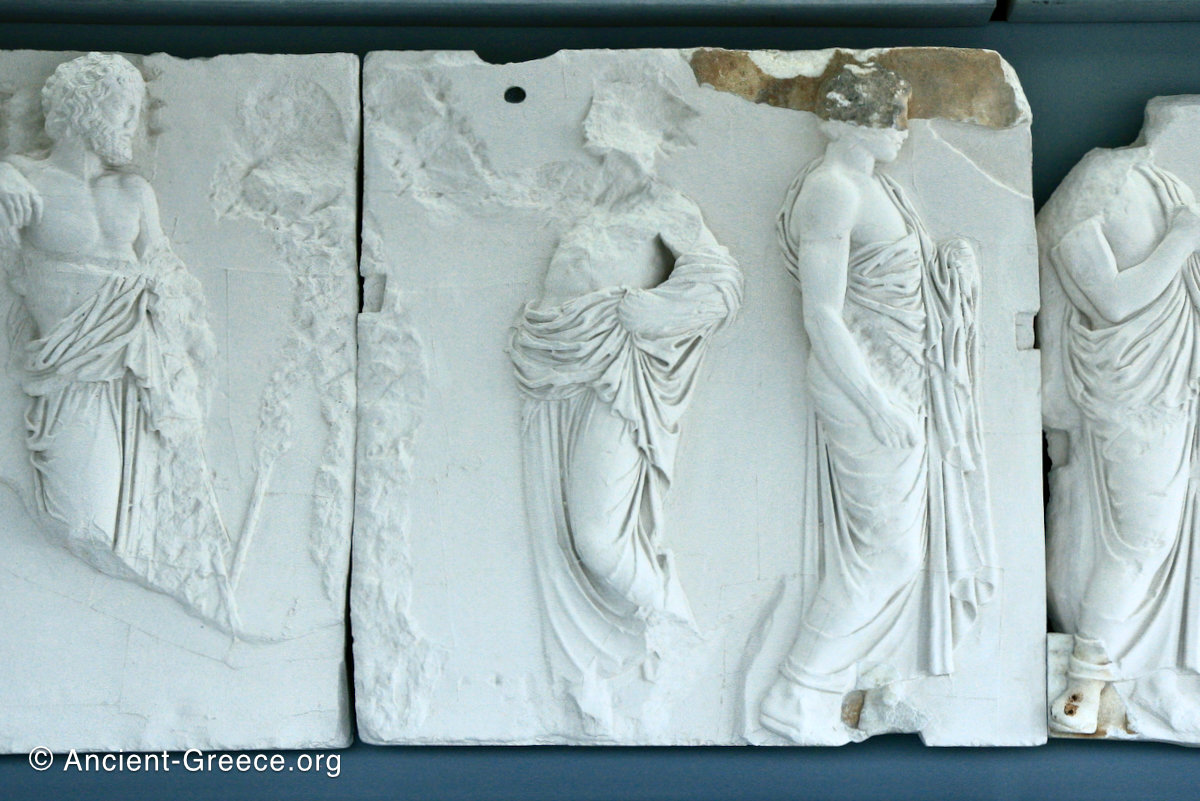
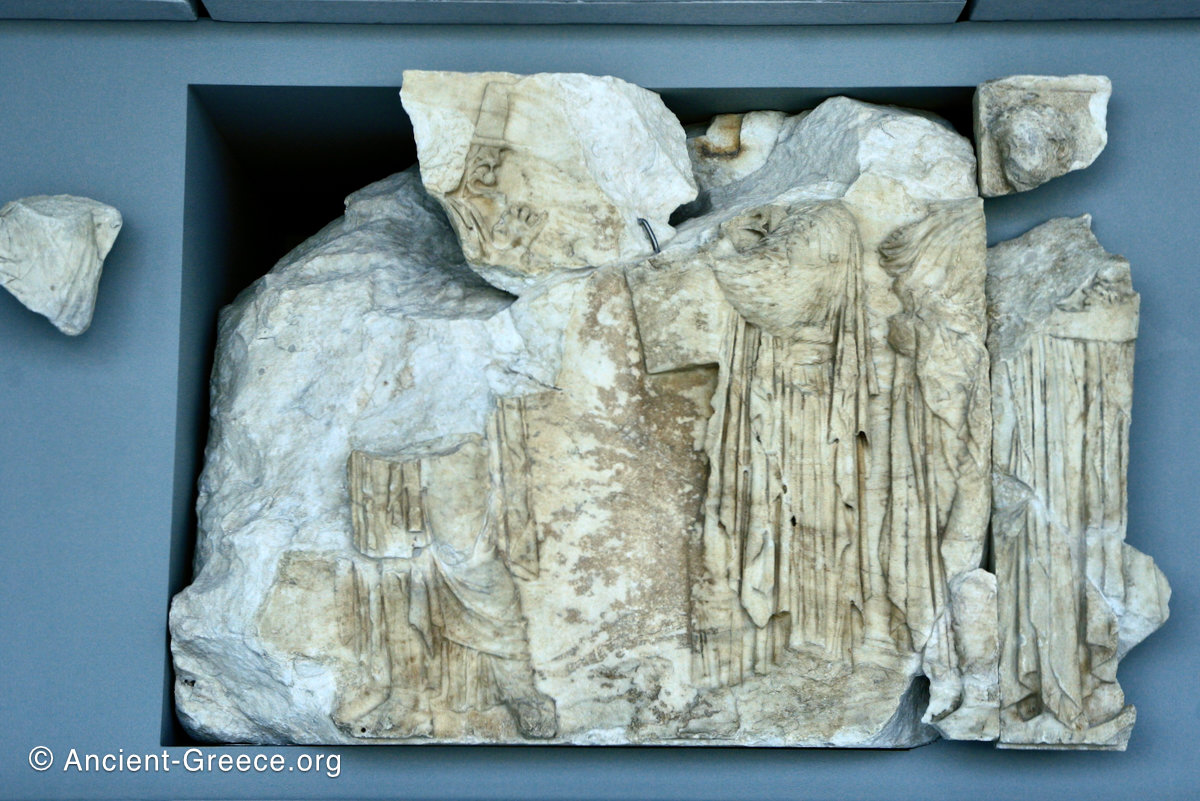
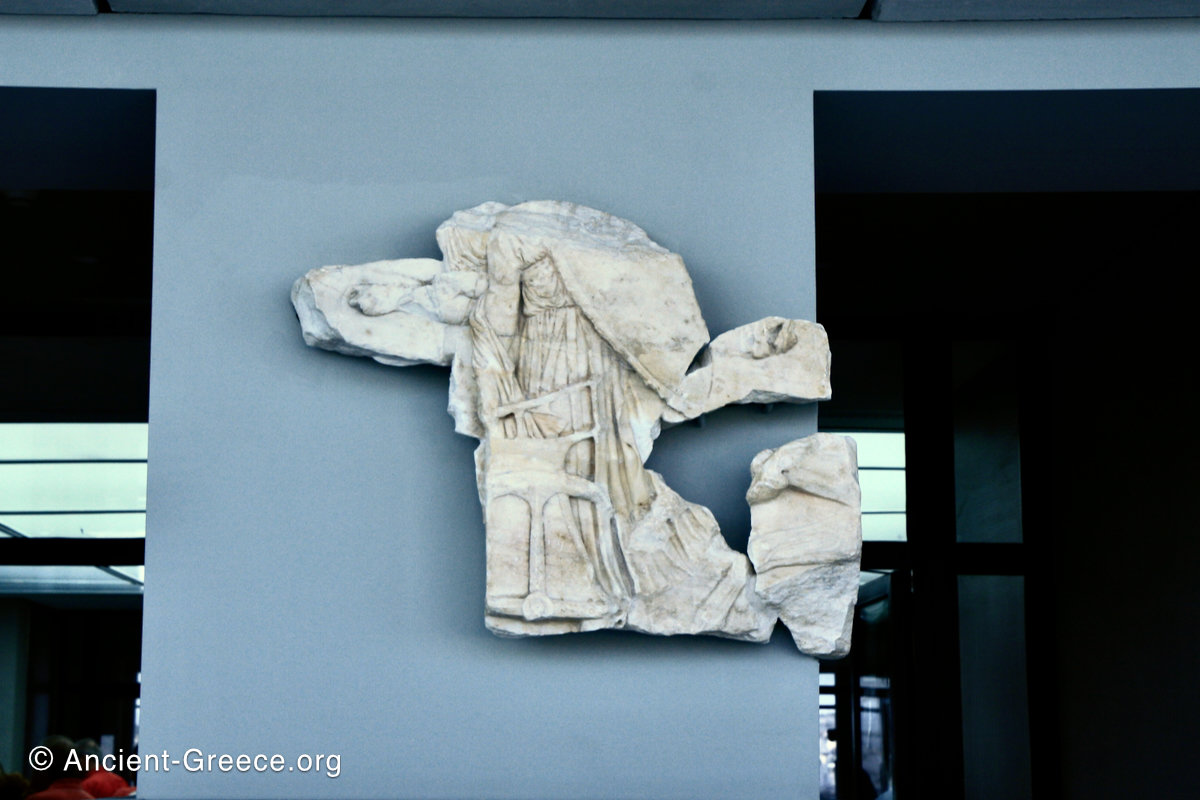
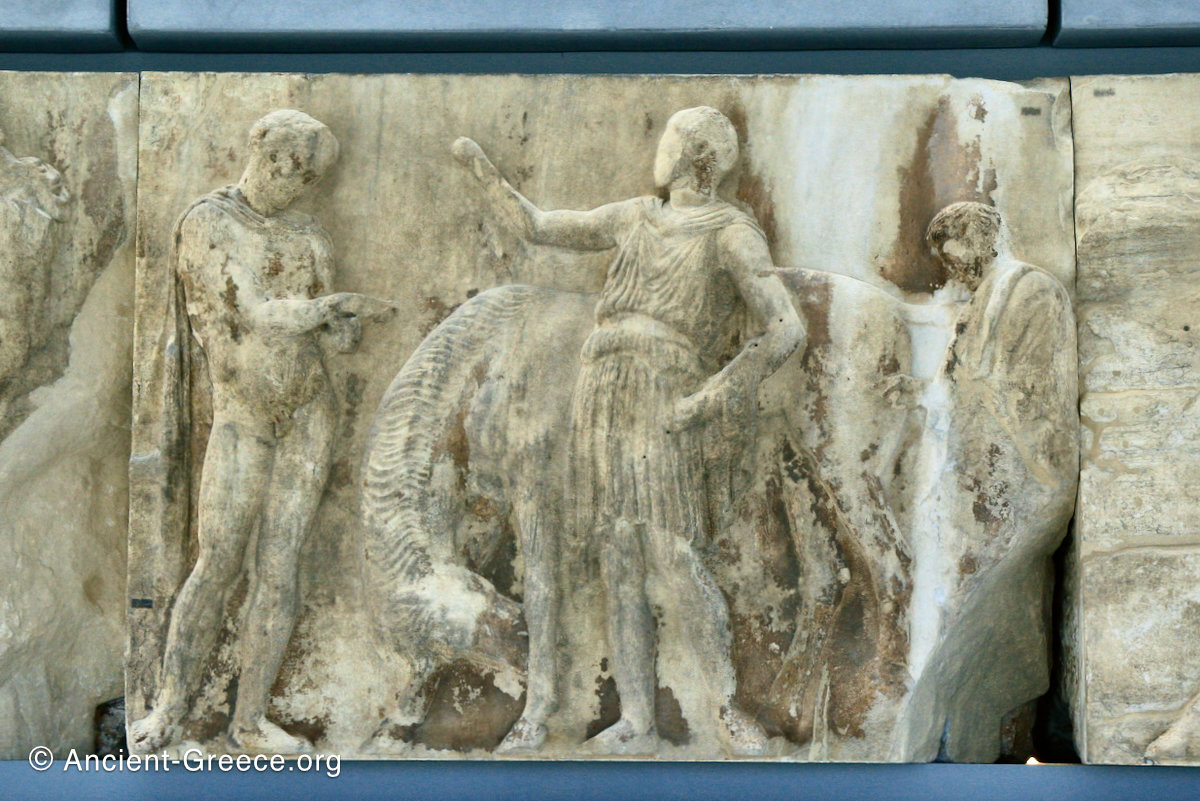
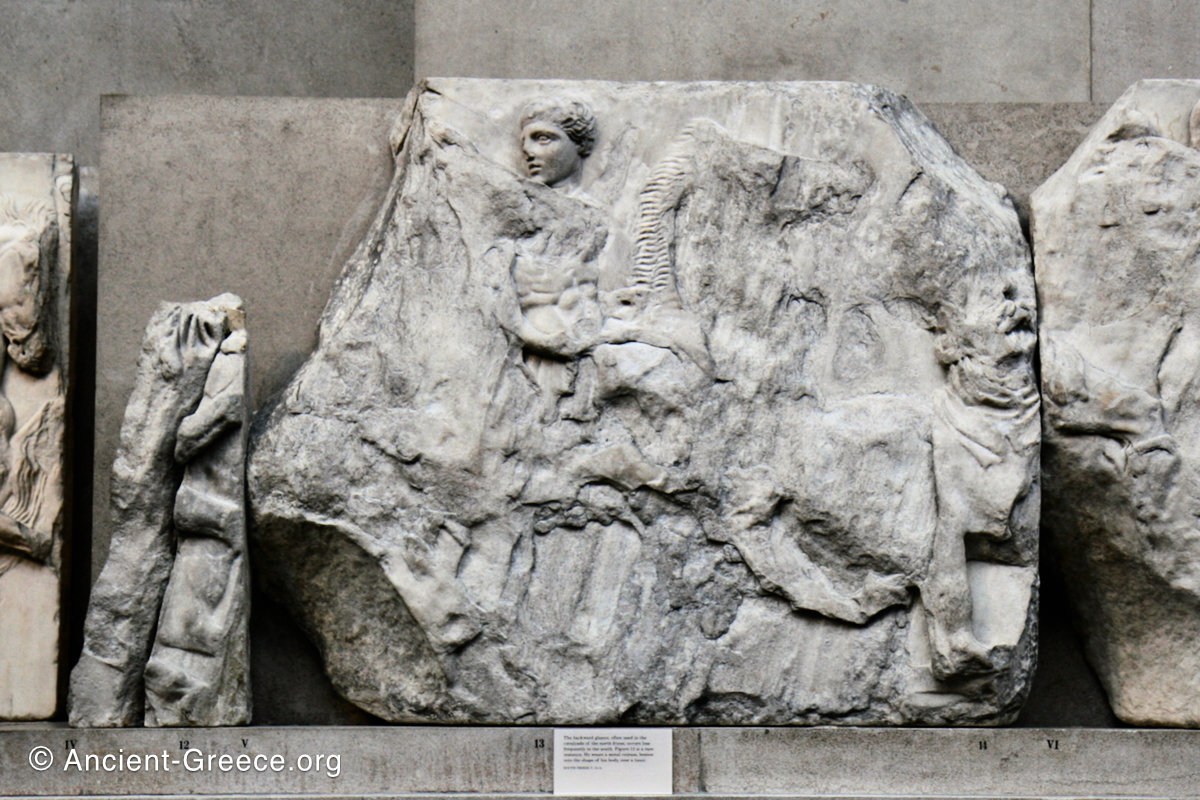
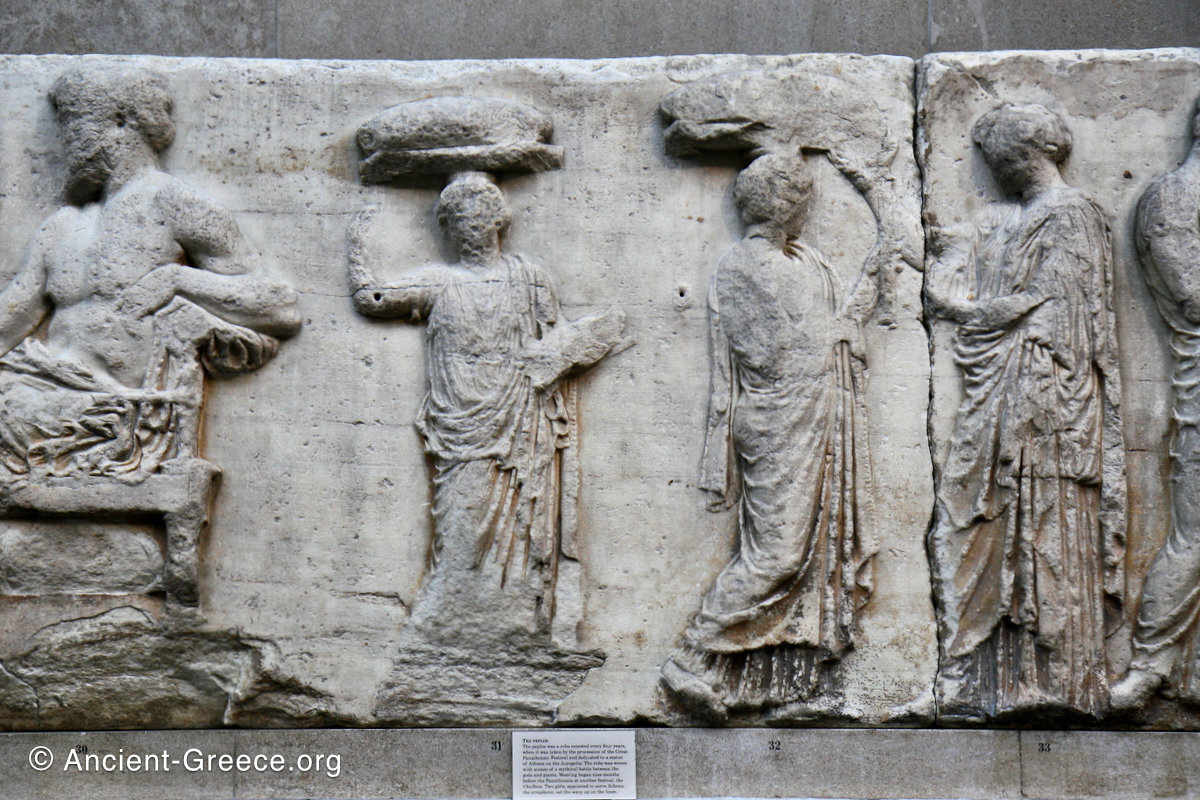
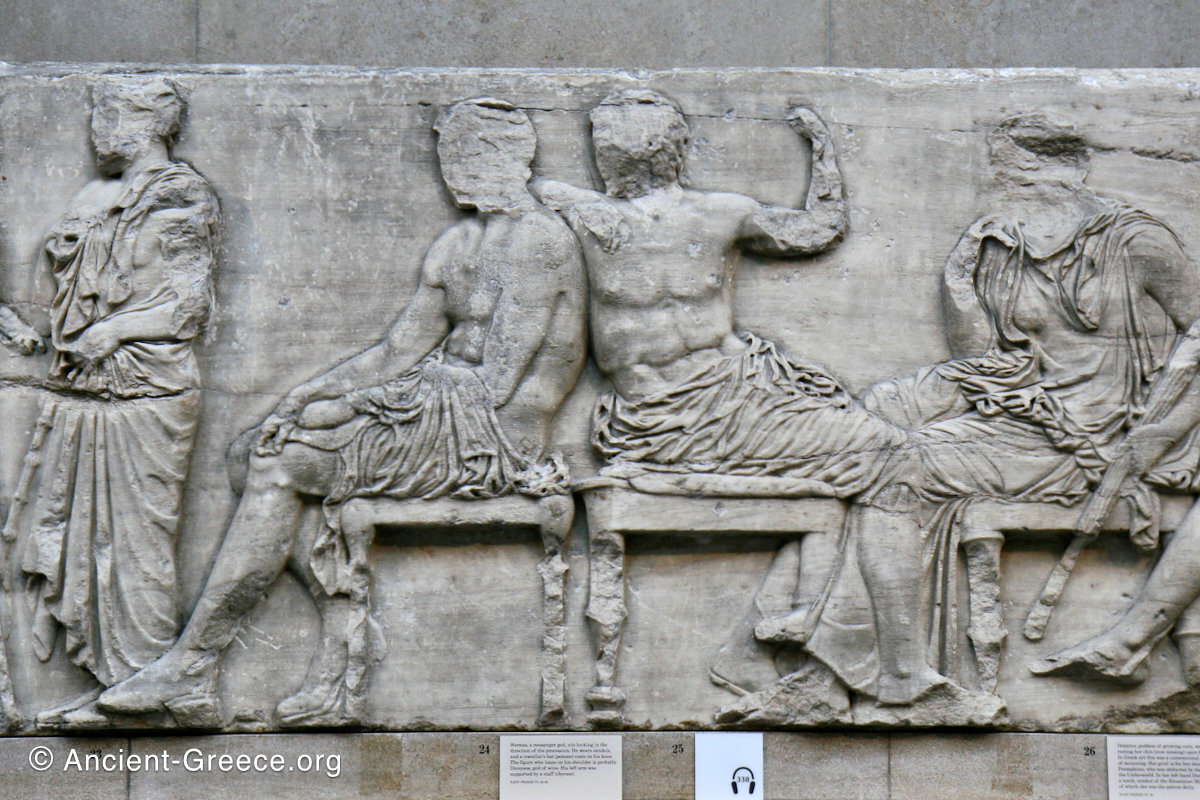
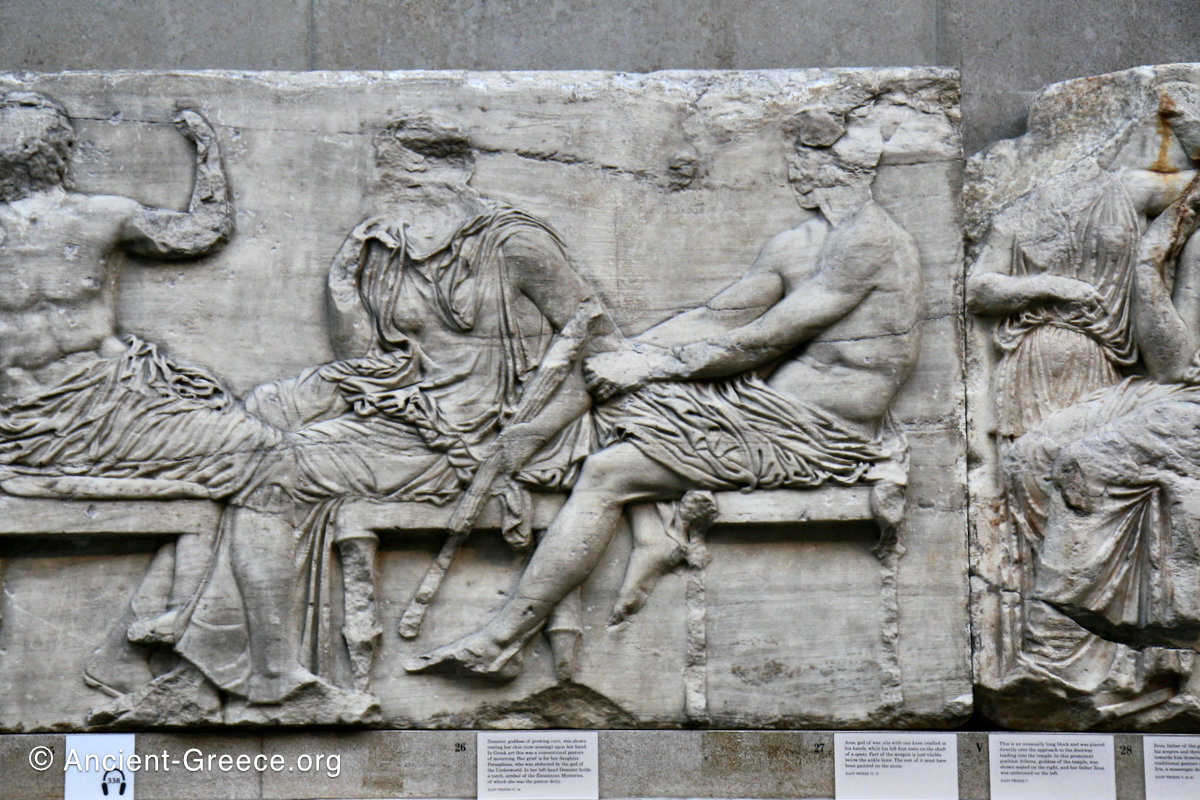
The east frieze over the Parthenon door has the “peplos scene” at the center: Two persons examine a piece of folded cloth and next to them gods and heroes are engaged in conversation. Several women are standing in their flaks.
The peplos was a central item in the Panathenaea ritual, and was woven by the virgins dedicated to the goddess Athena exclusively for use during the procession.
The gods are seated, making them twice as large as the rest of the figures who are standing or riding, and they appear in the typical realistic mortal form we are accustomed to seeing in Classical art.
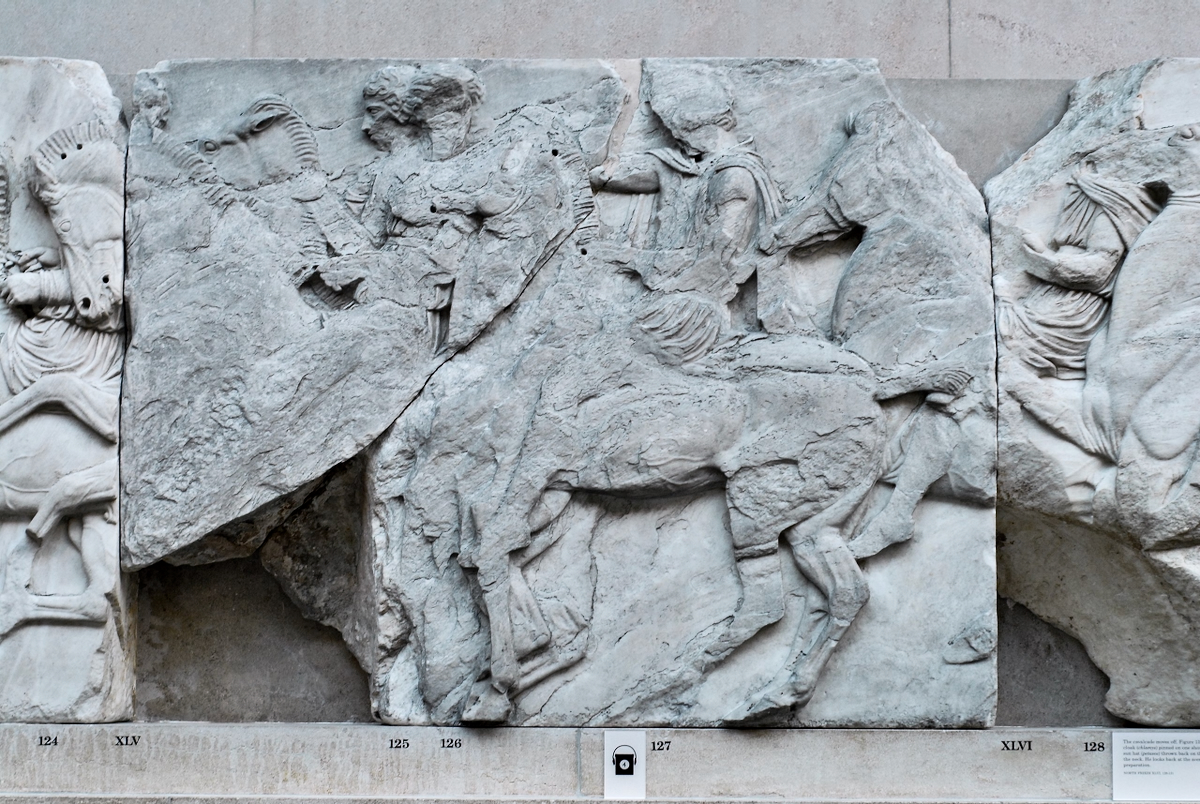
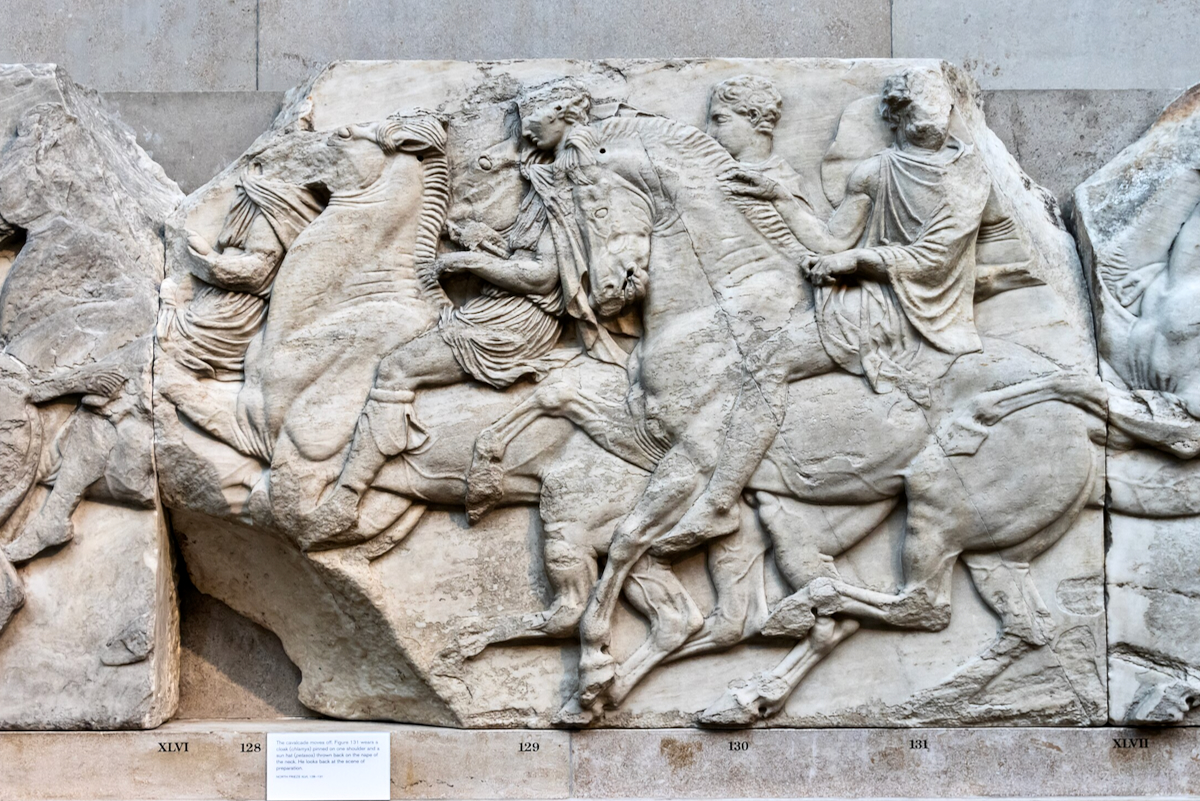
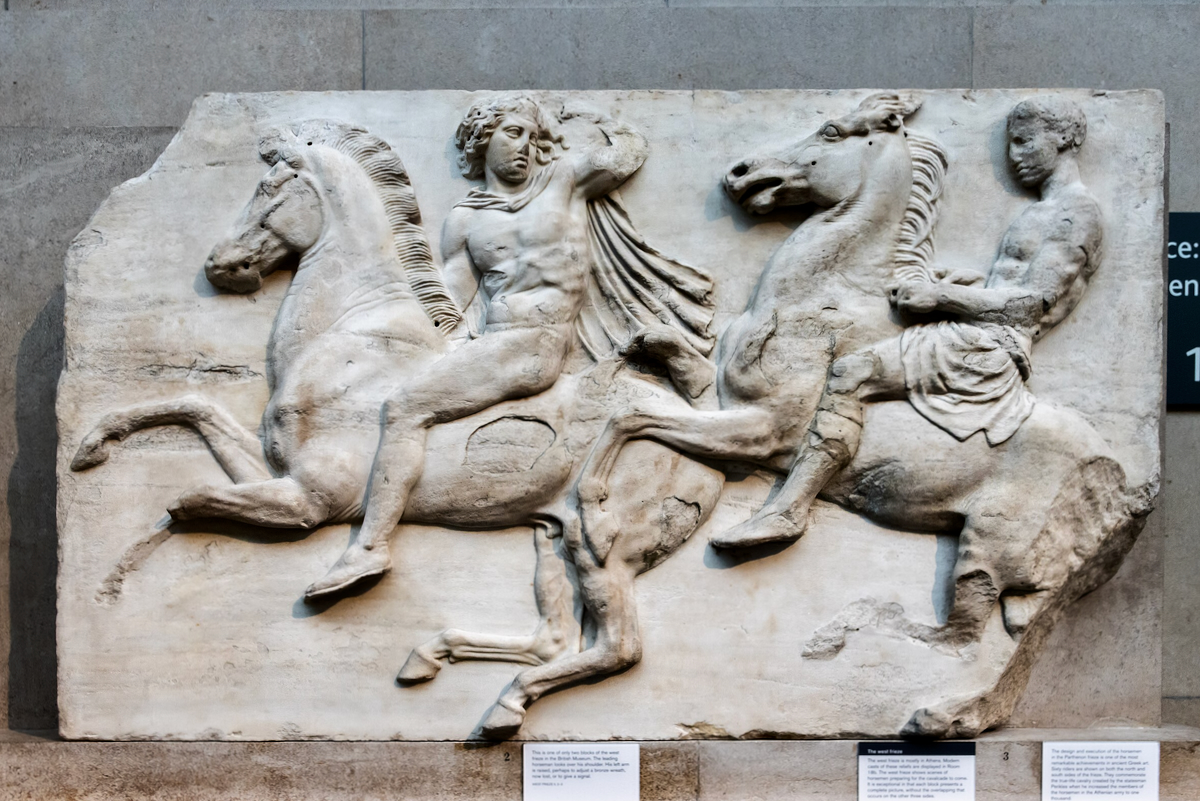
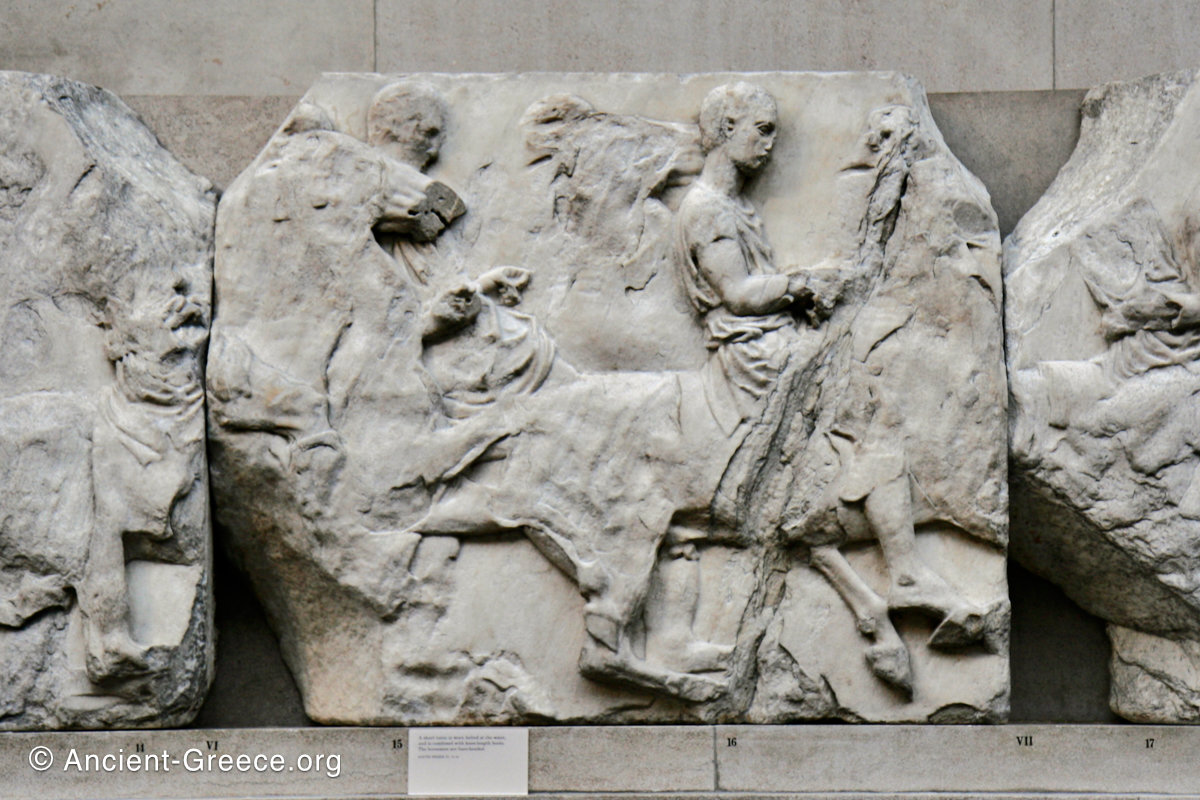
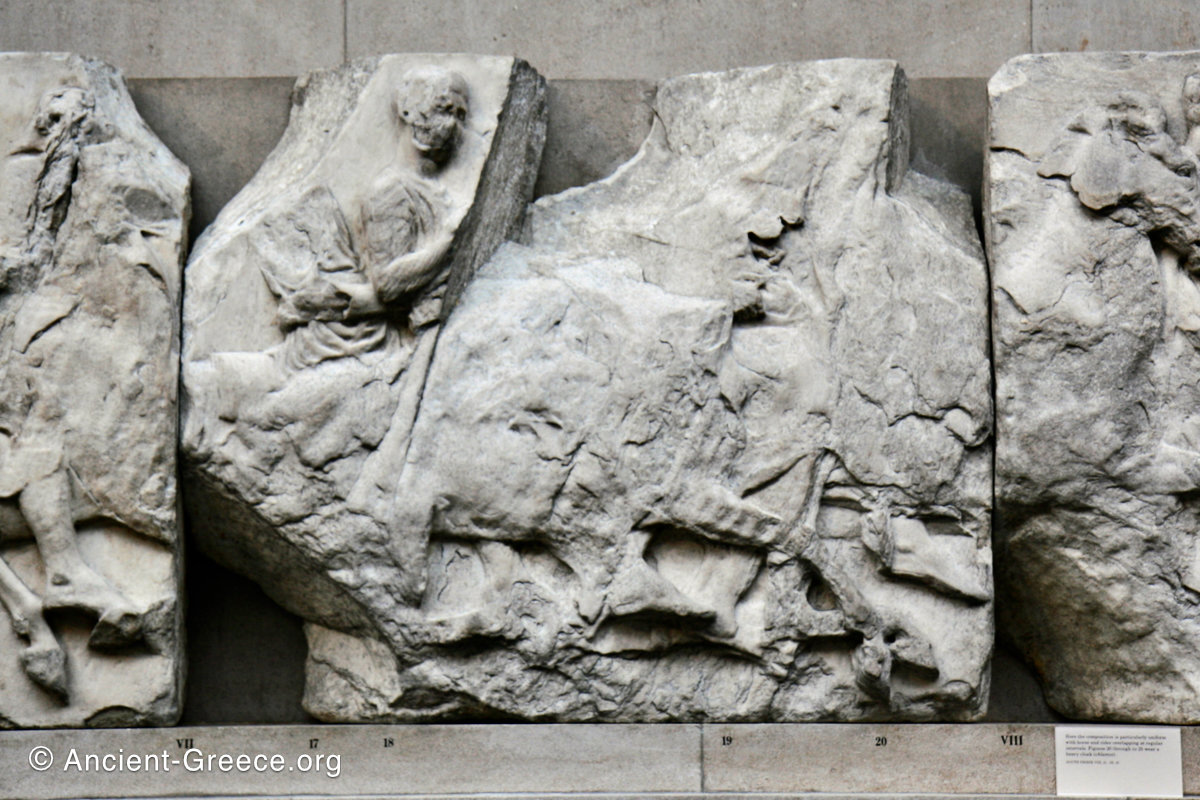
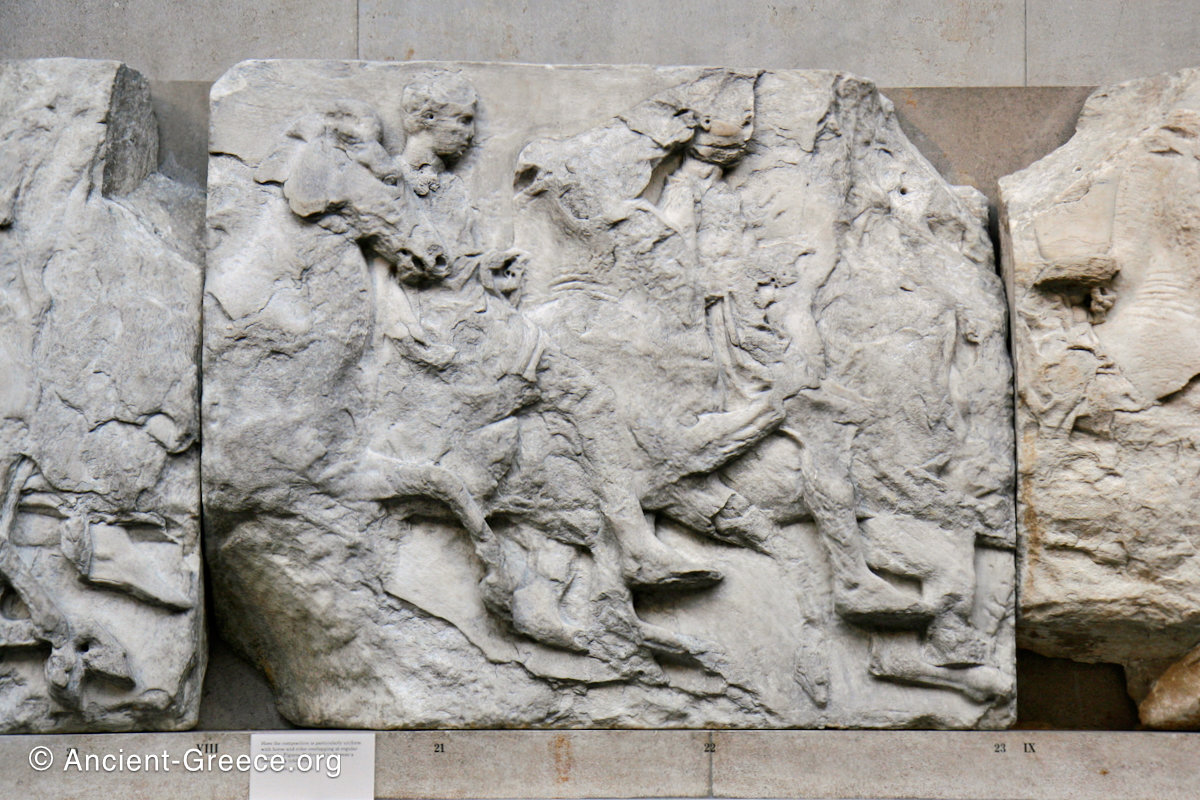
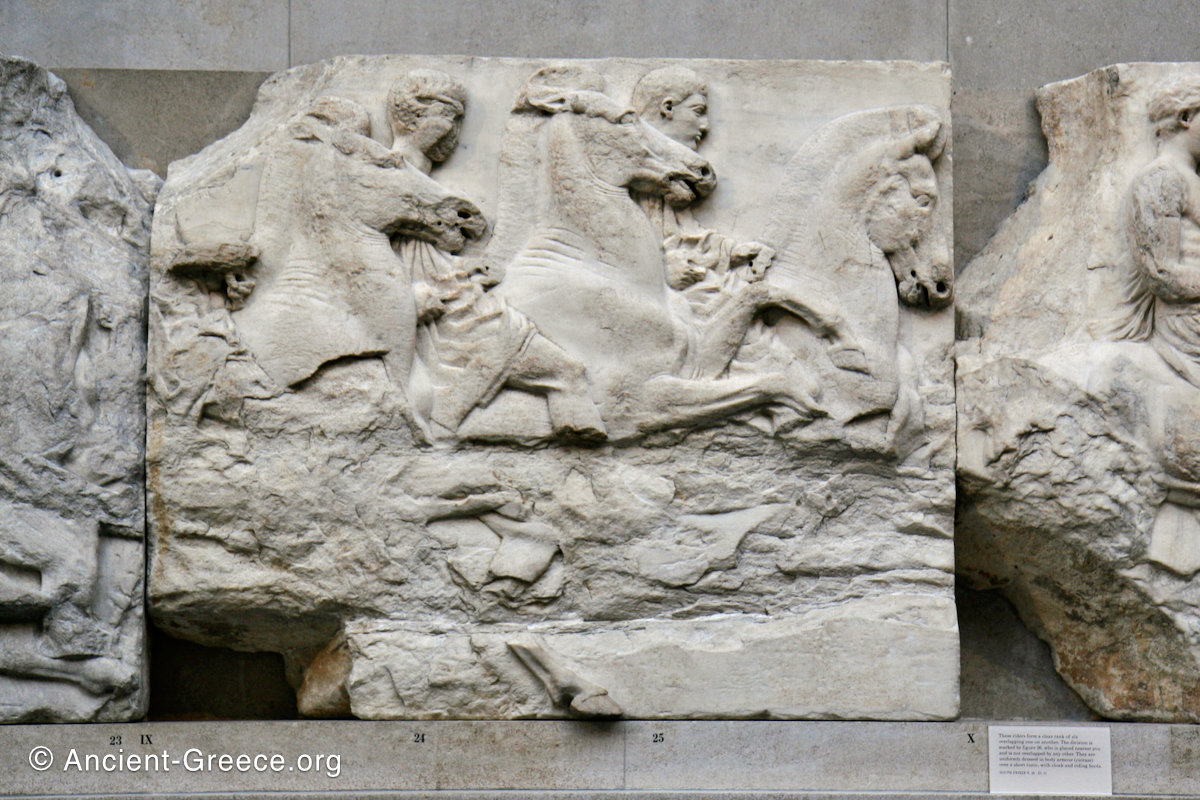
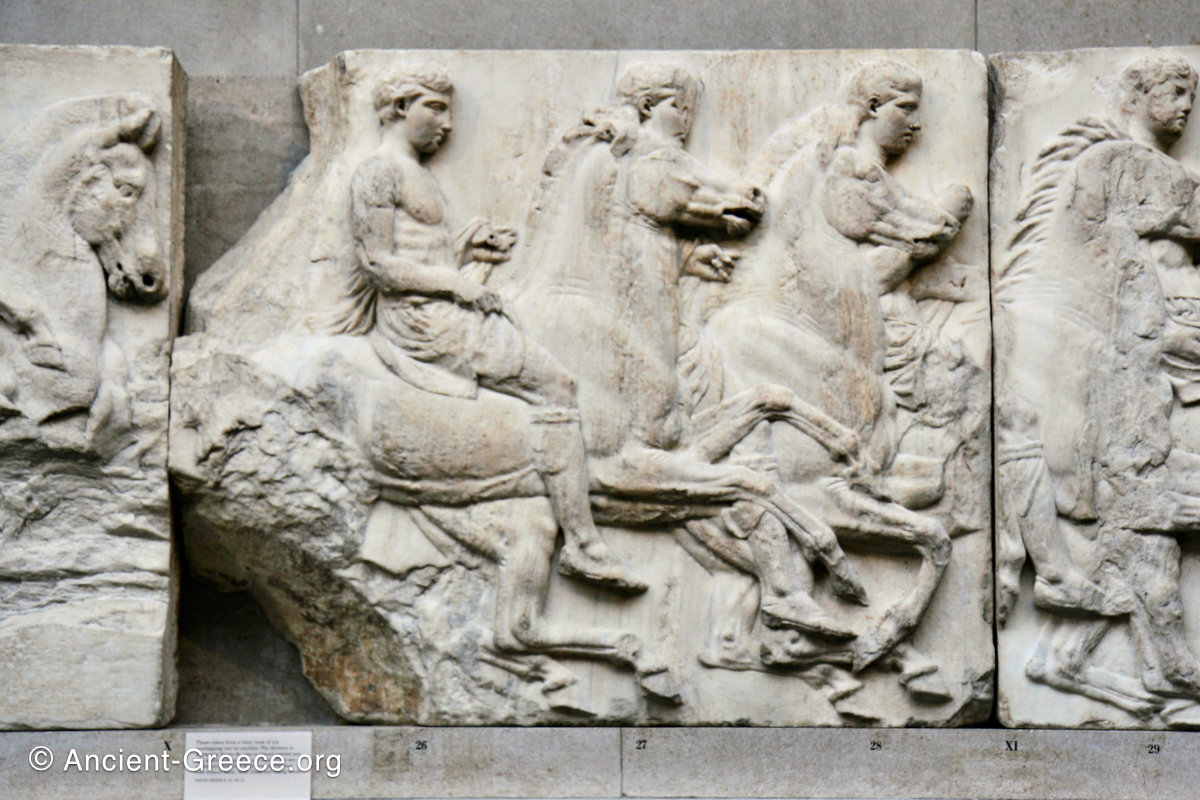
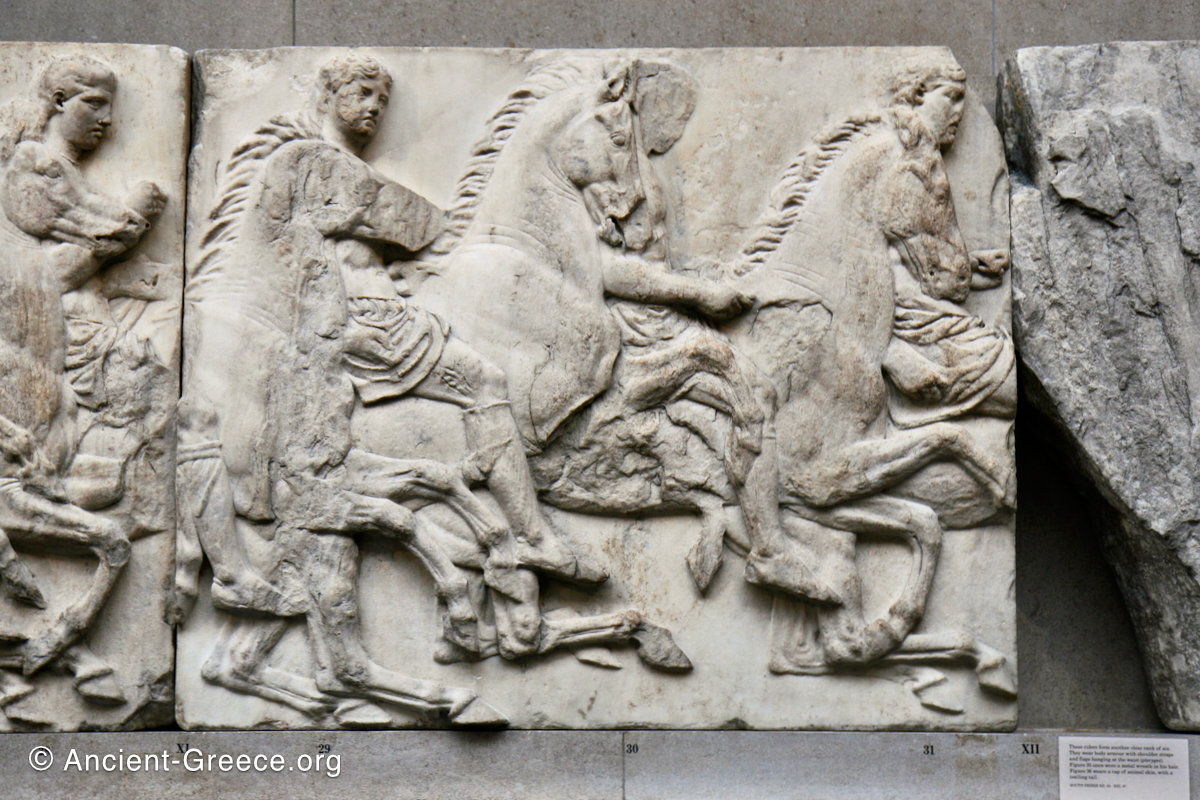
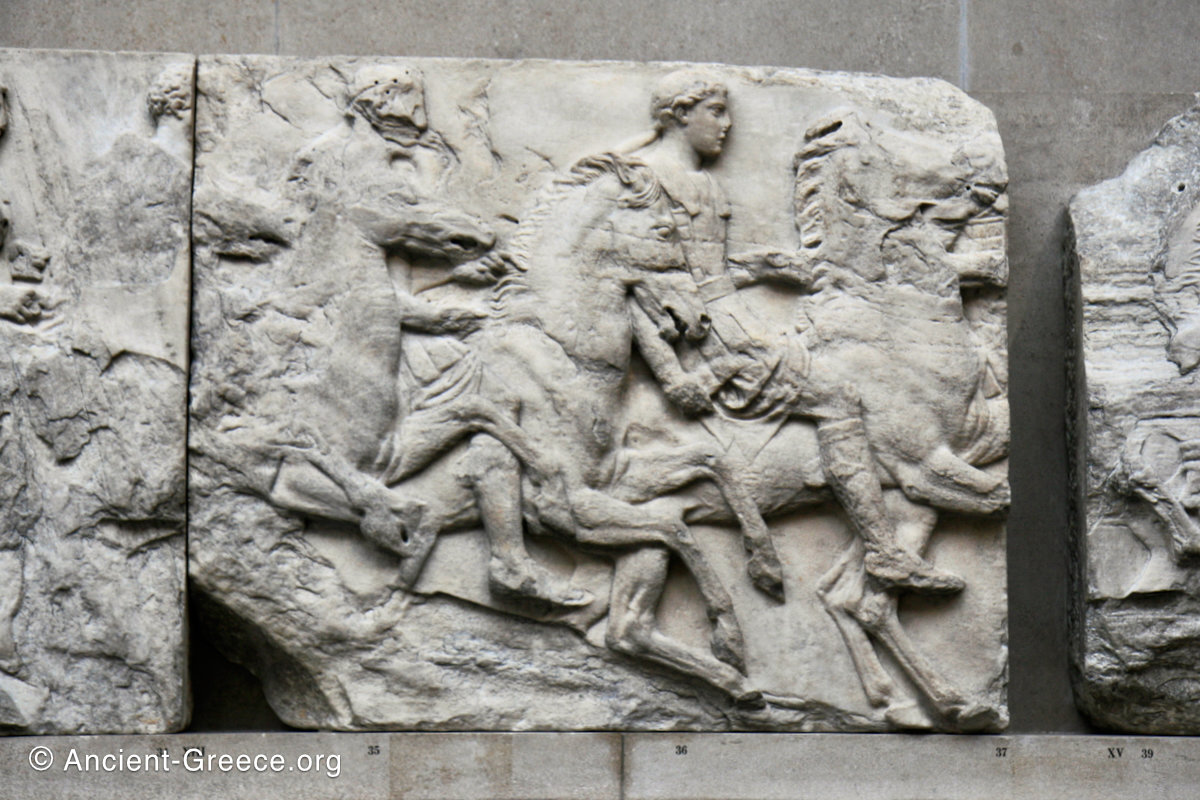
West Frieze















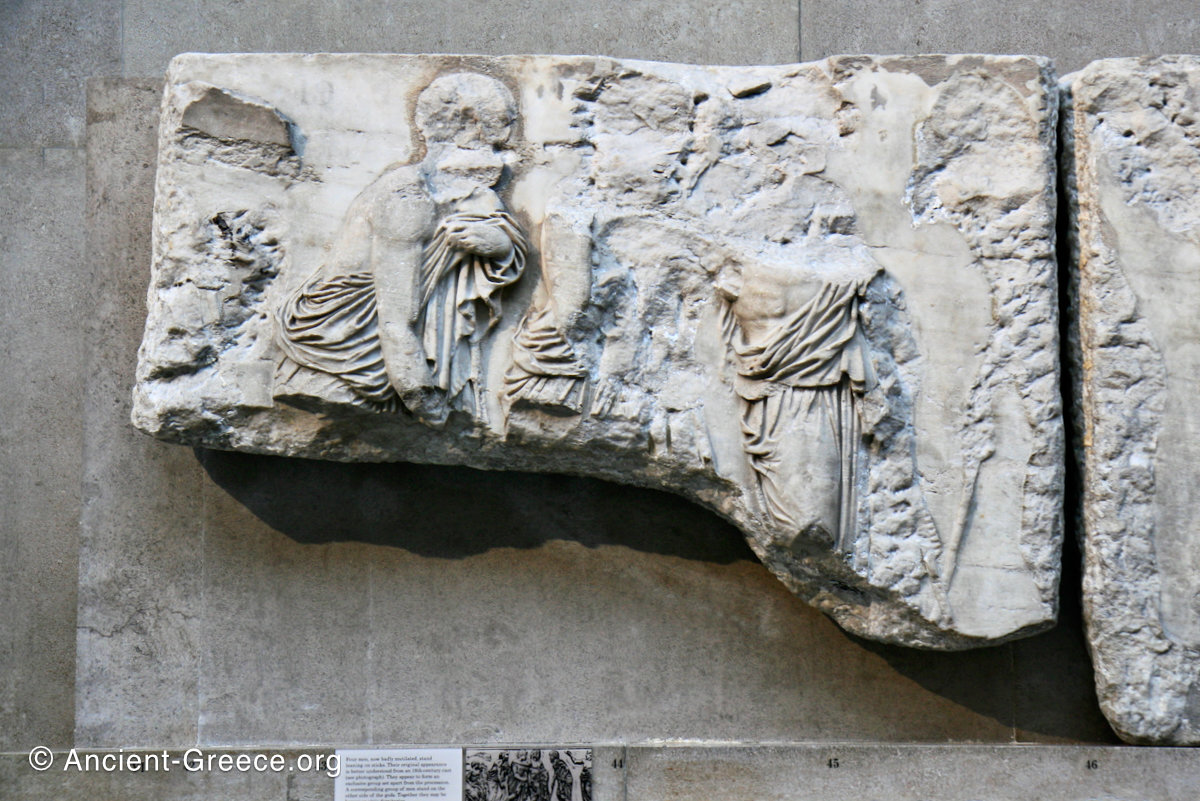
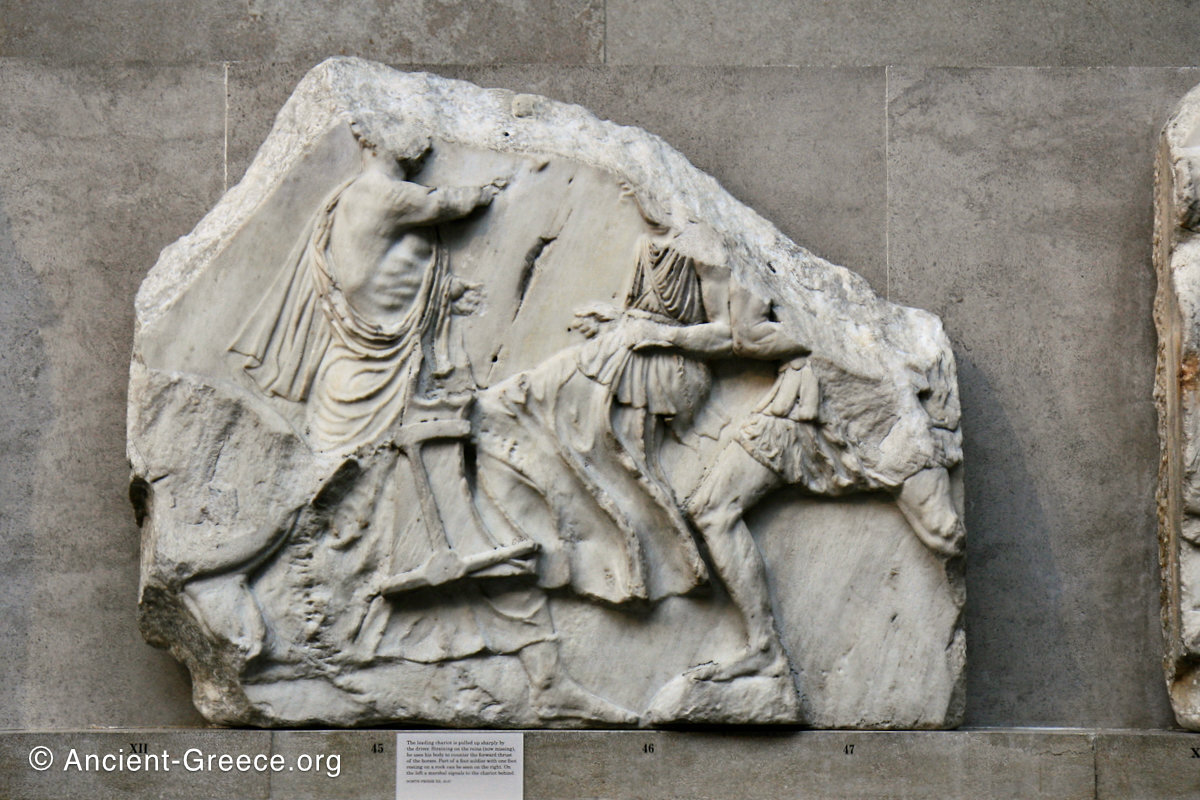
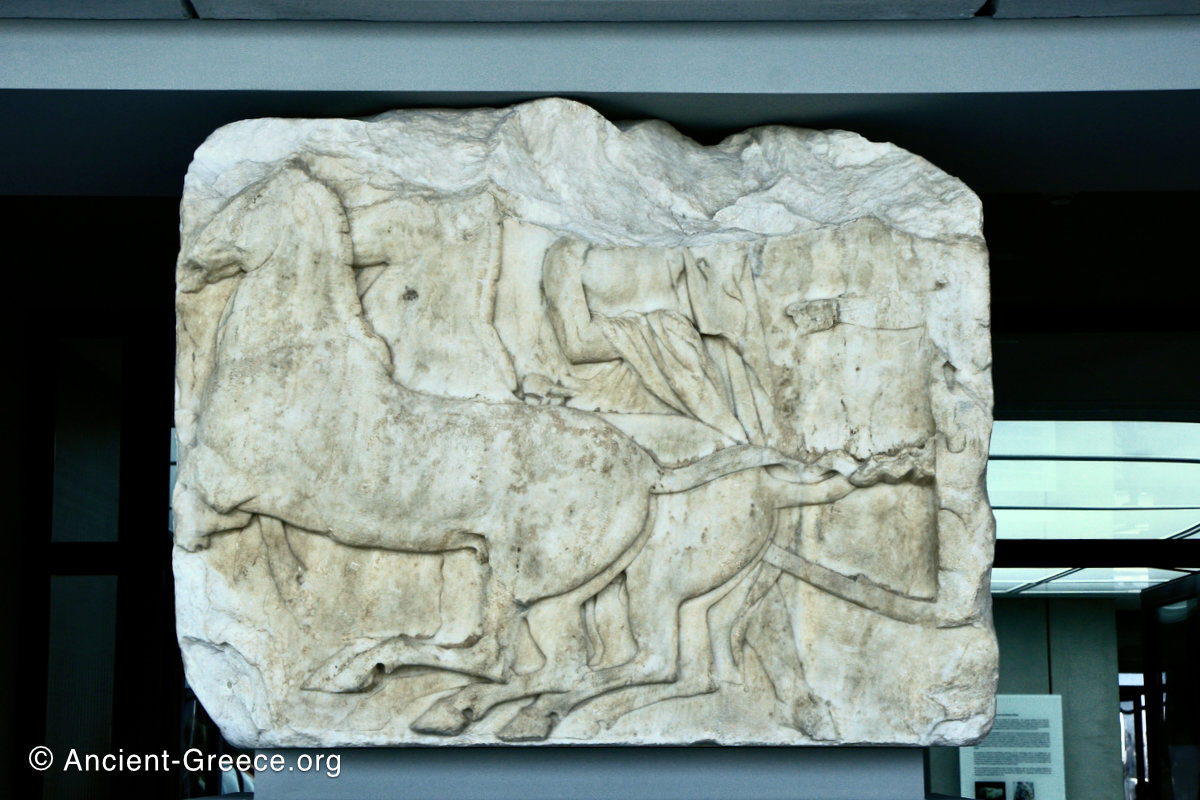
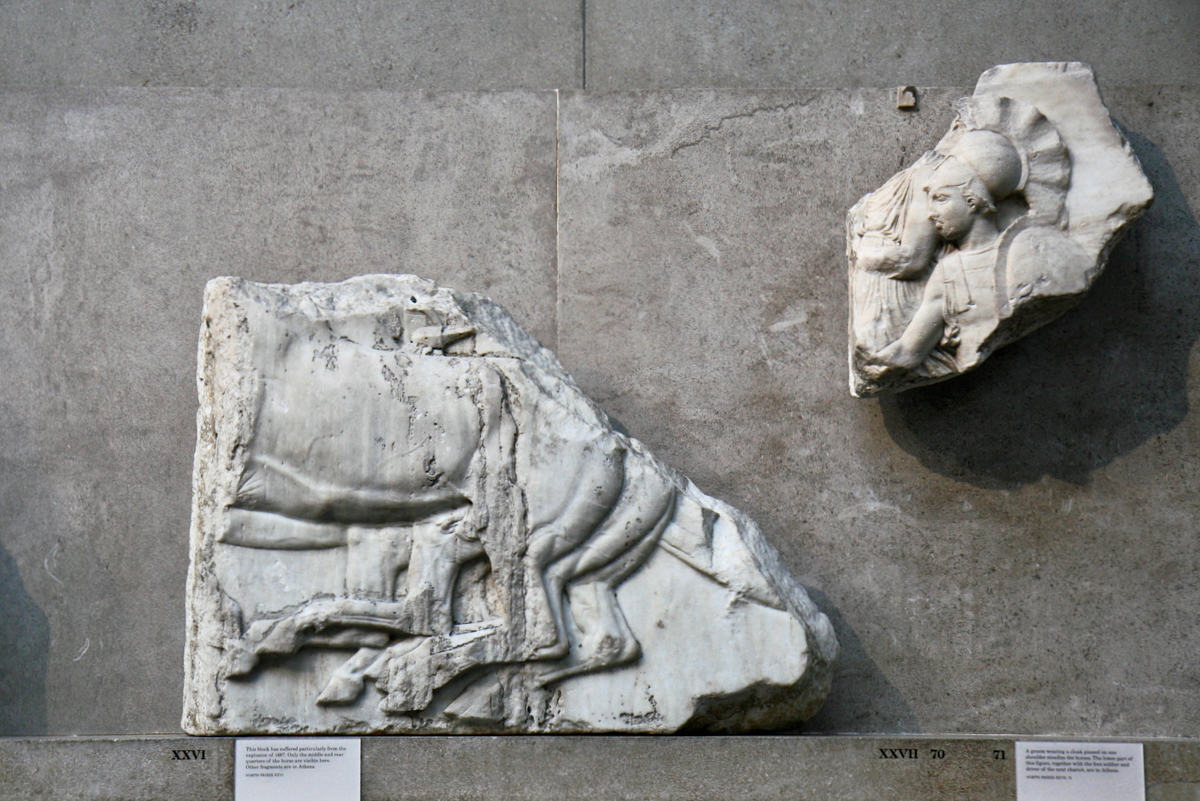
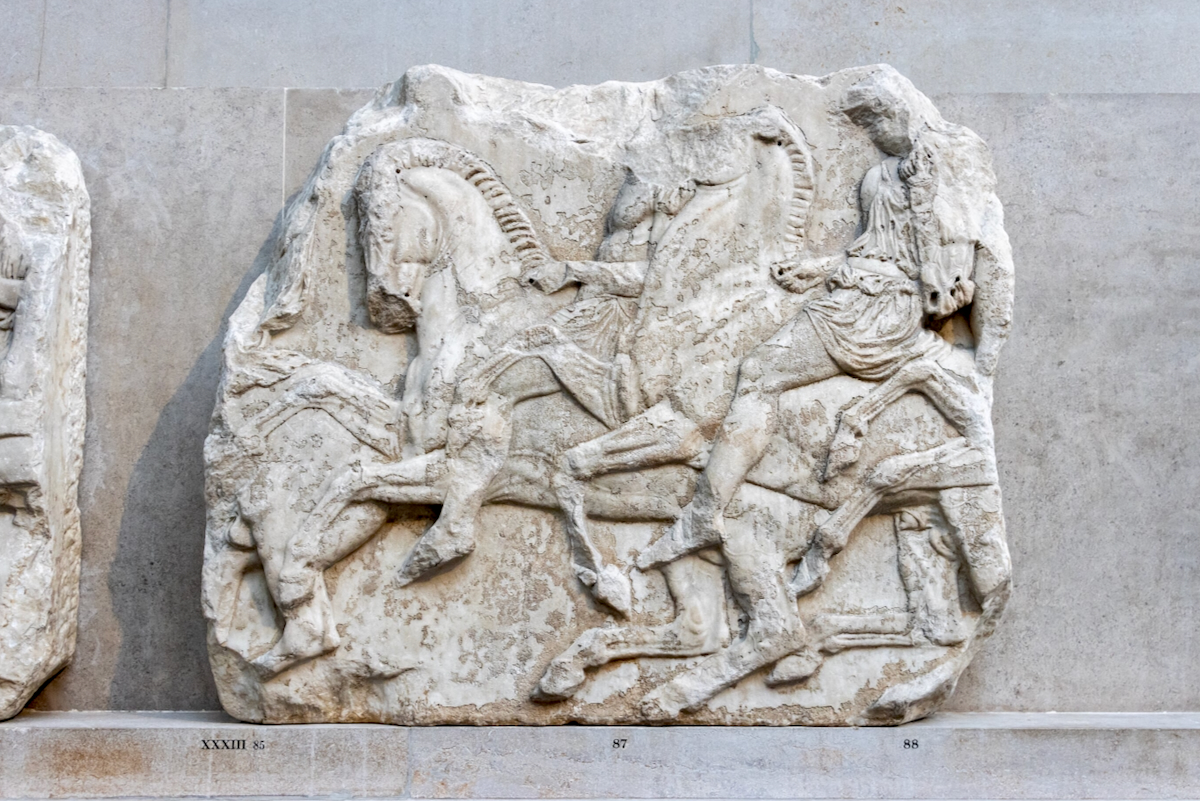
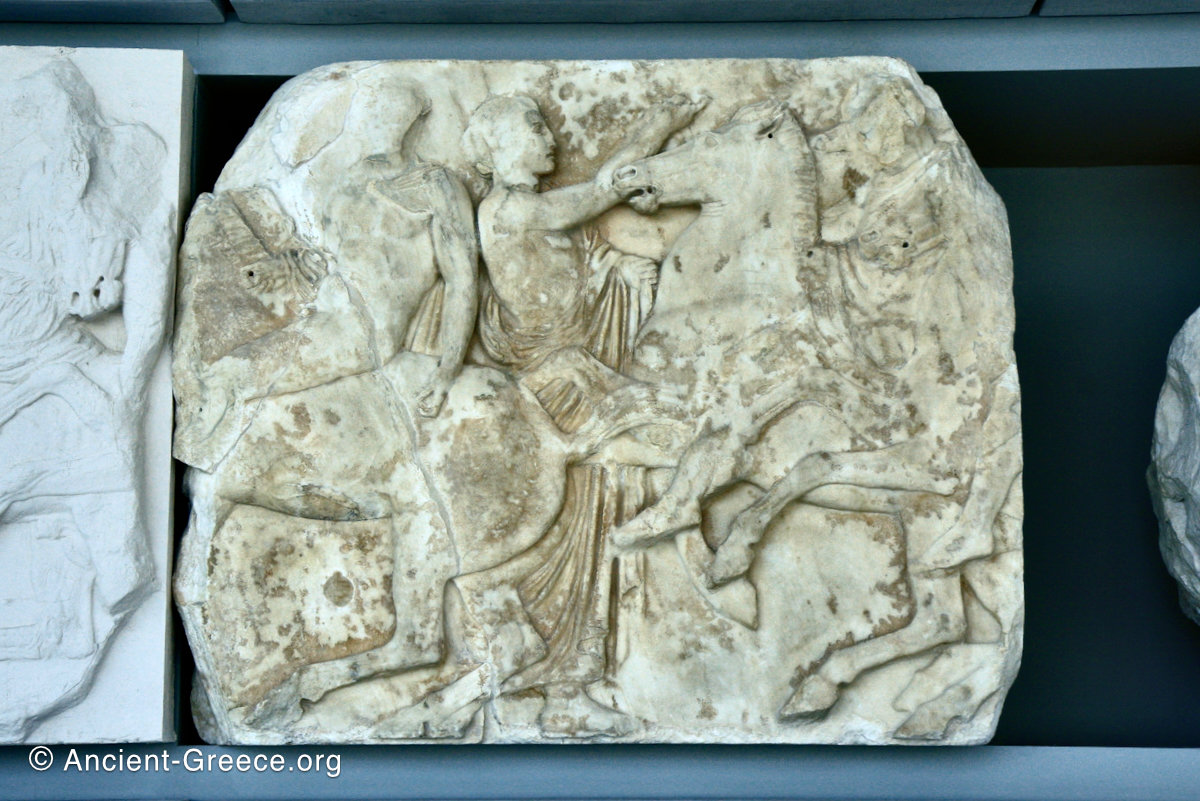
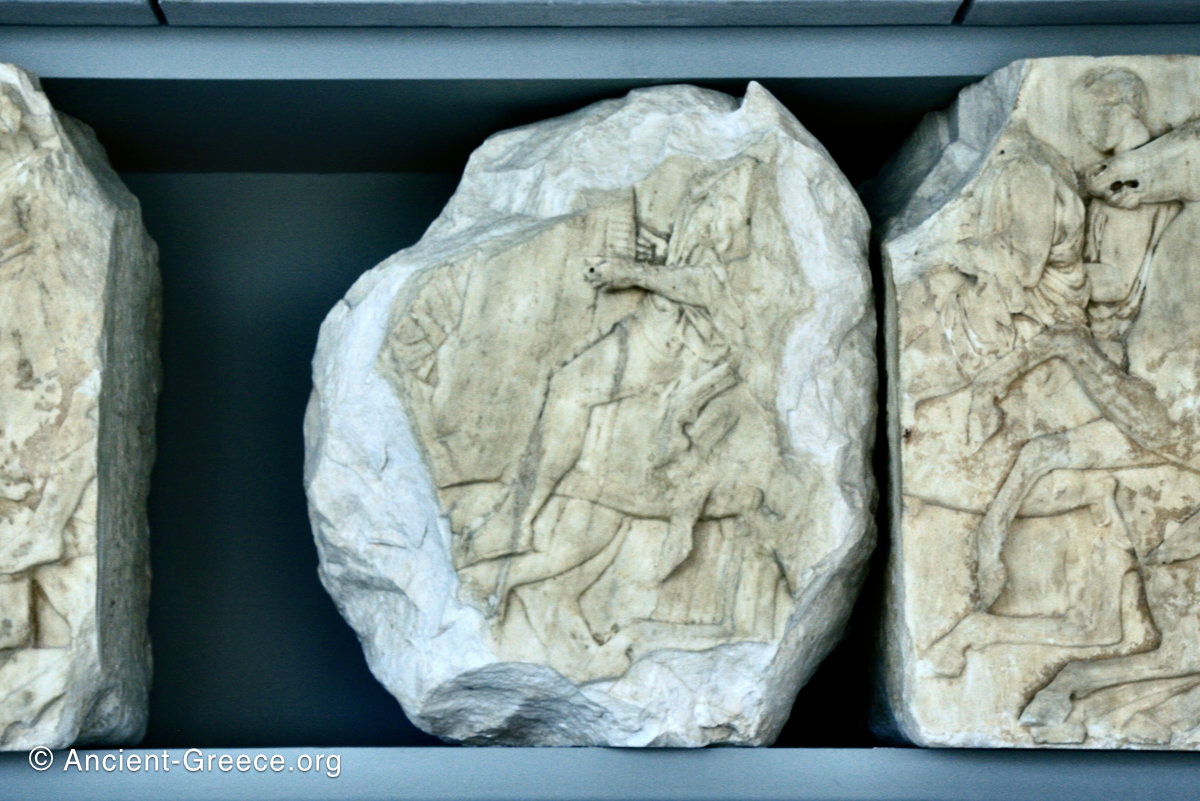
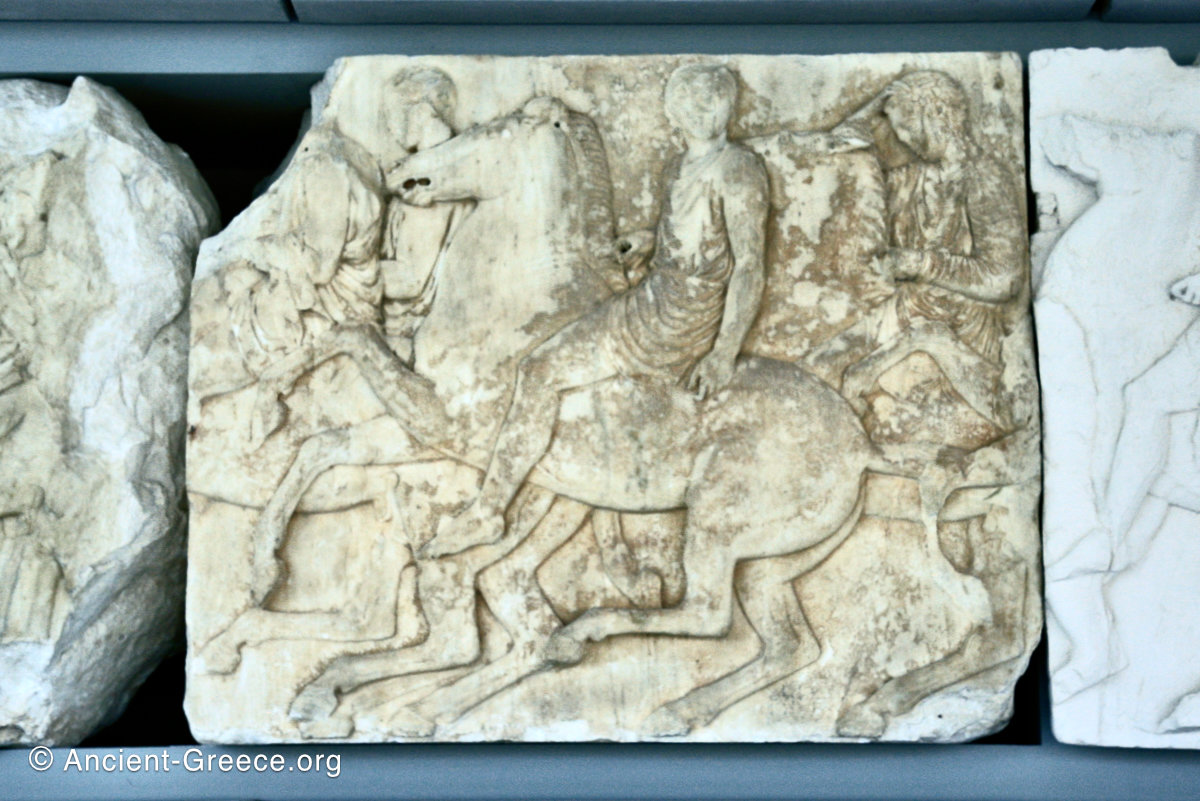
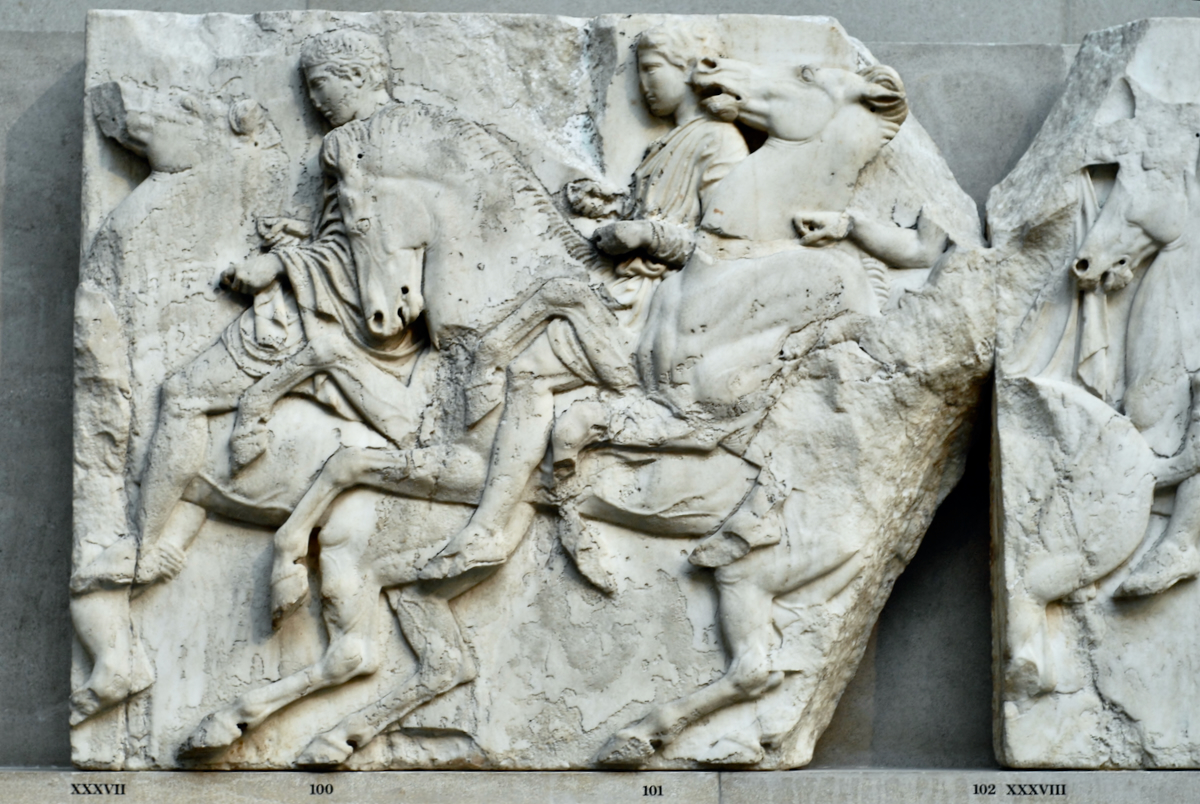
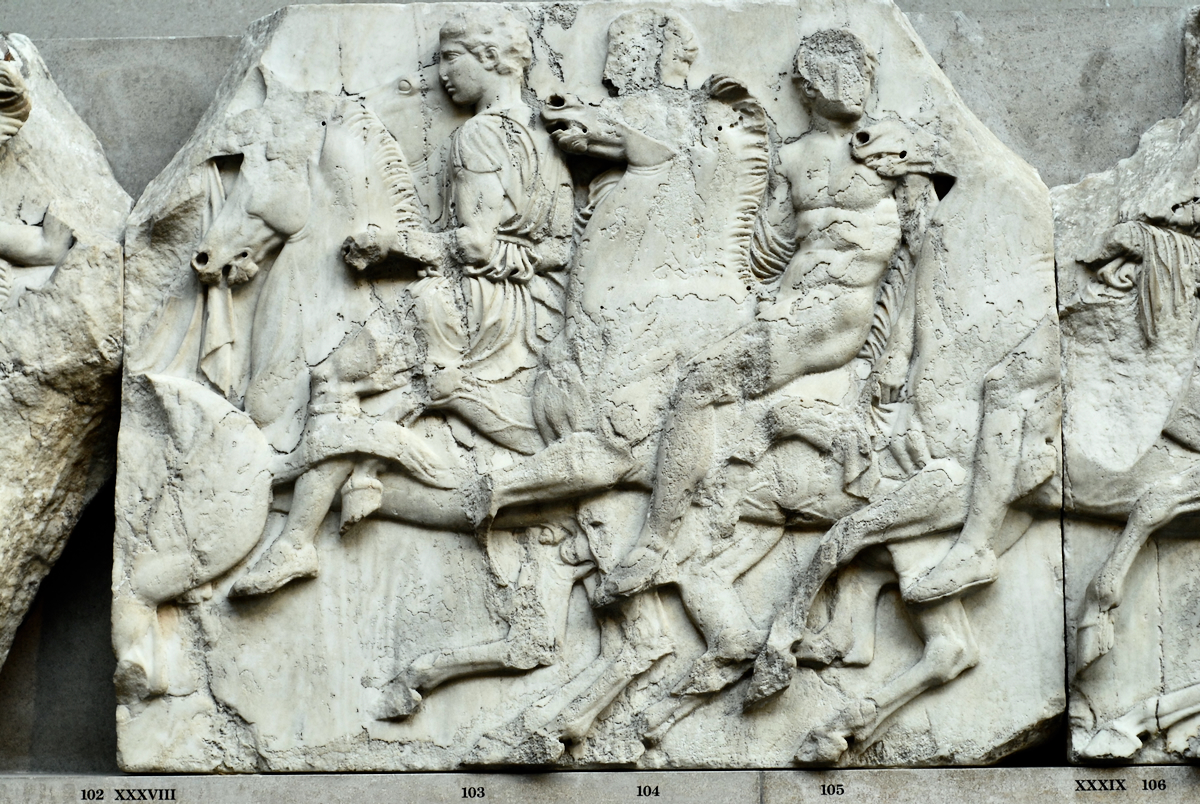
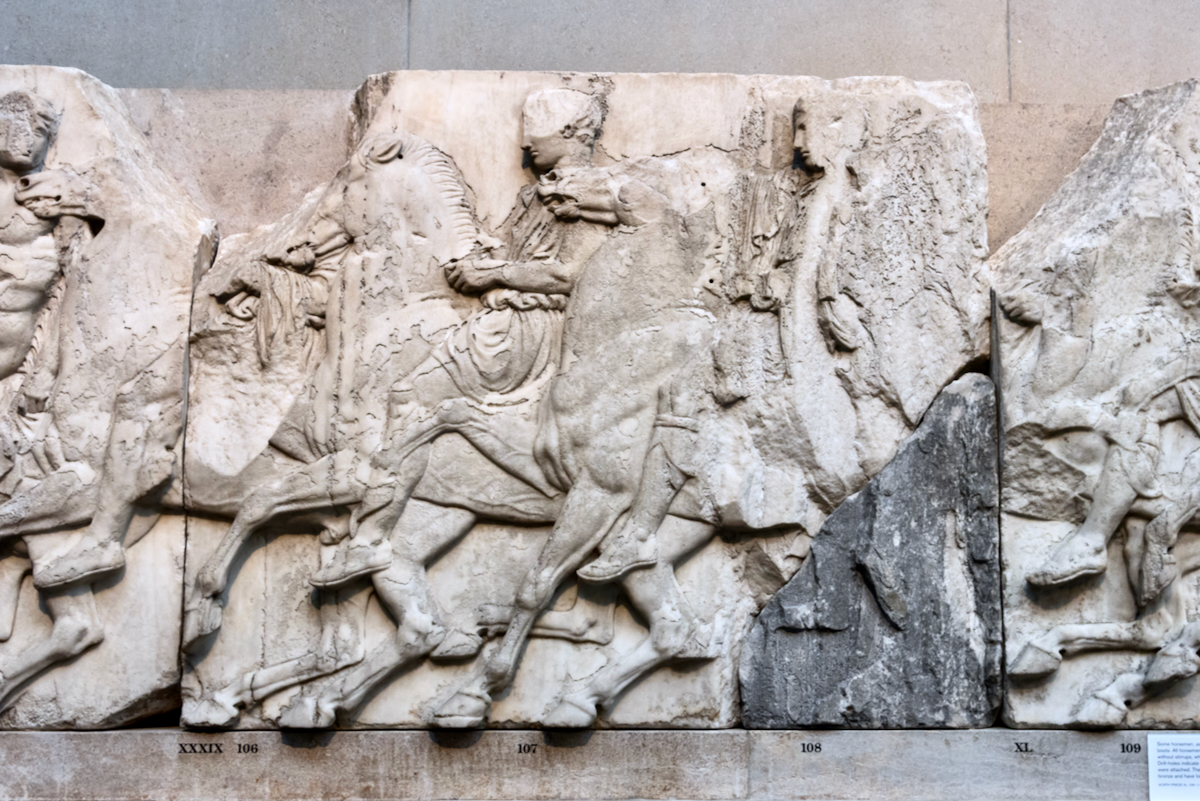
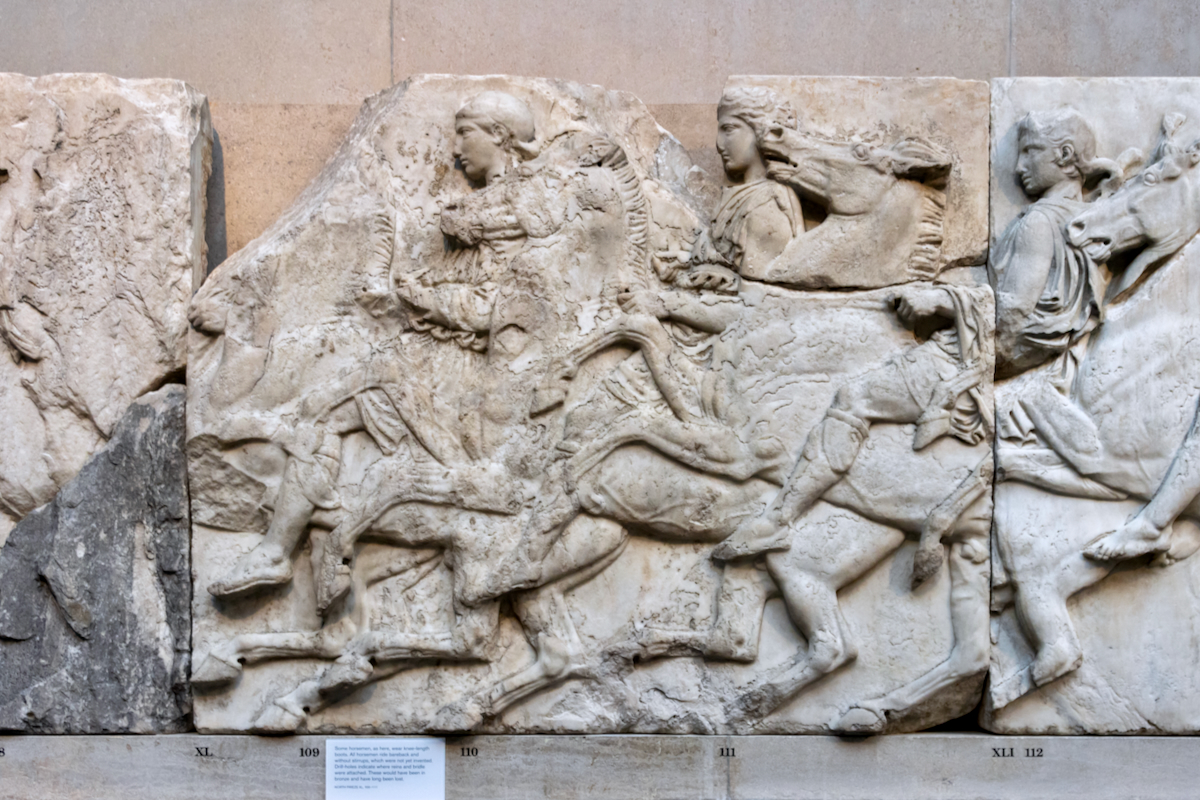
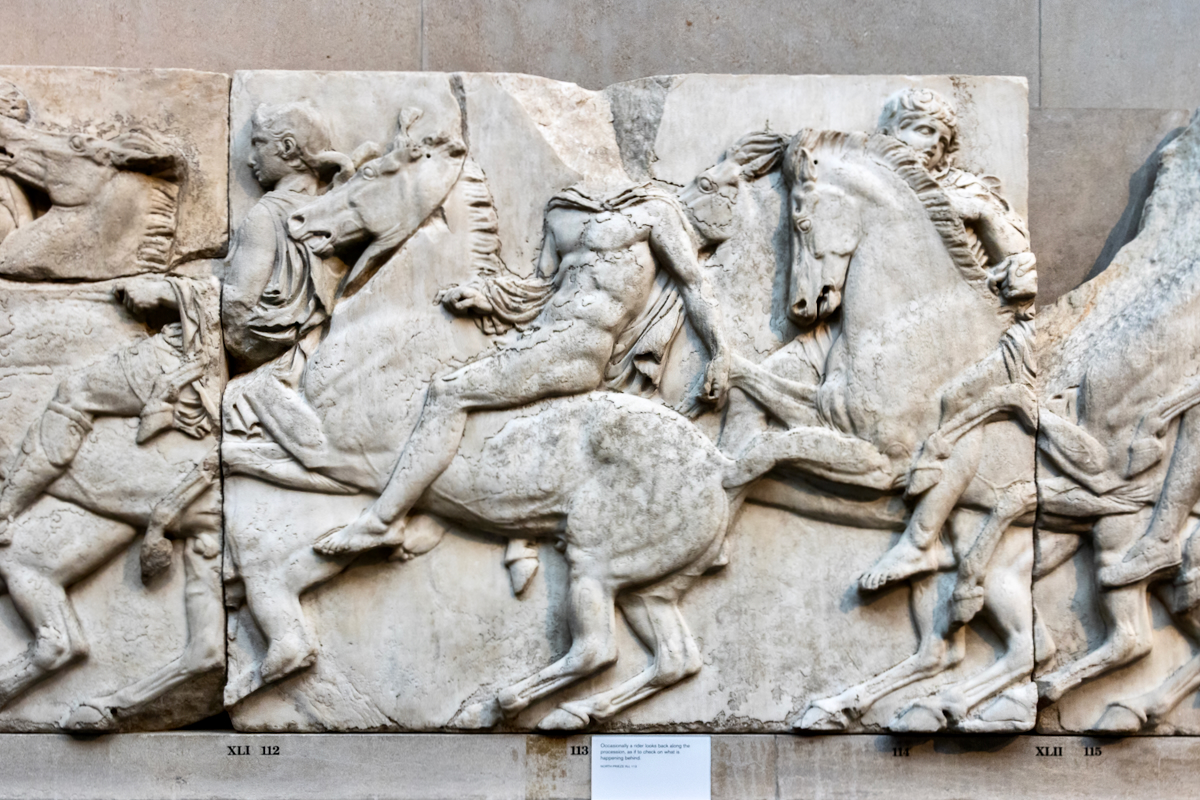
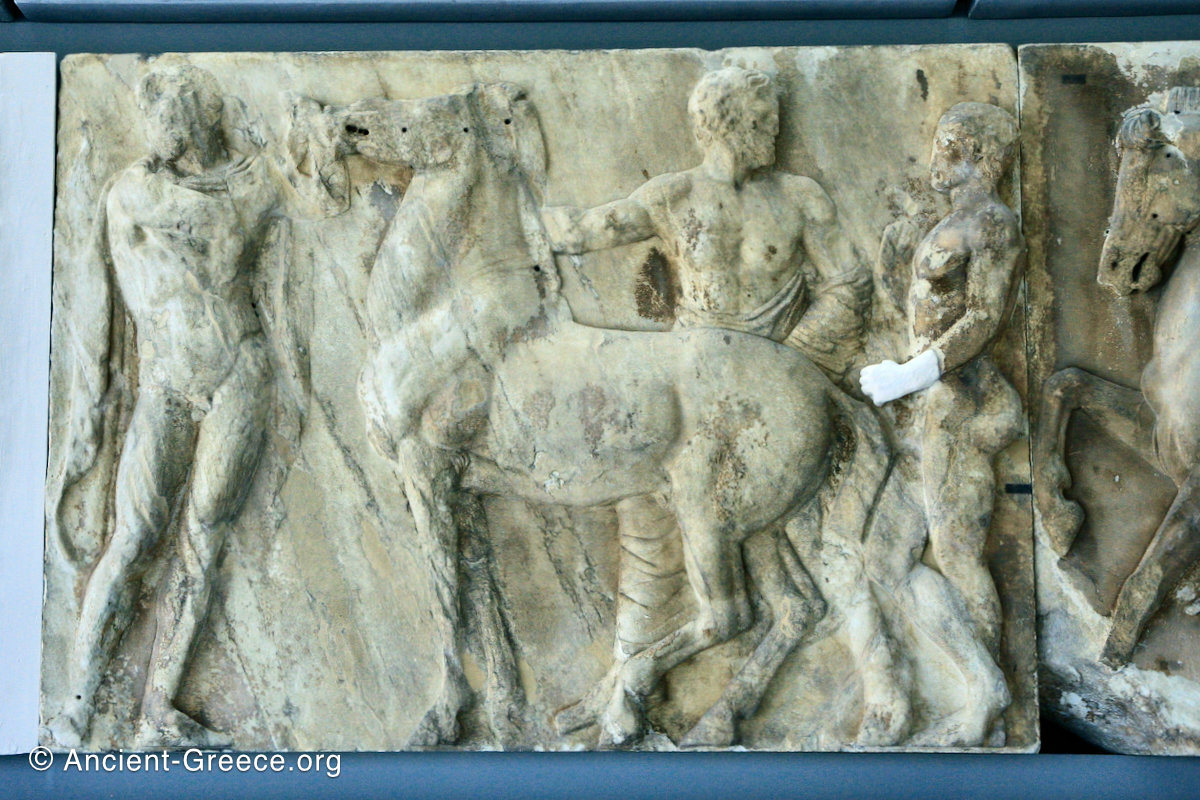
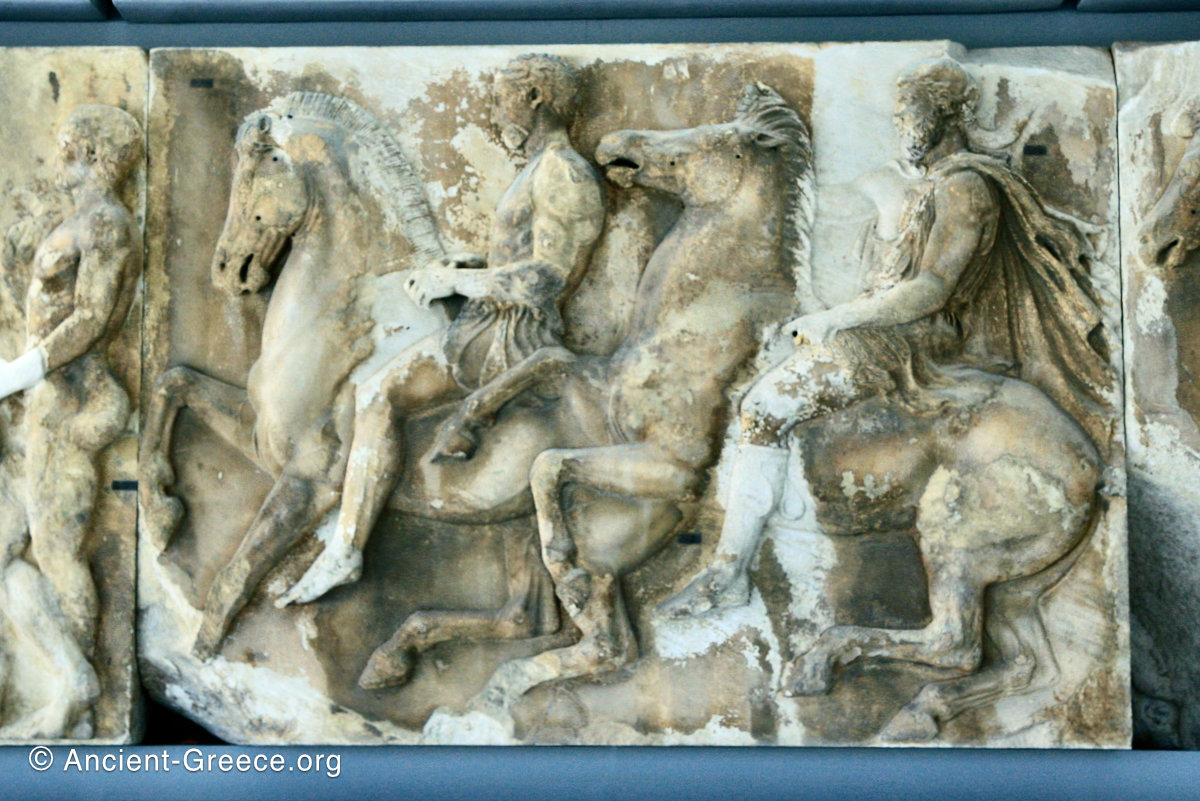
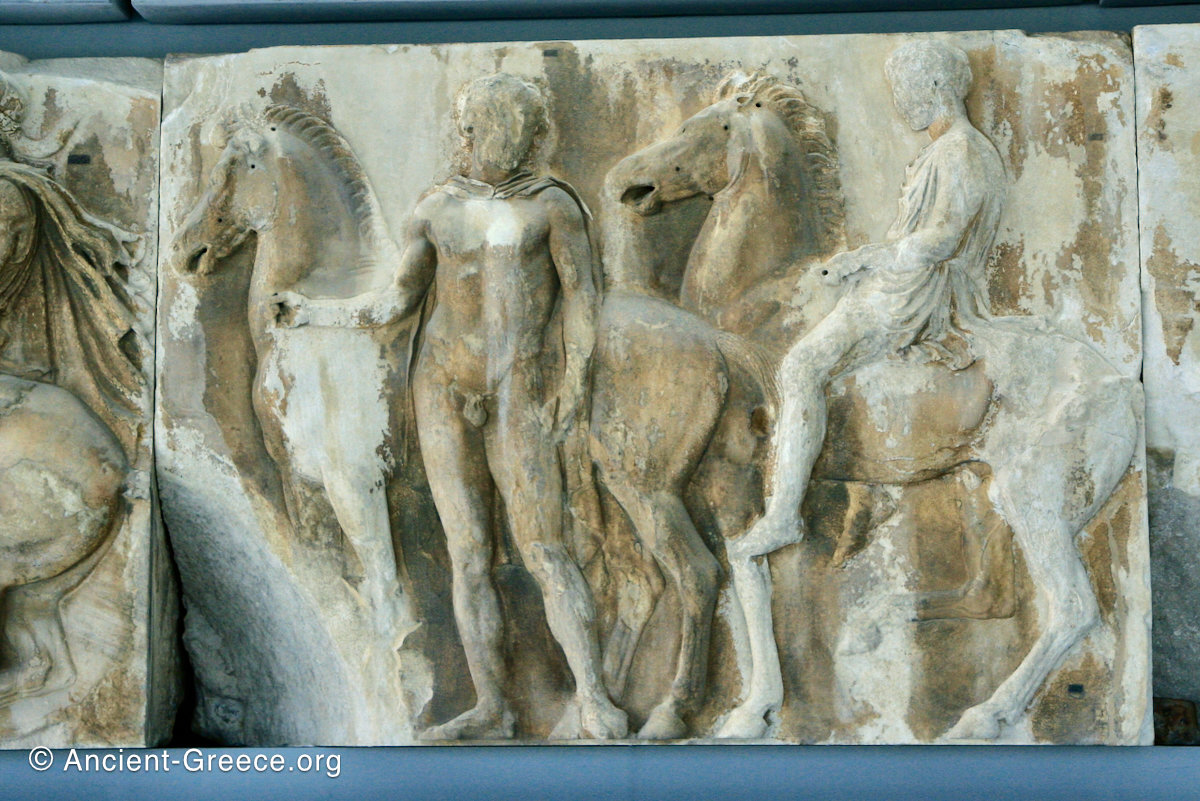
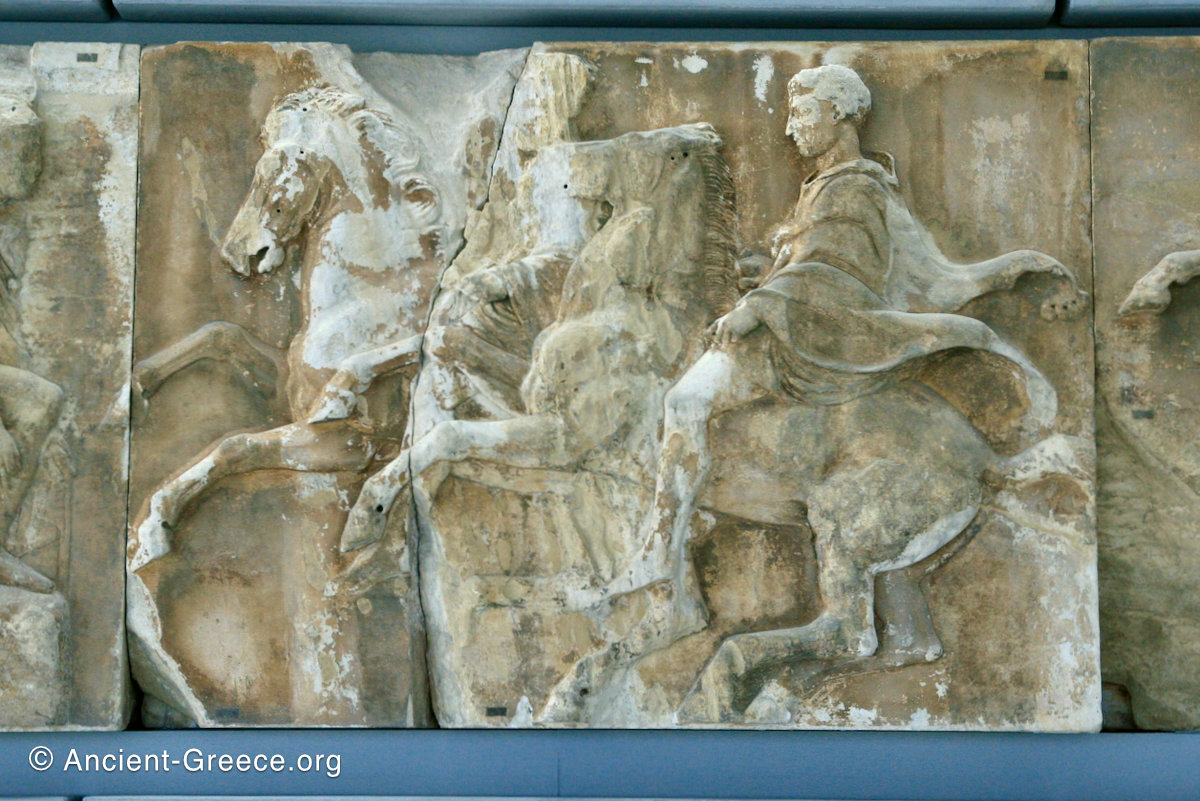
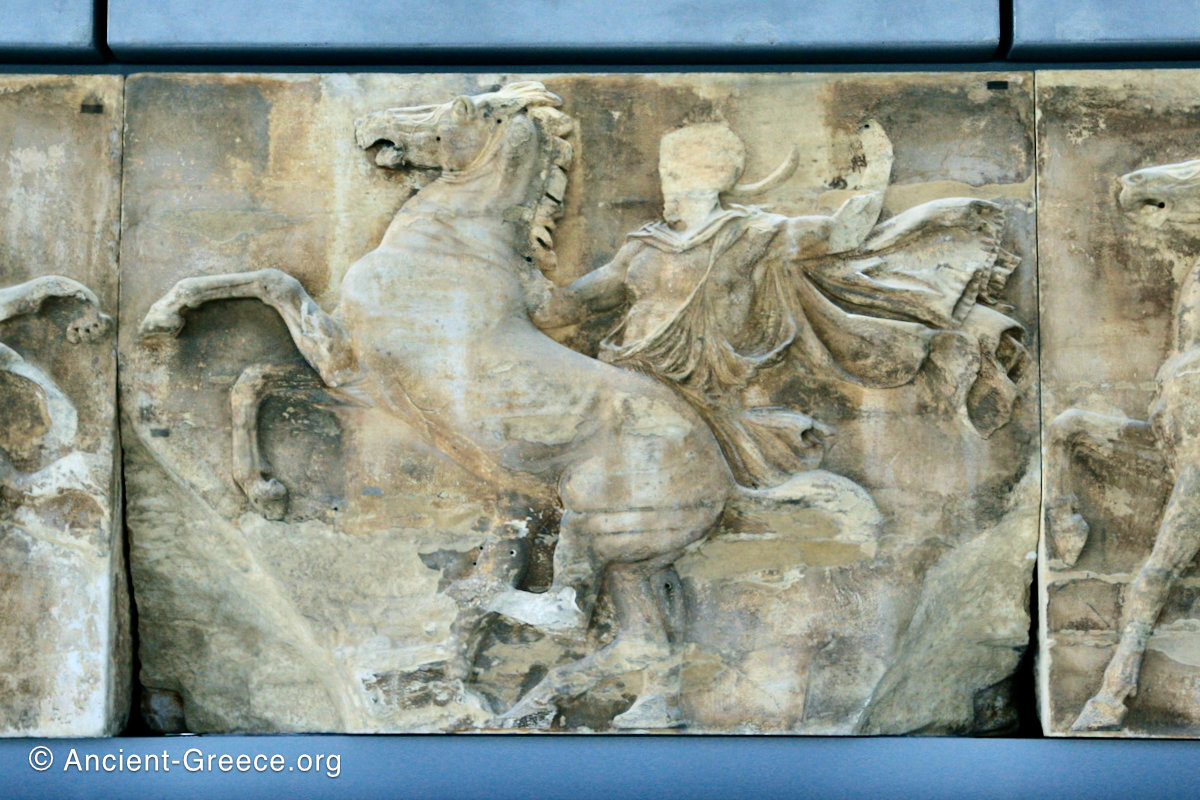
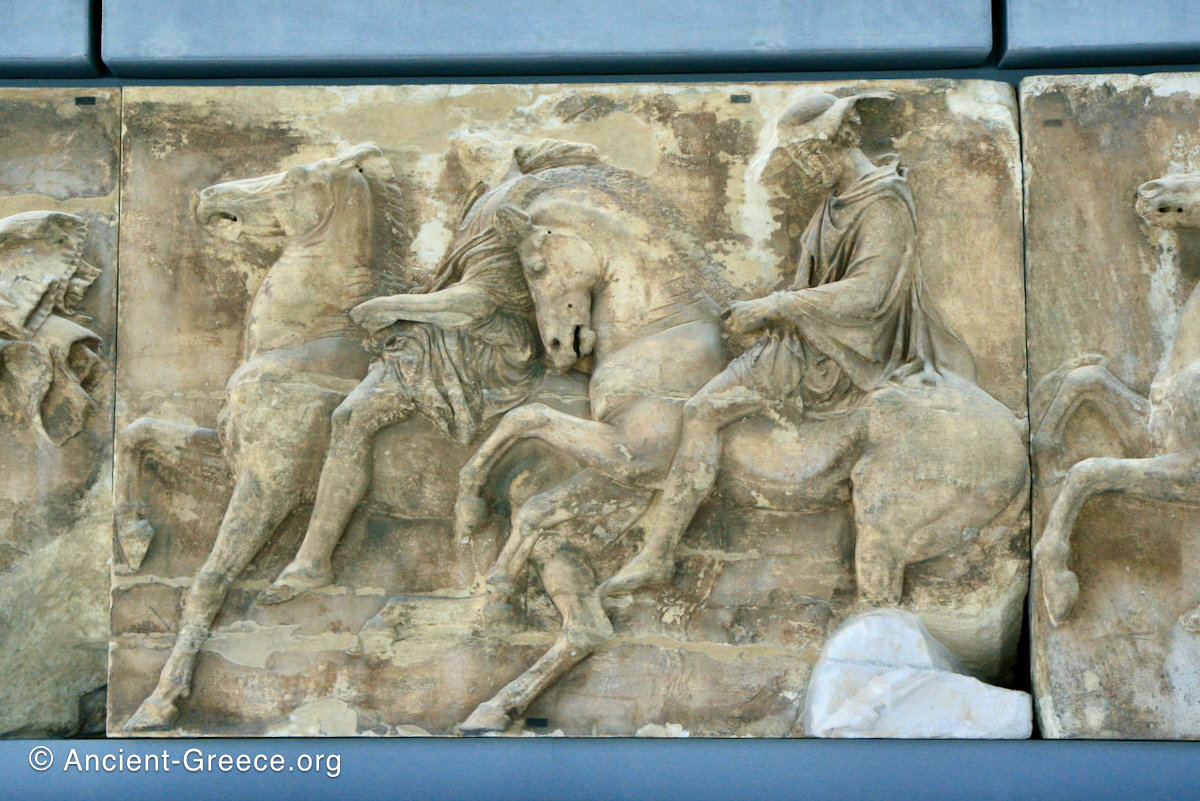
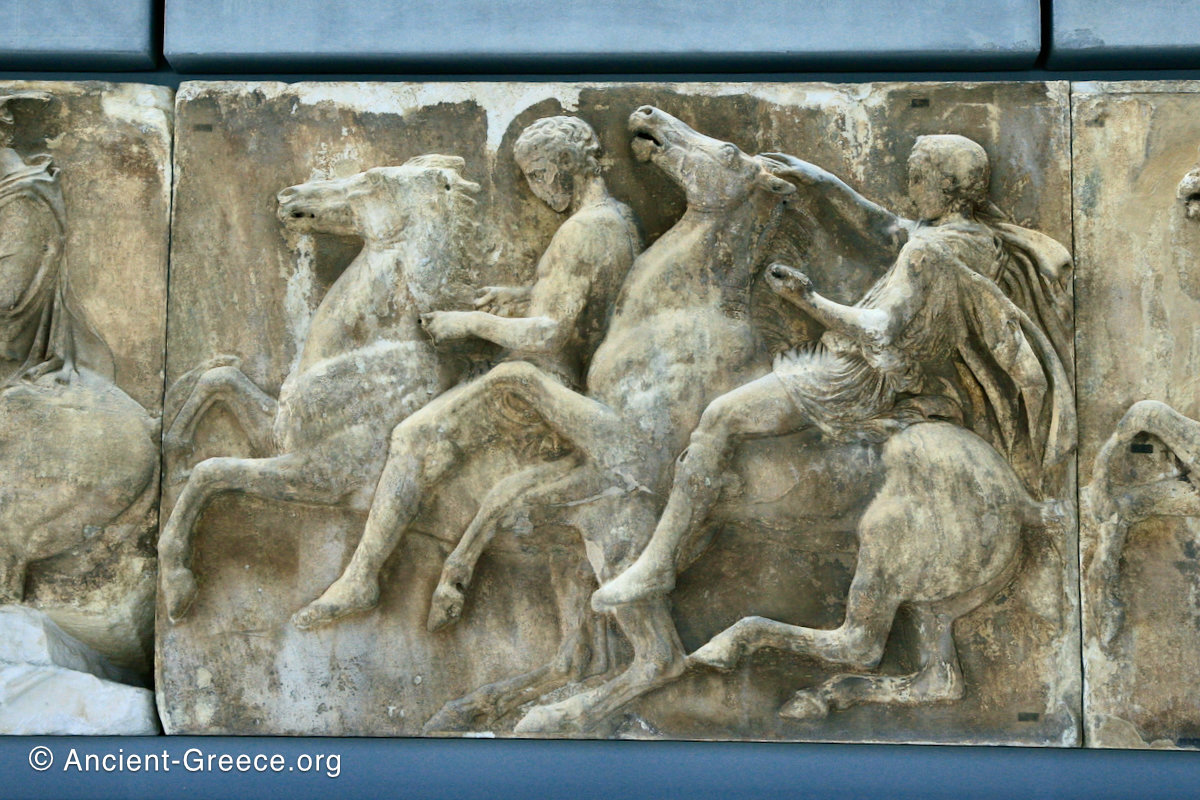
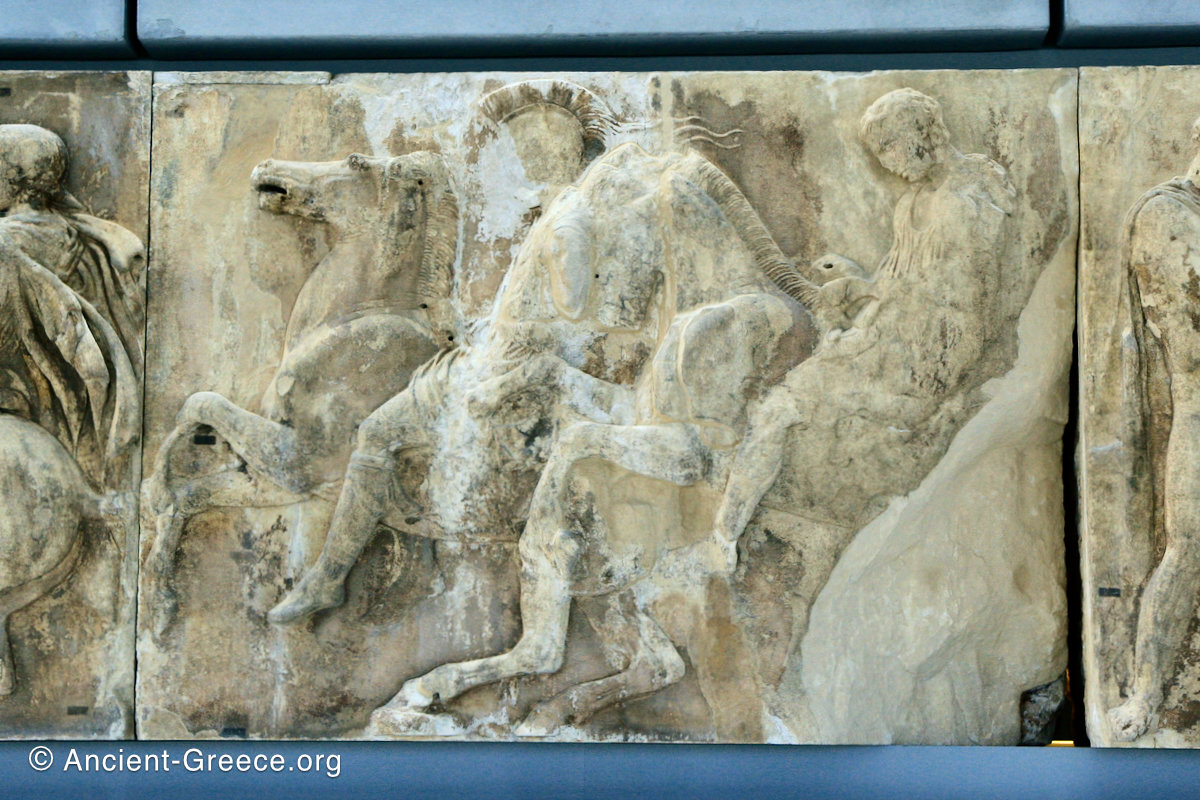
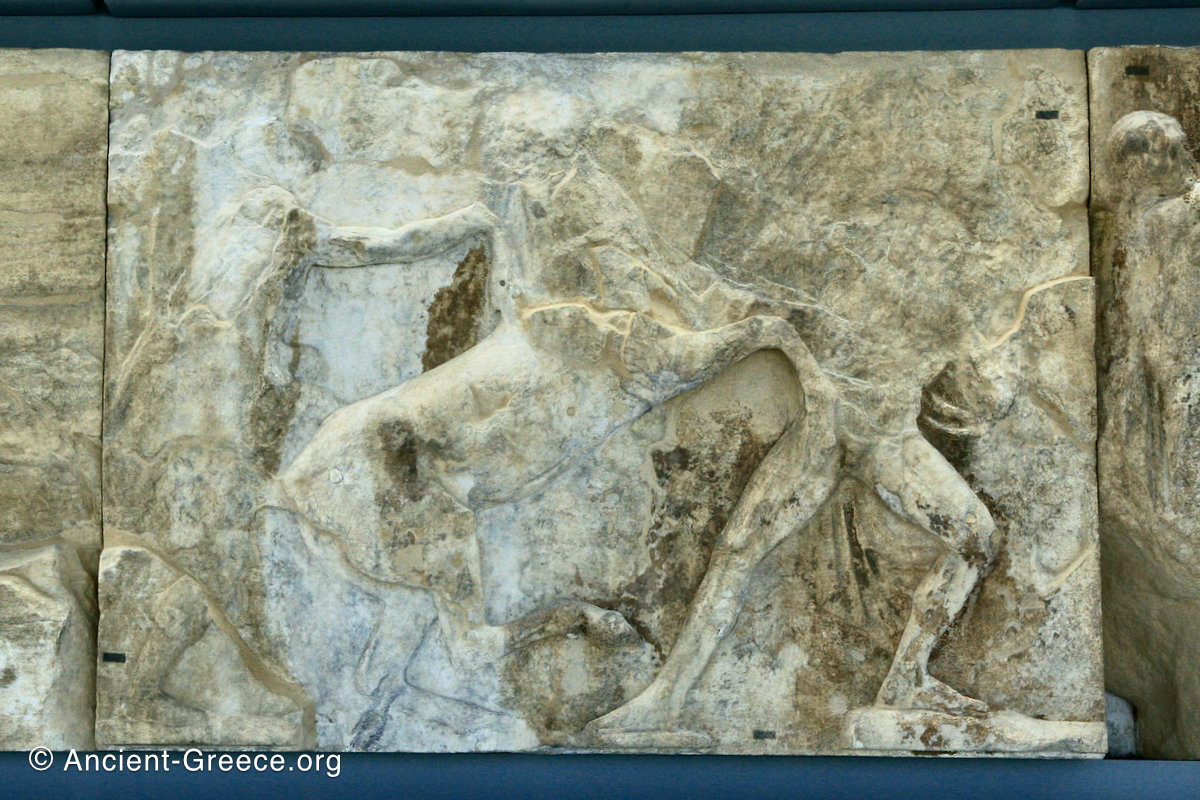
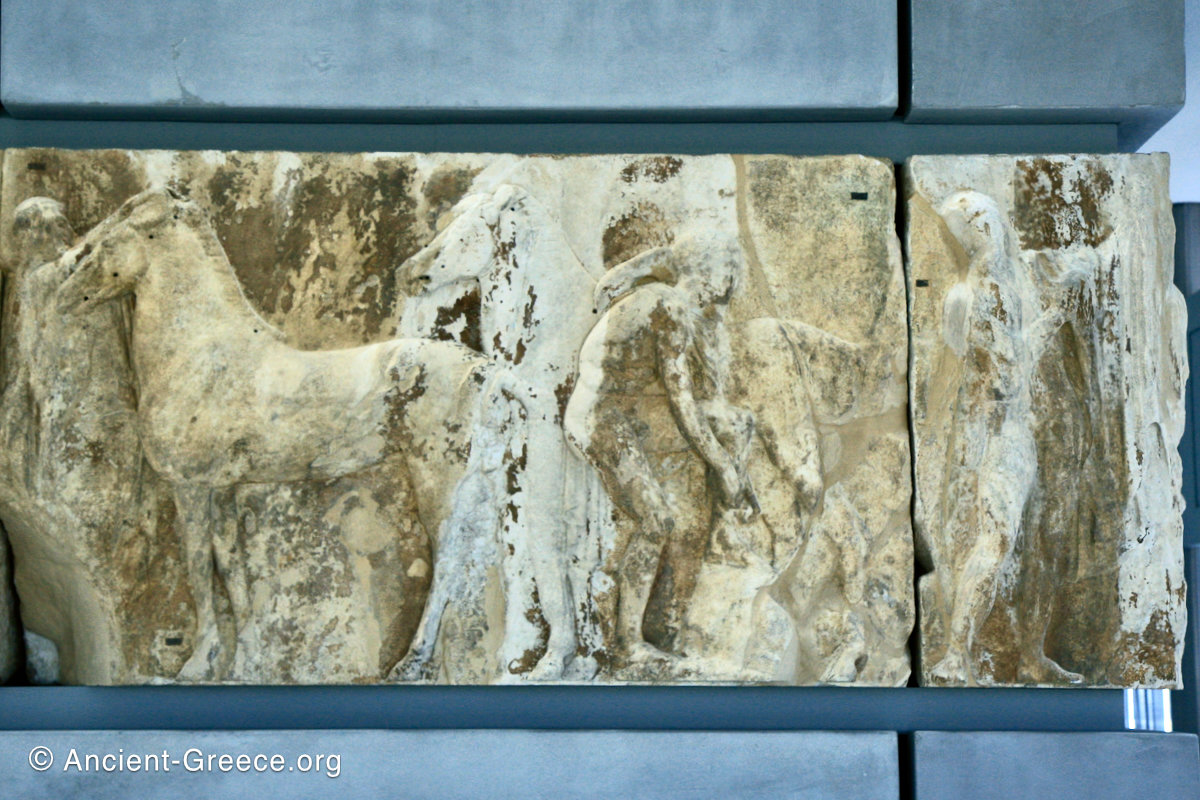
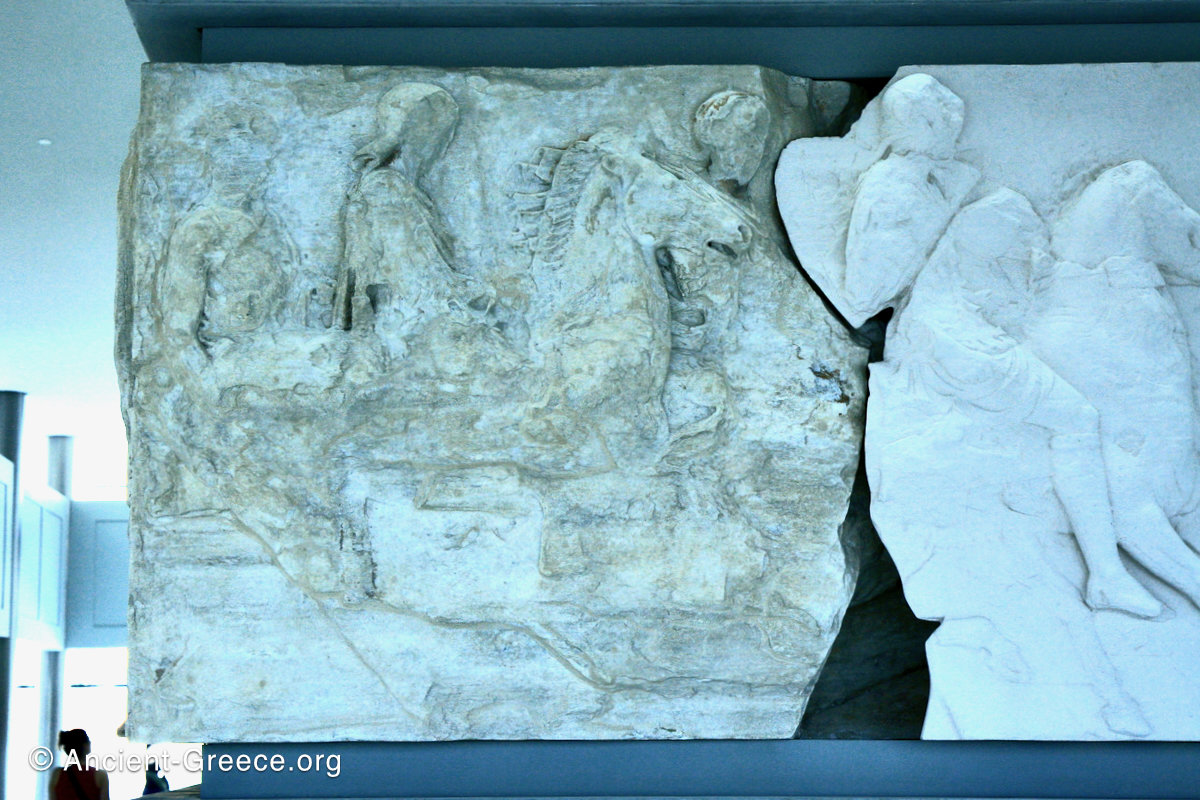
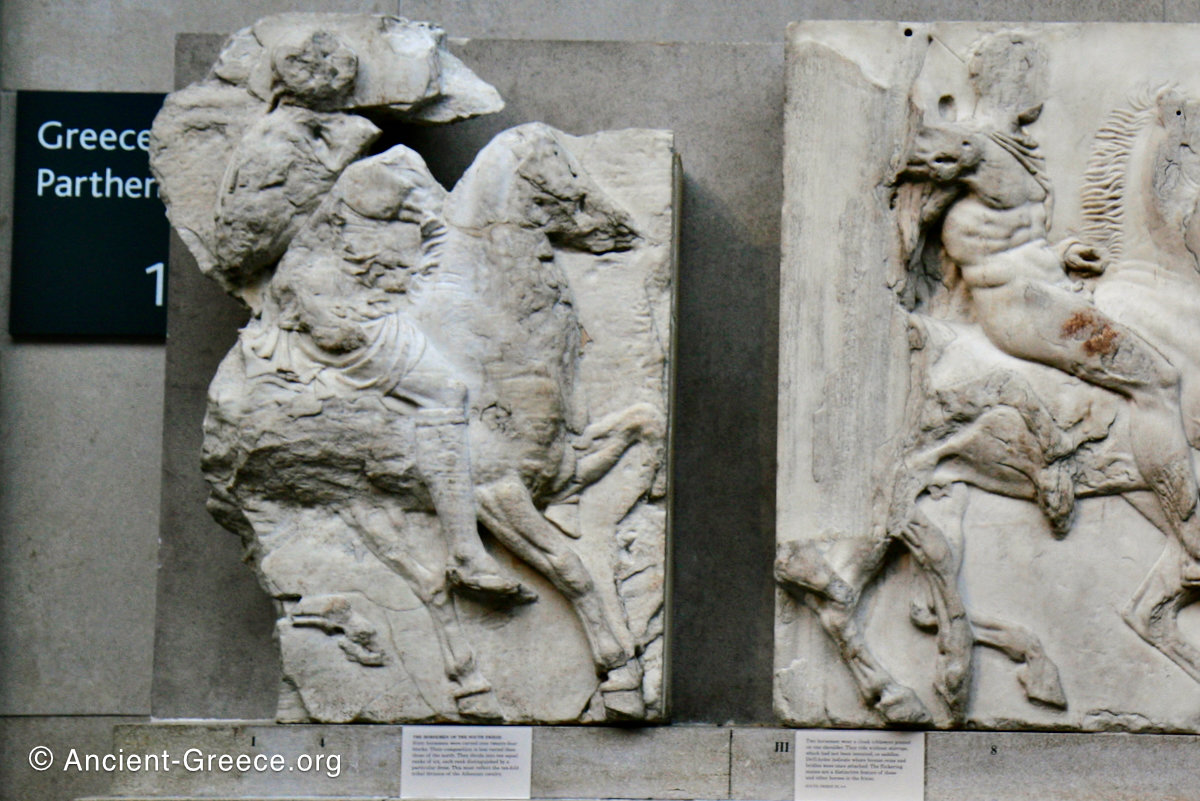
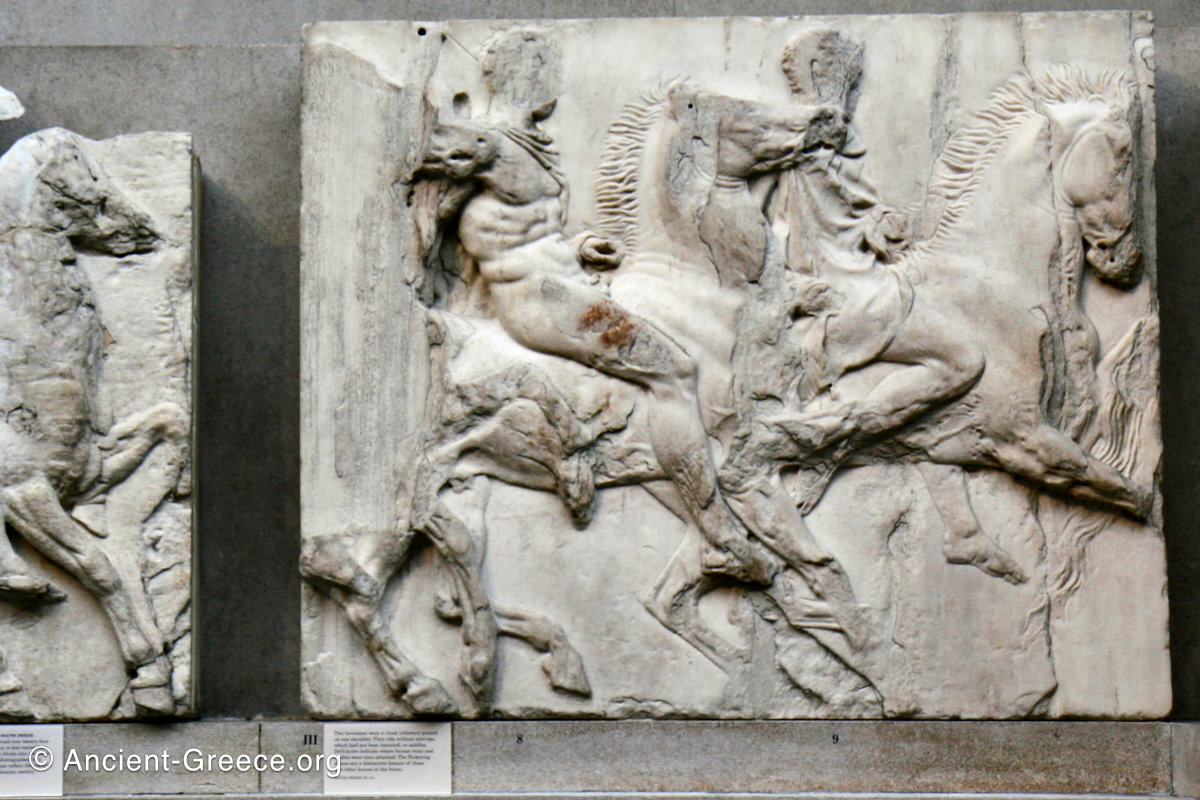
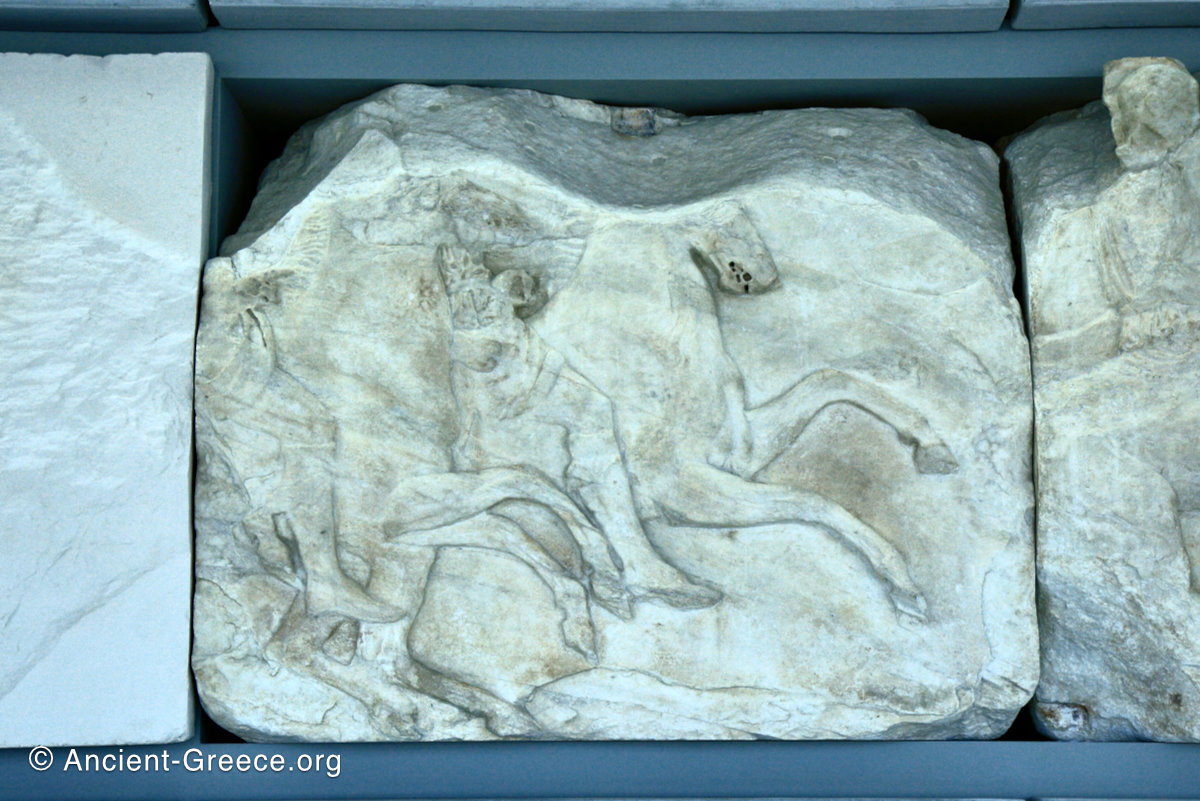
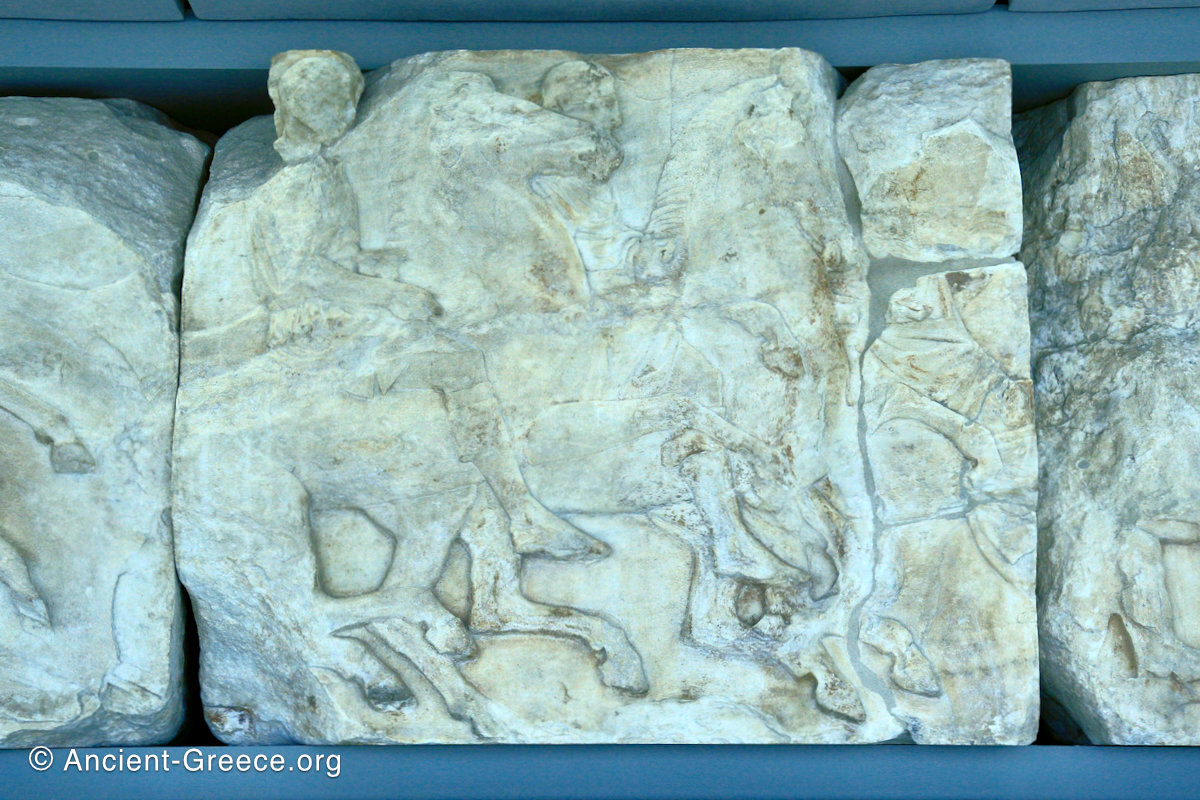
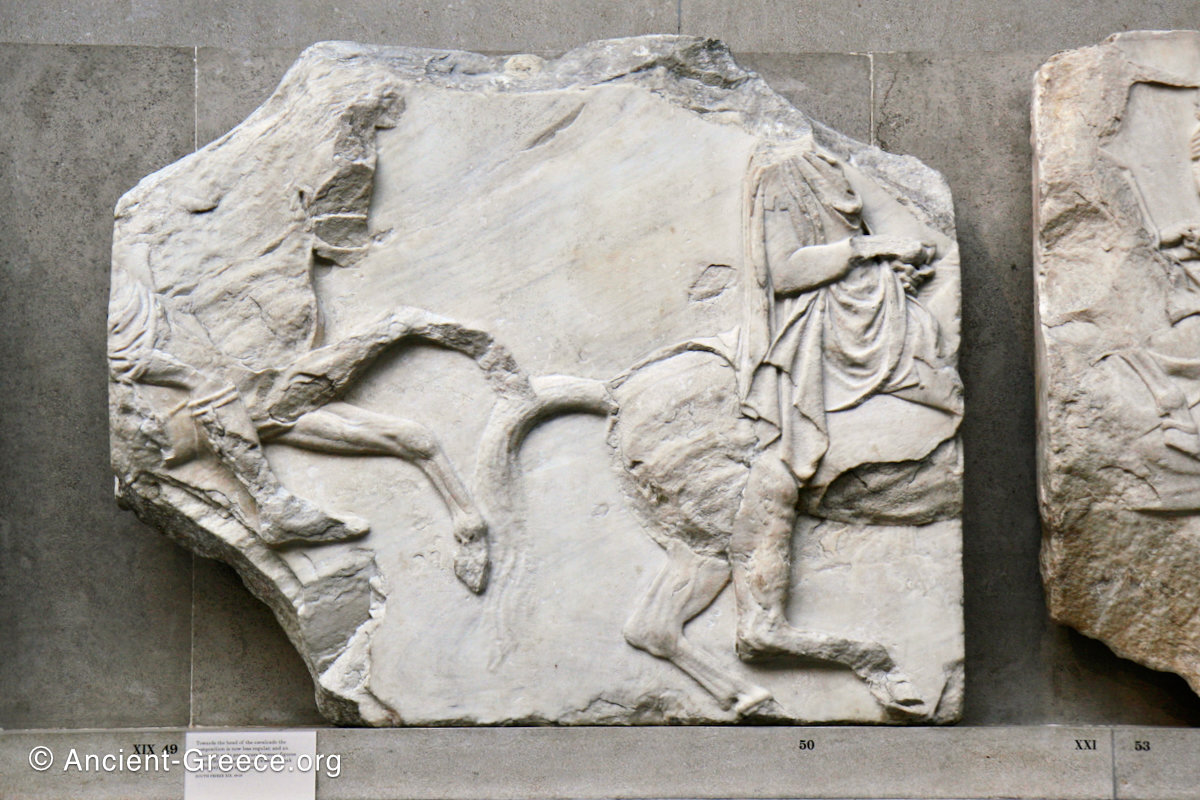
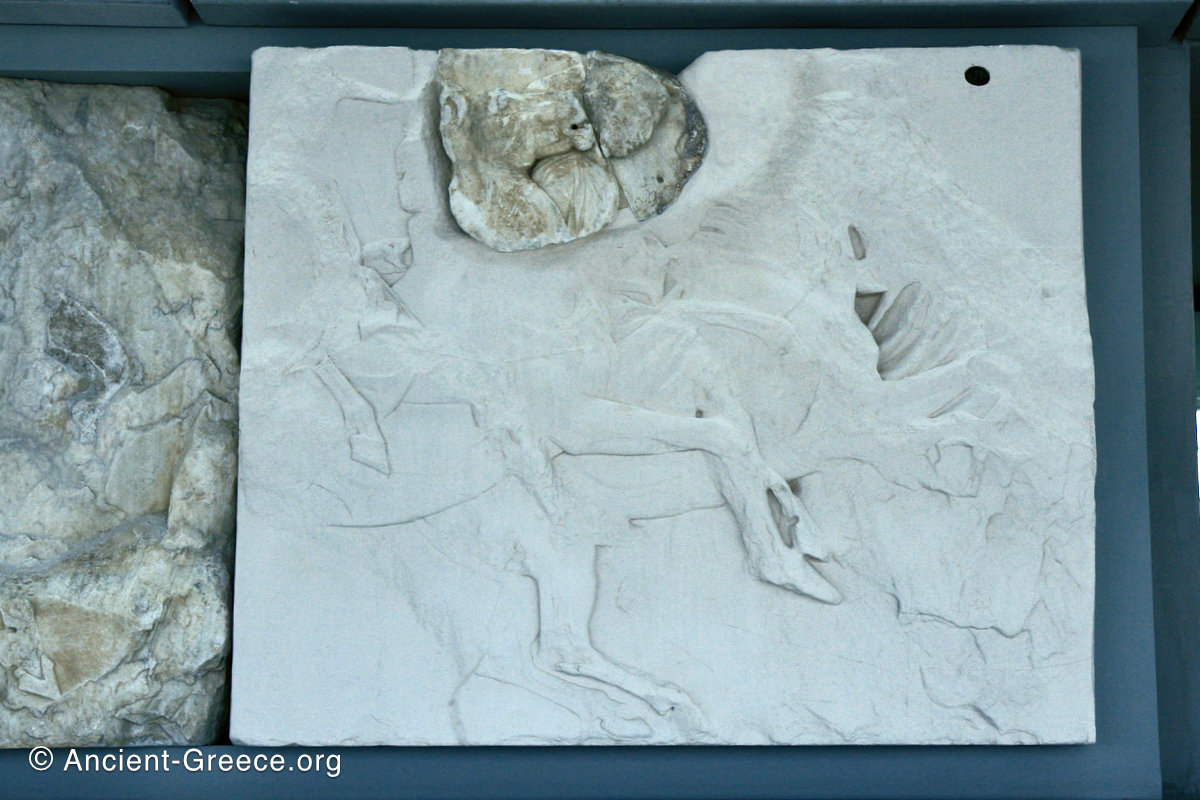
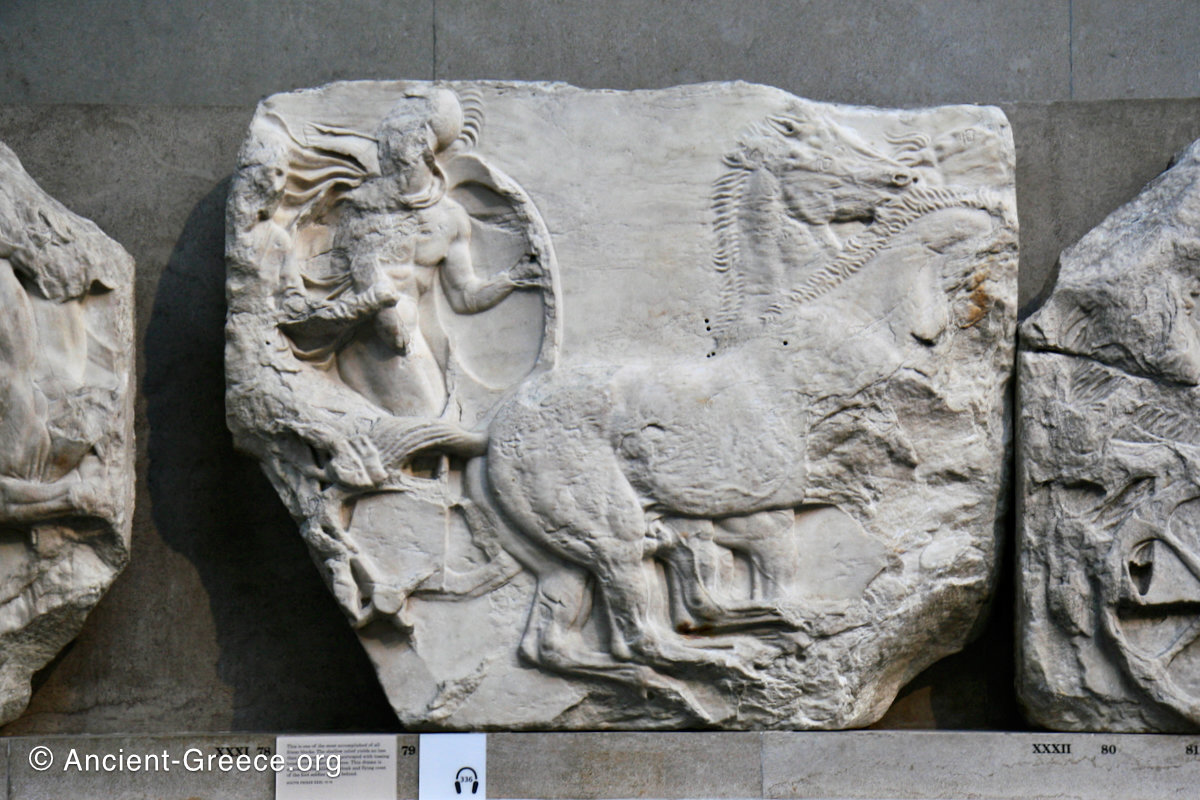
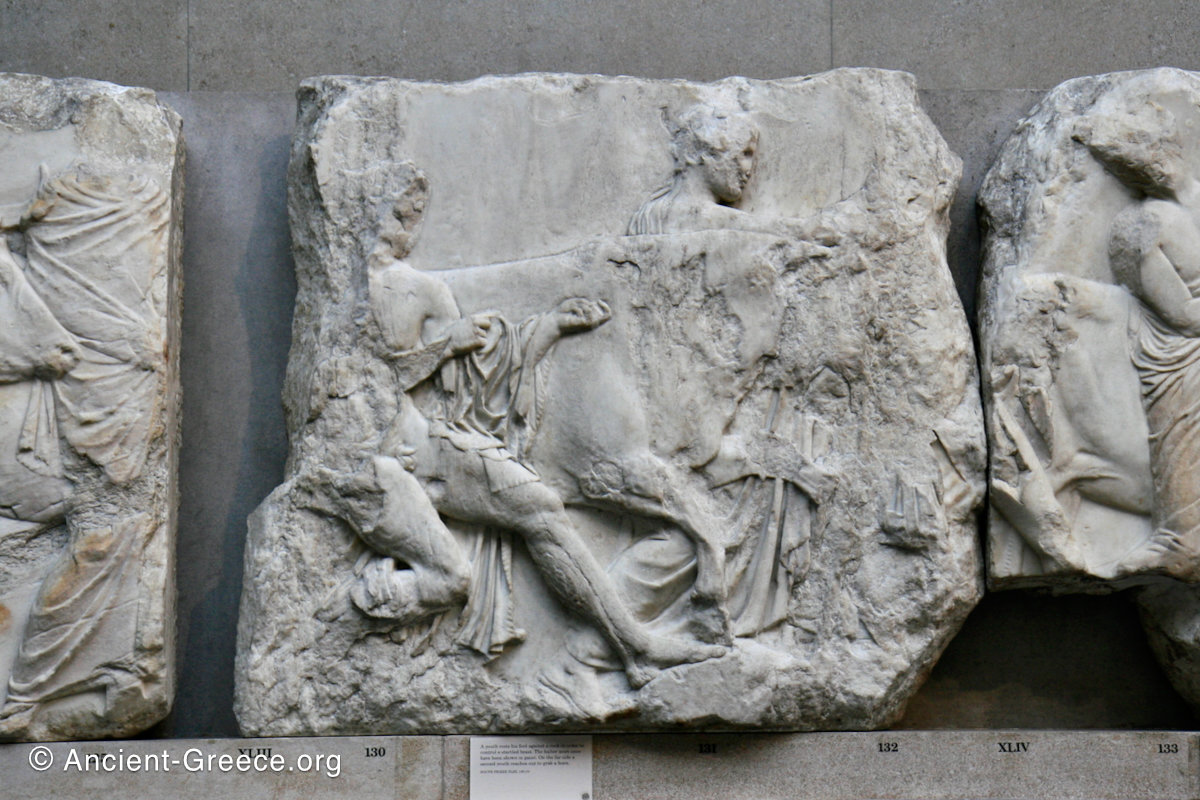
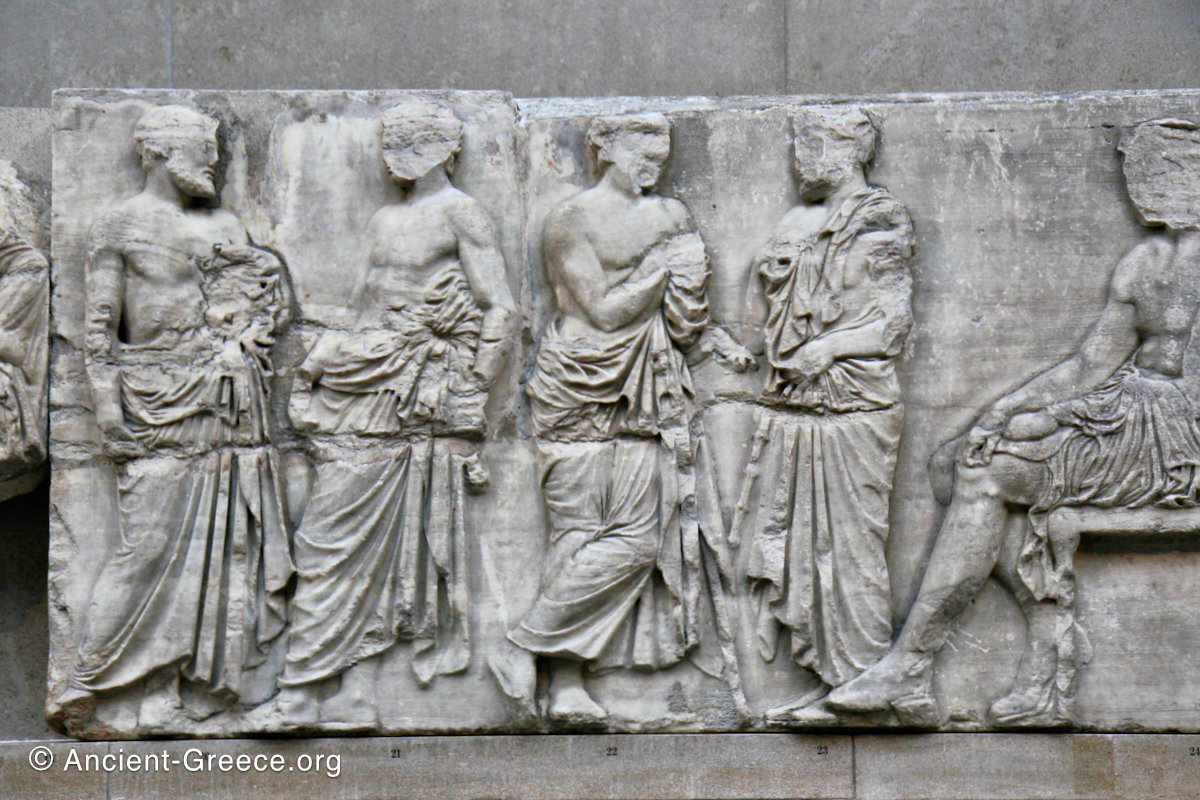
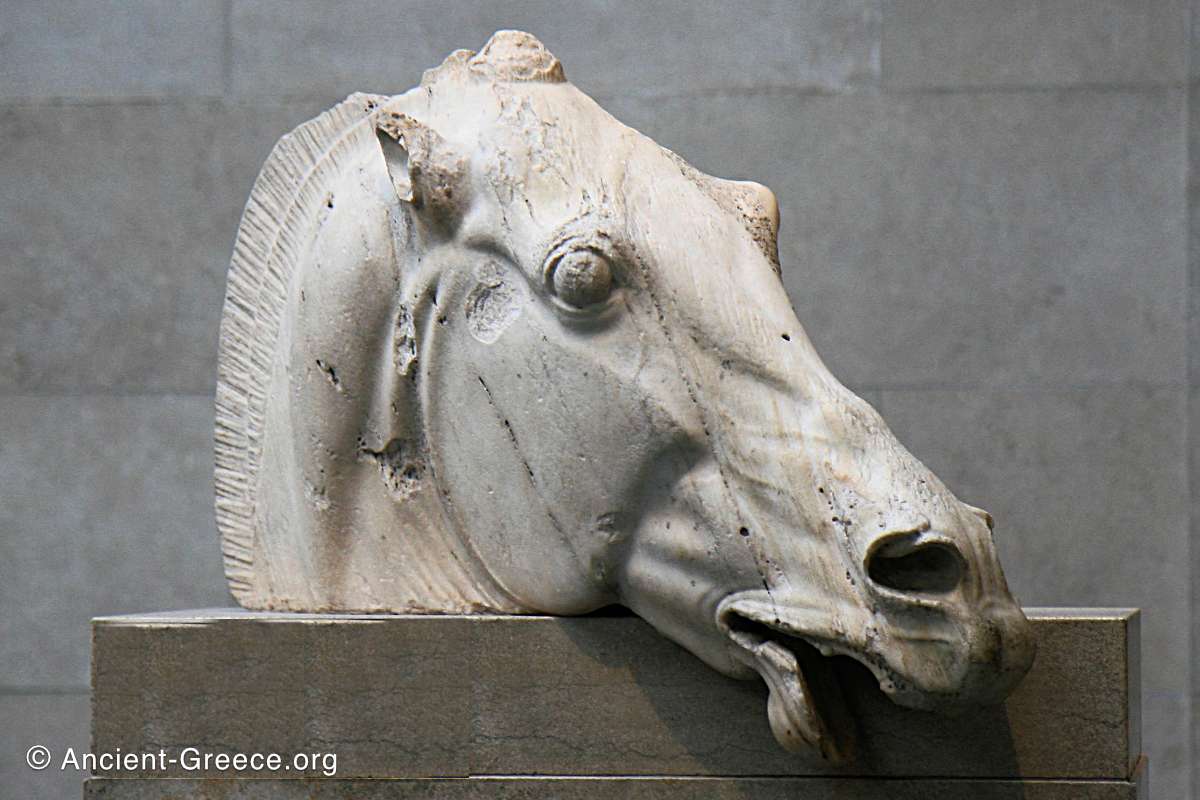
The sculptures of the west frieze depict groups of people and horses getting ready for the procession. A large number of cavalry dominates the west end of the frieze, with many horses appearing agitated, adding an atmosphere of energetic unrest.
South Frieze






































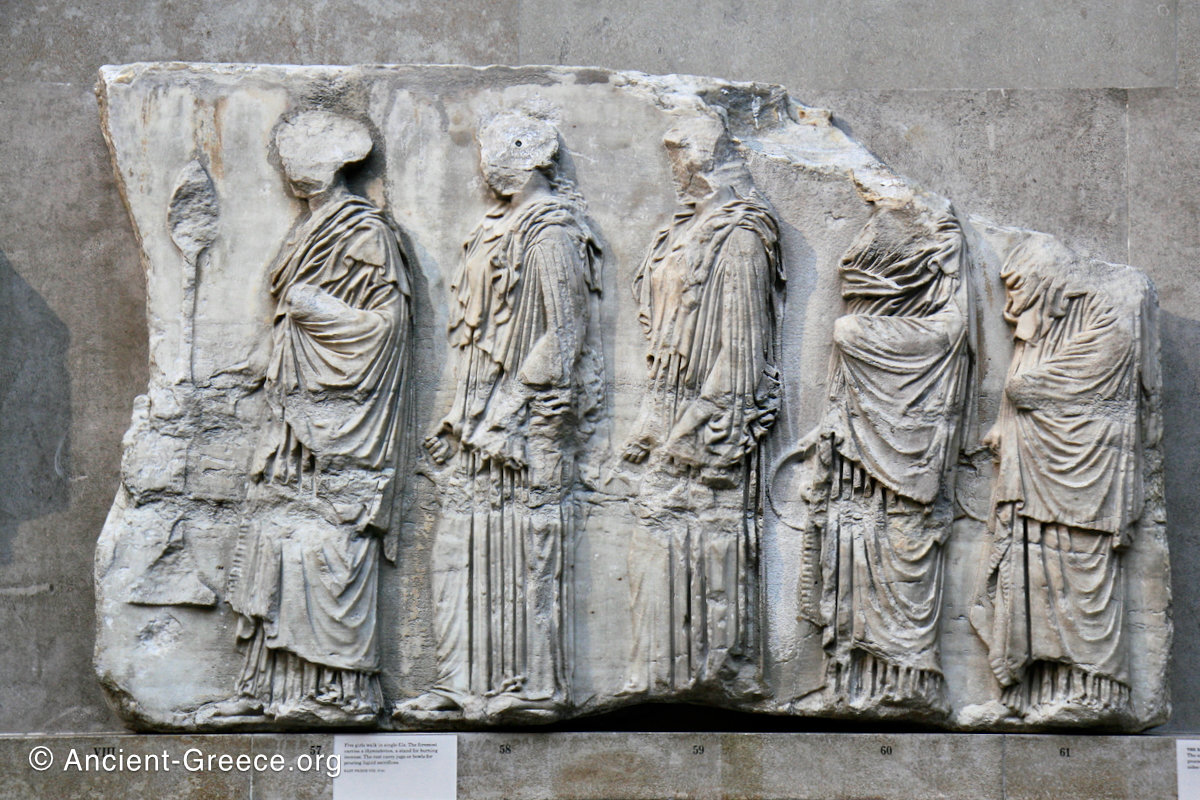
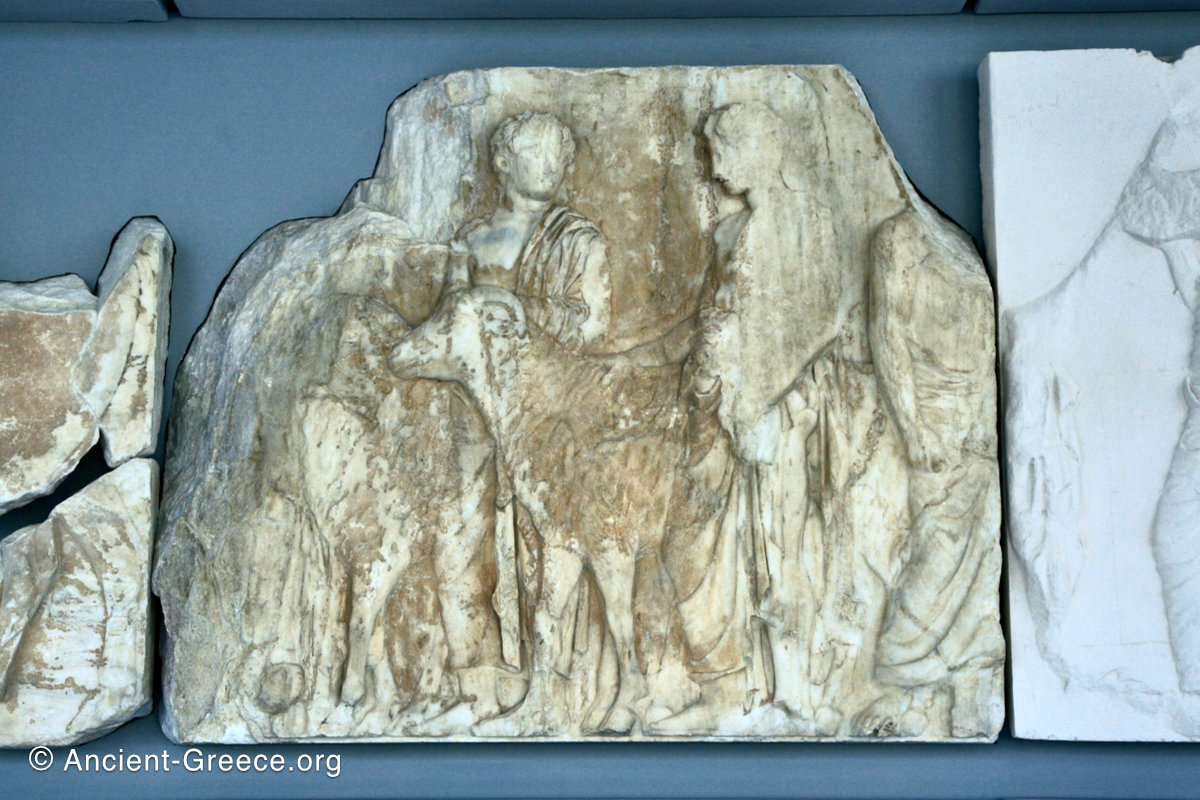
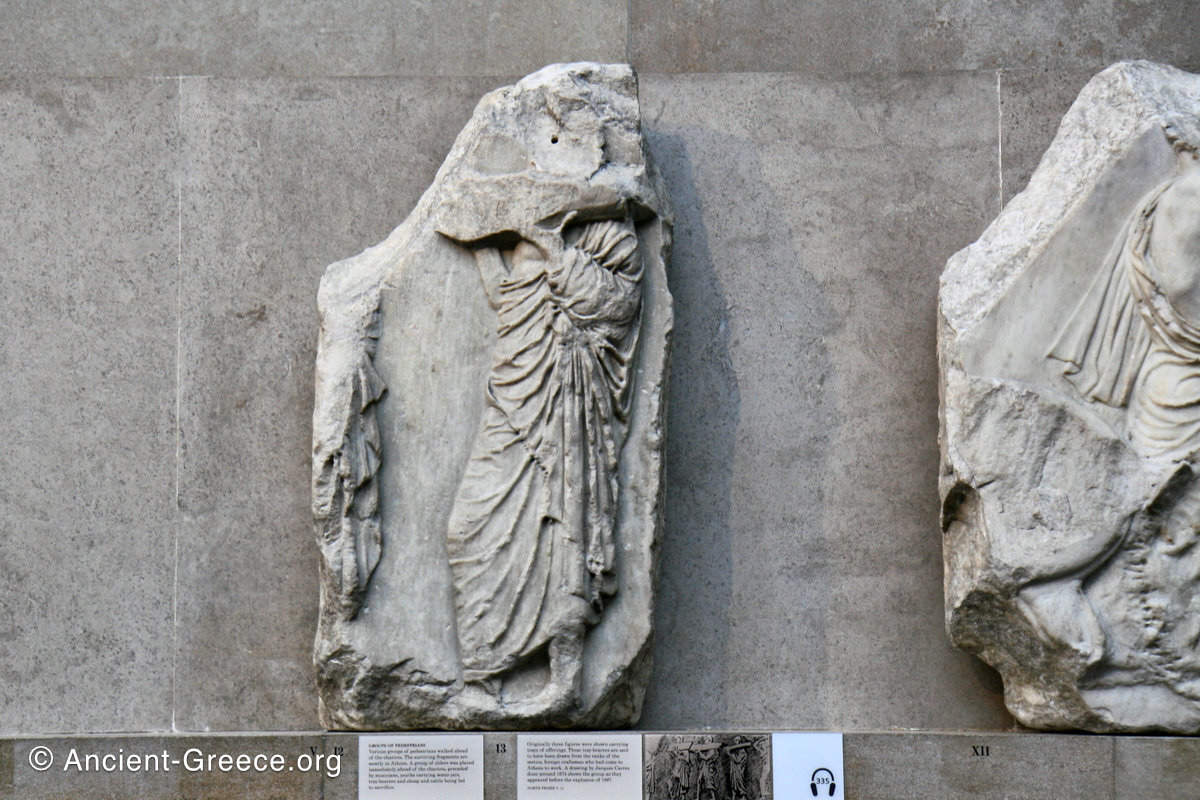
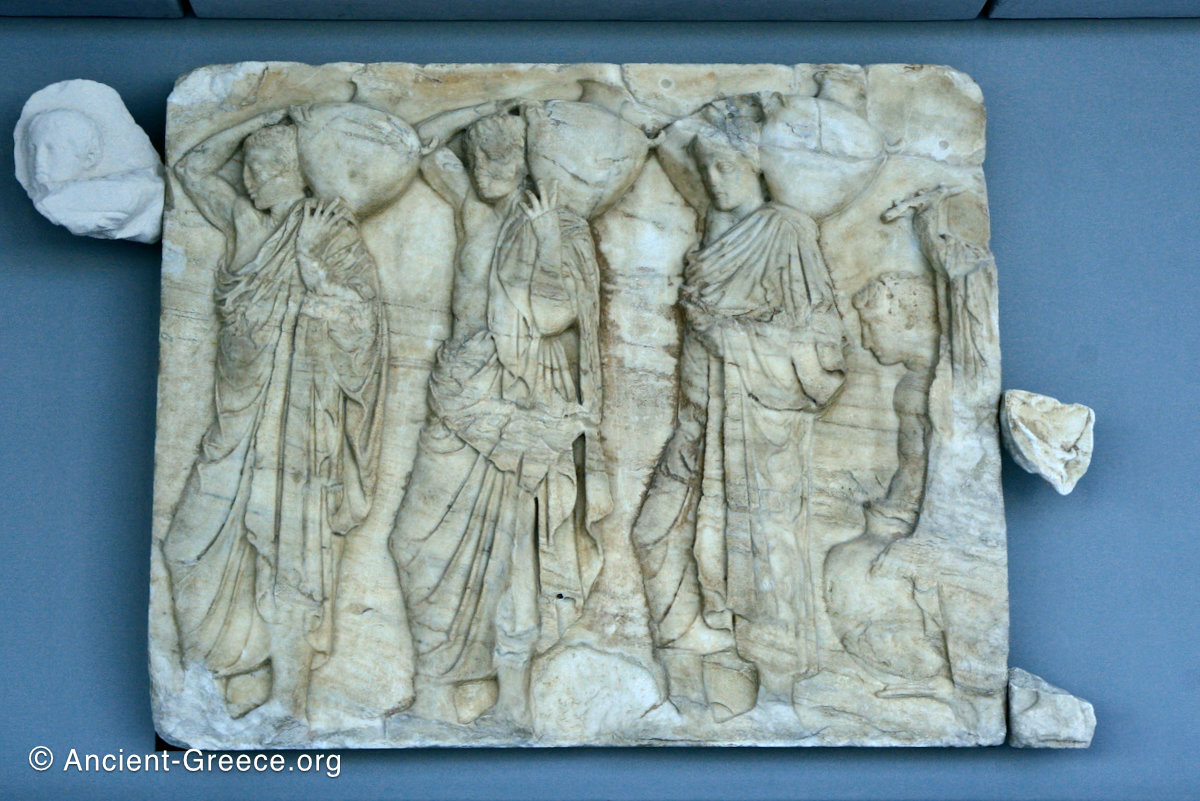
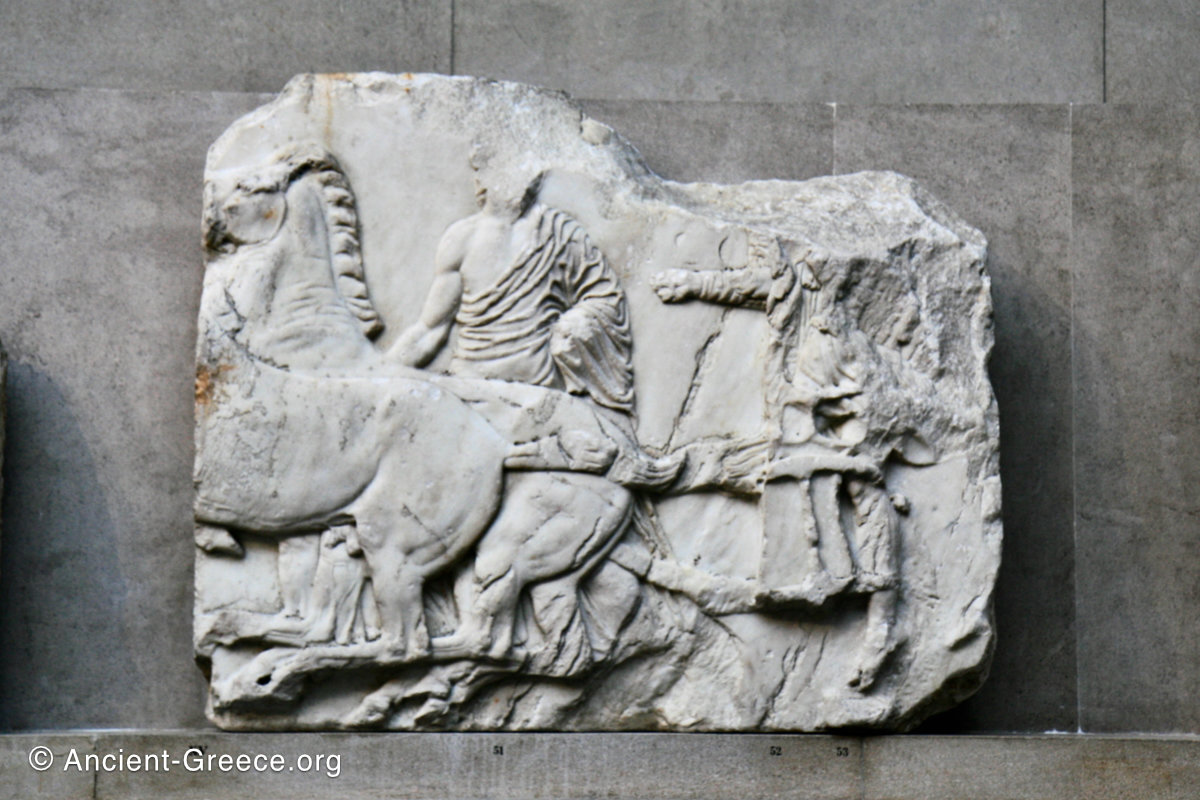
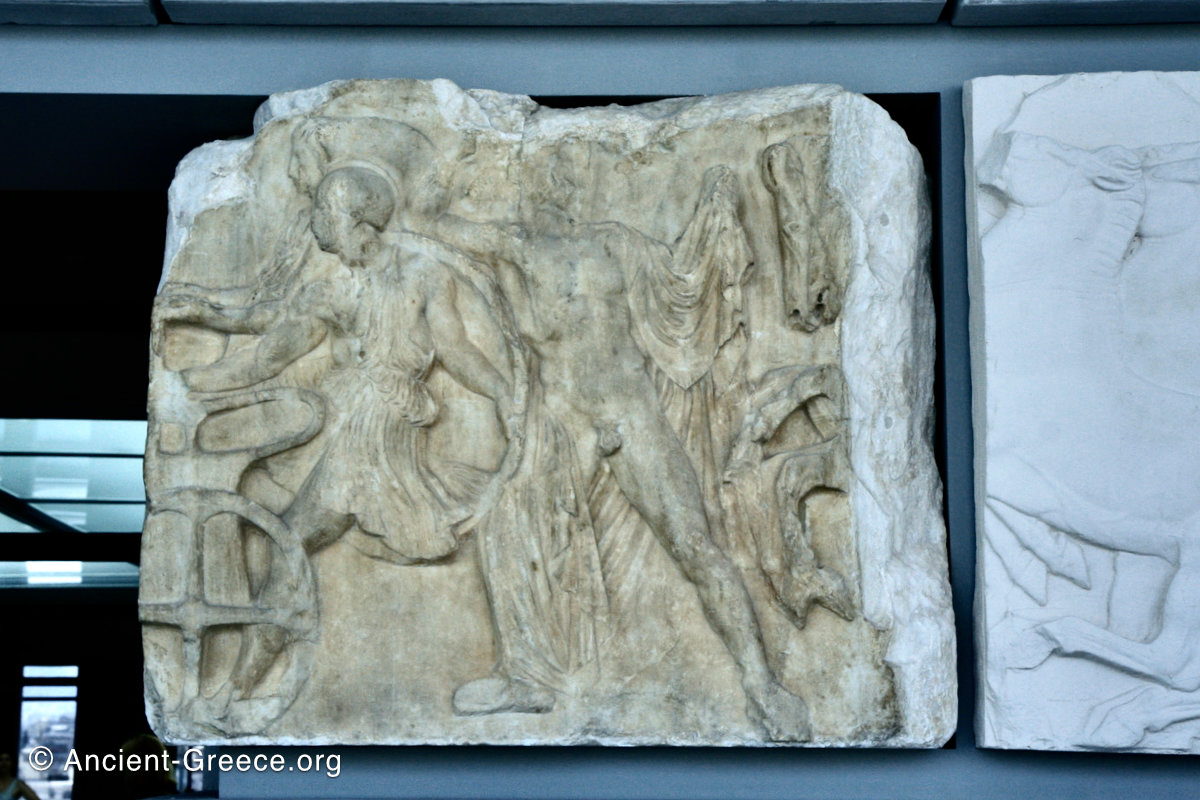
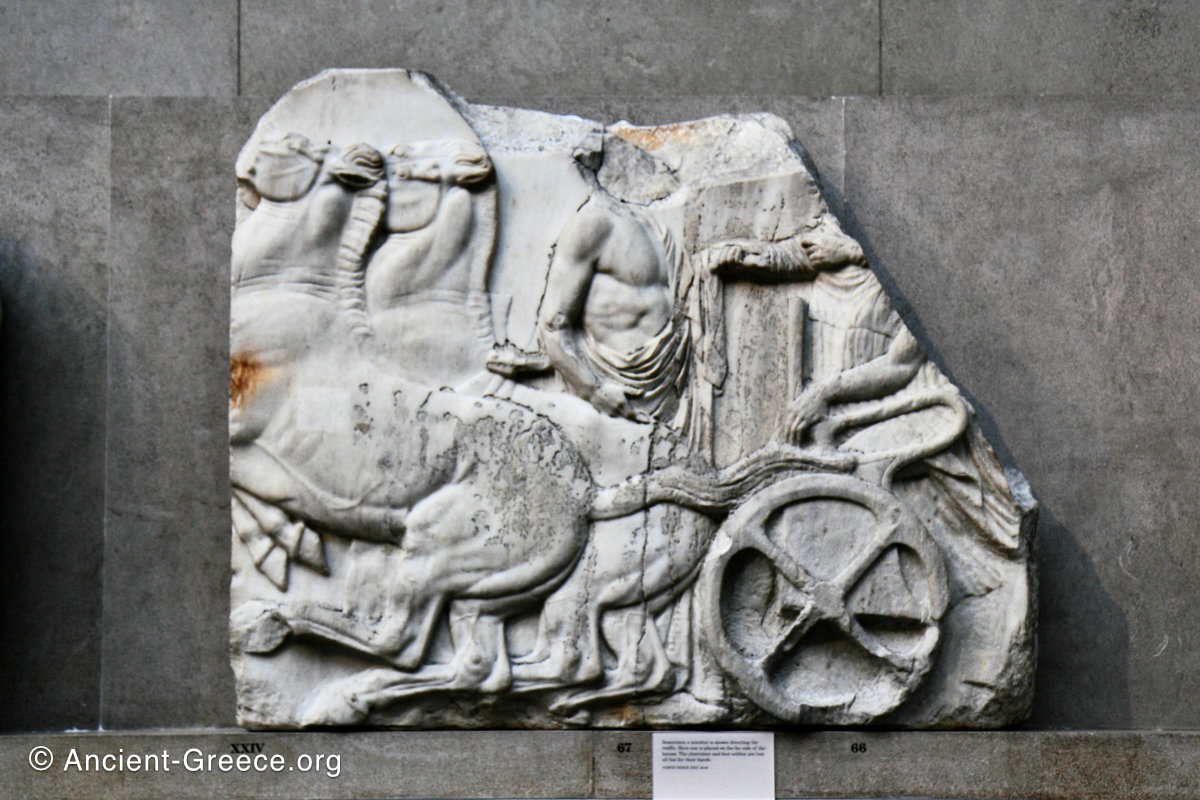
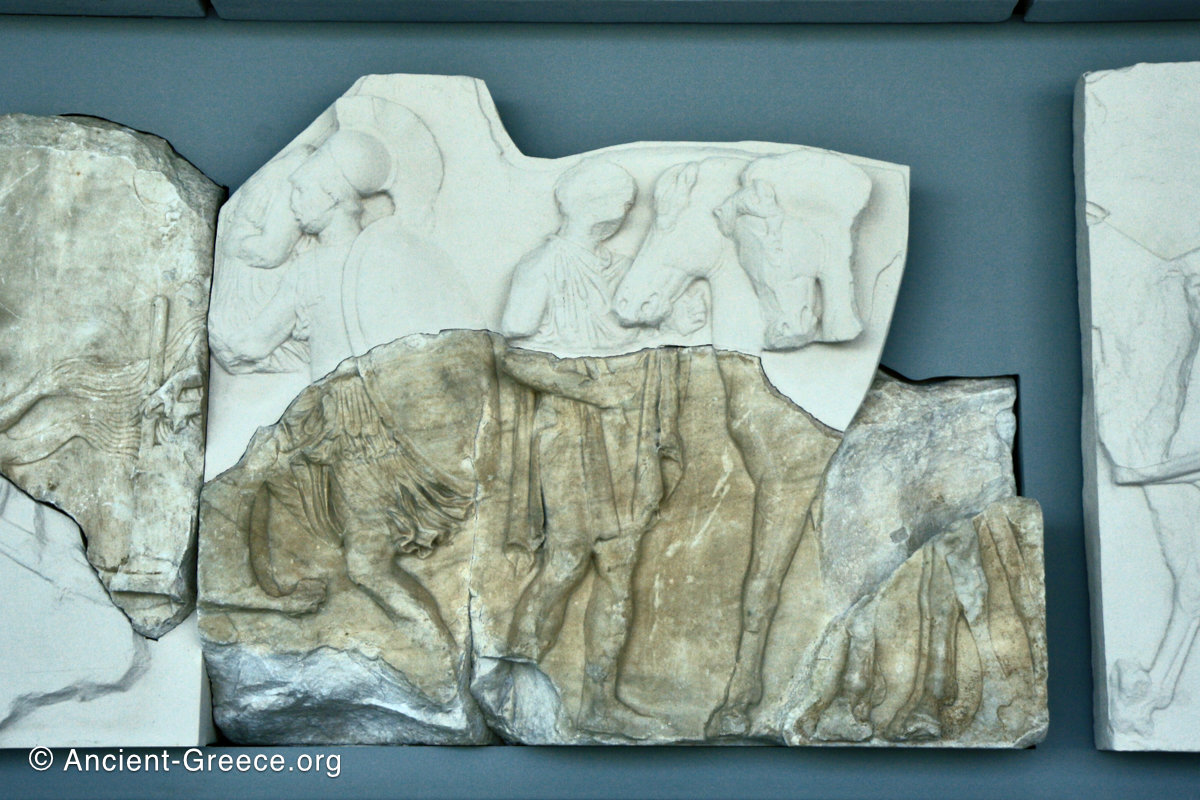
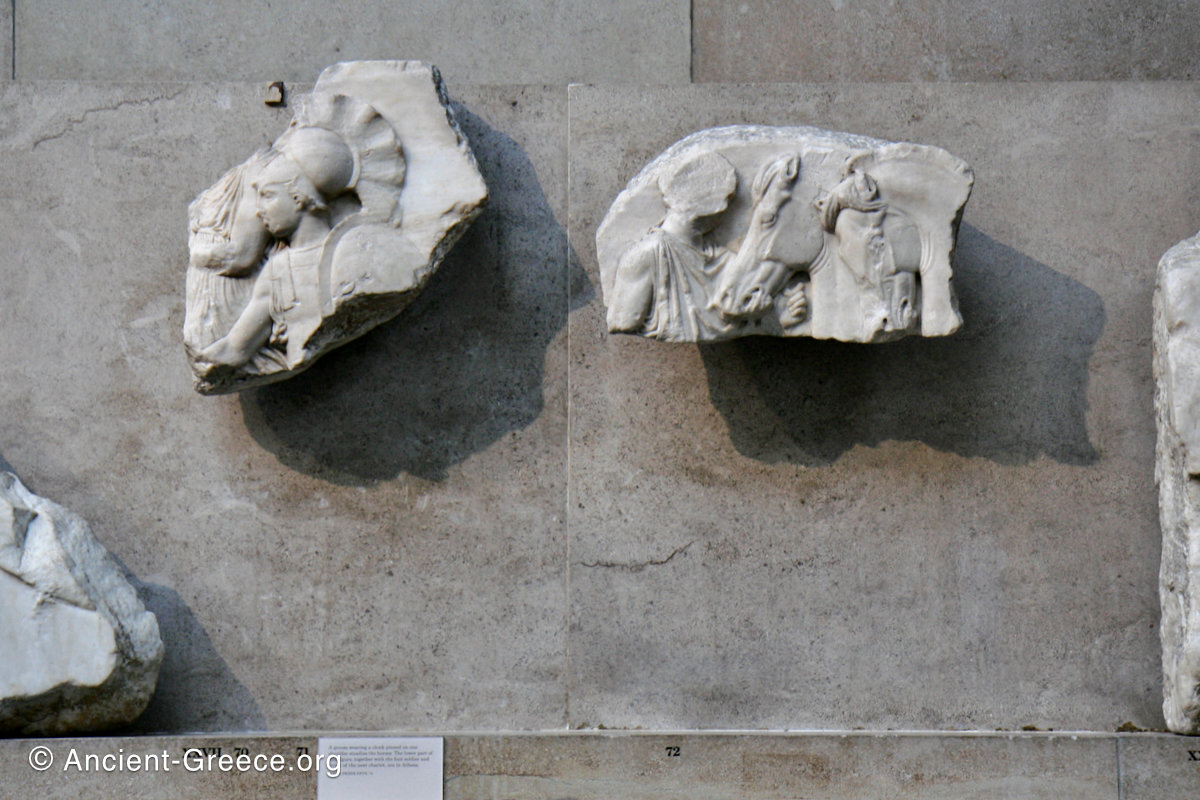
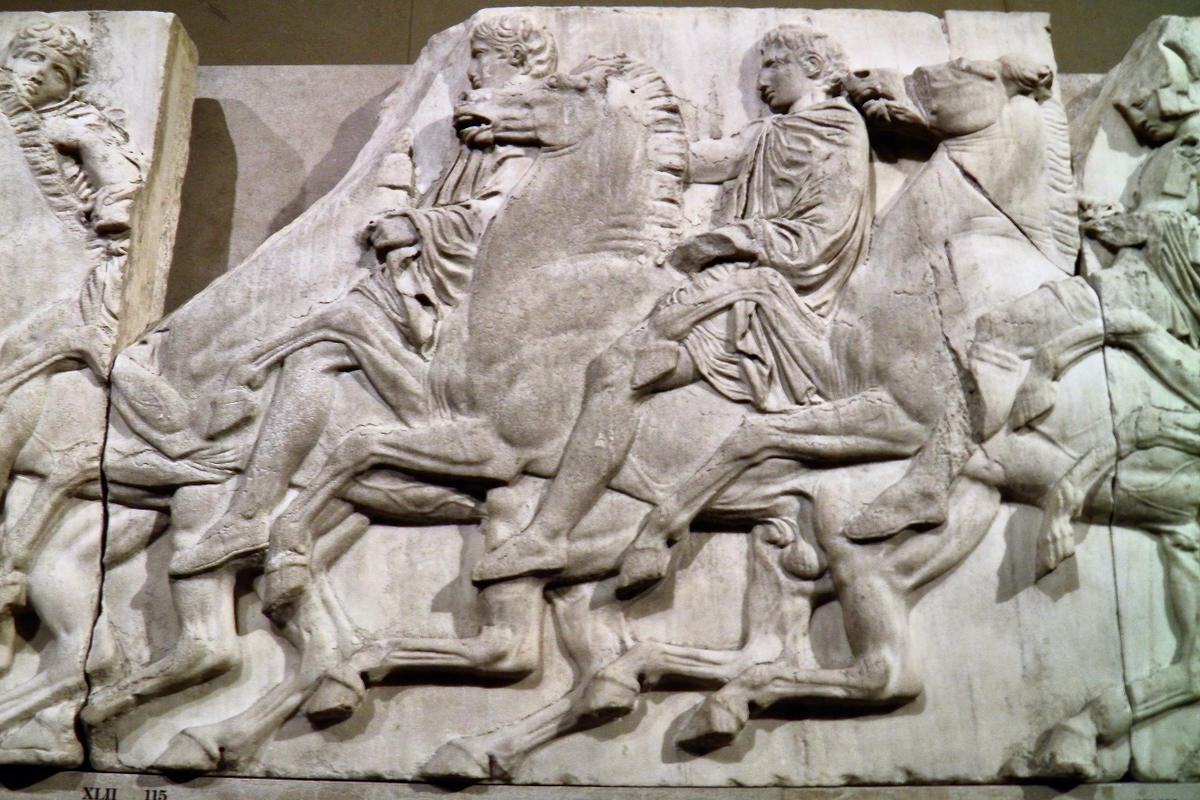
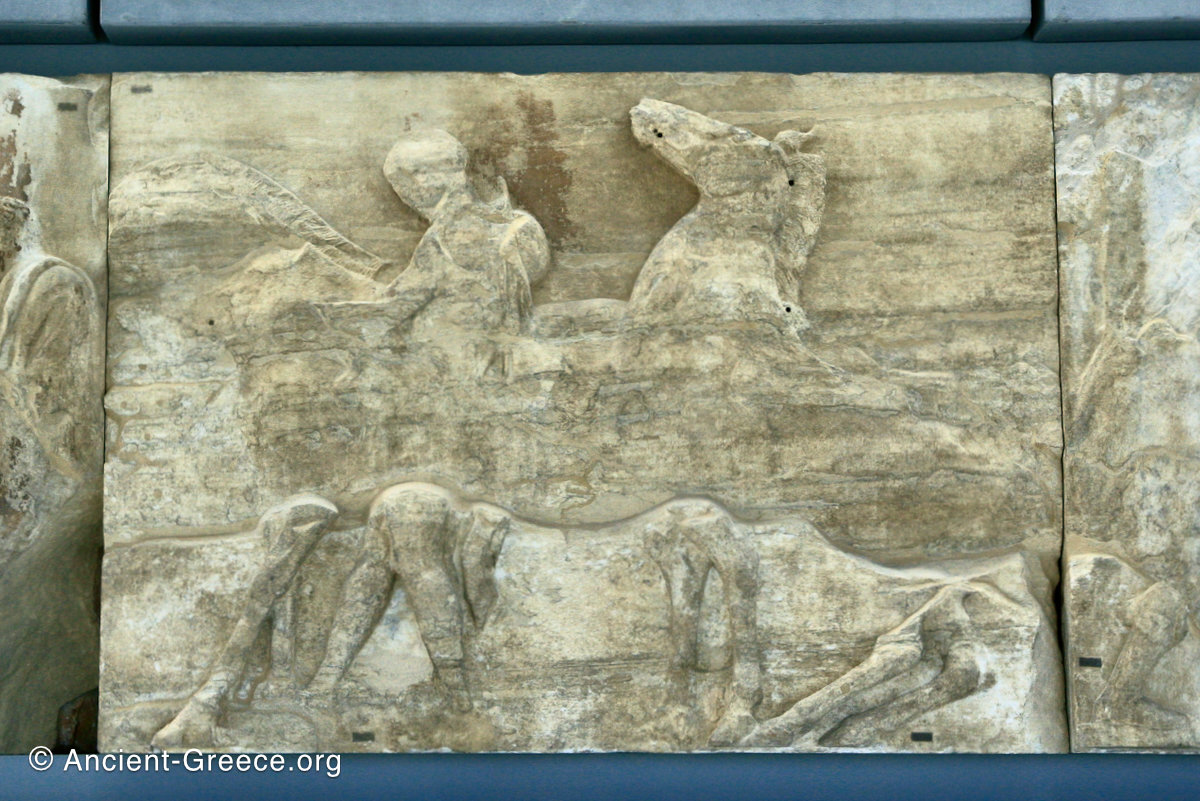
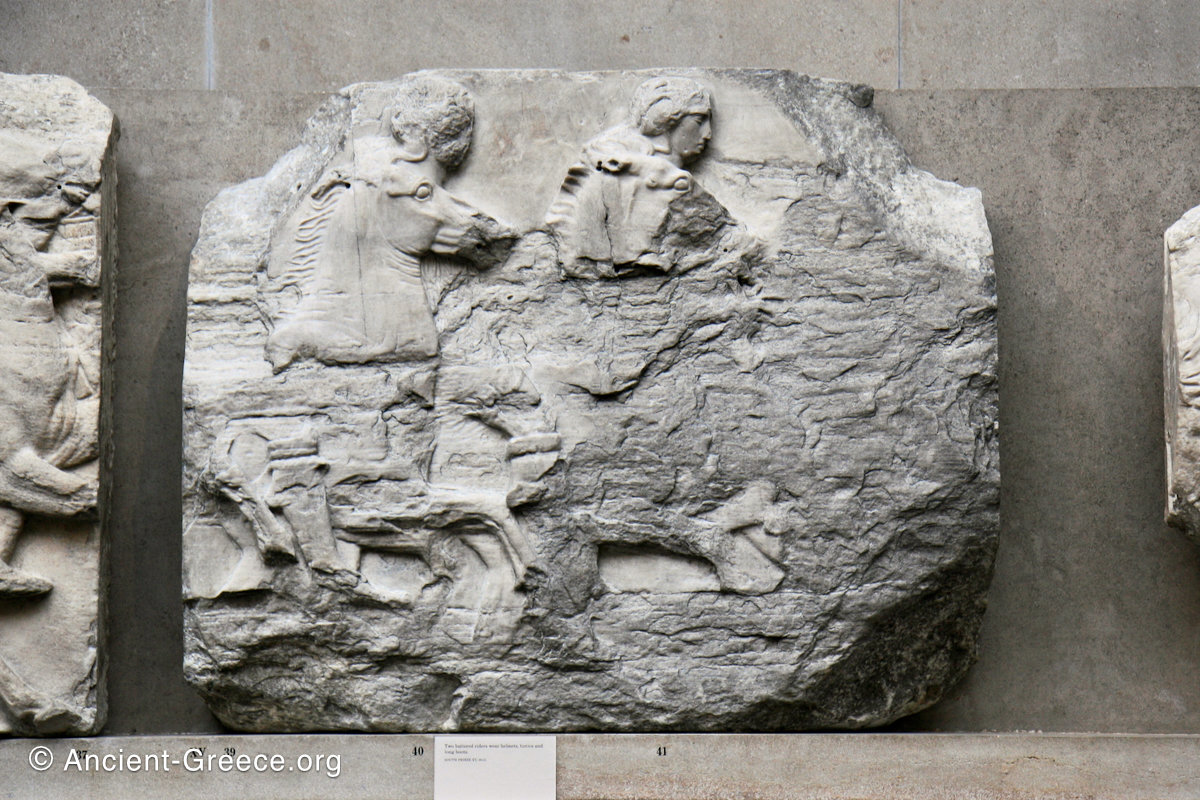
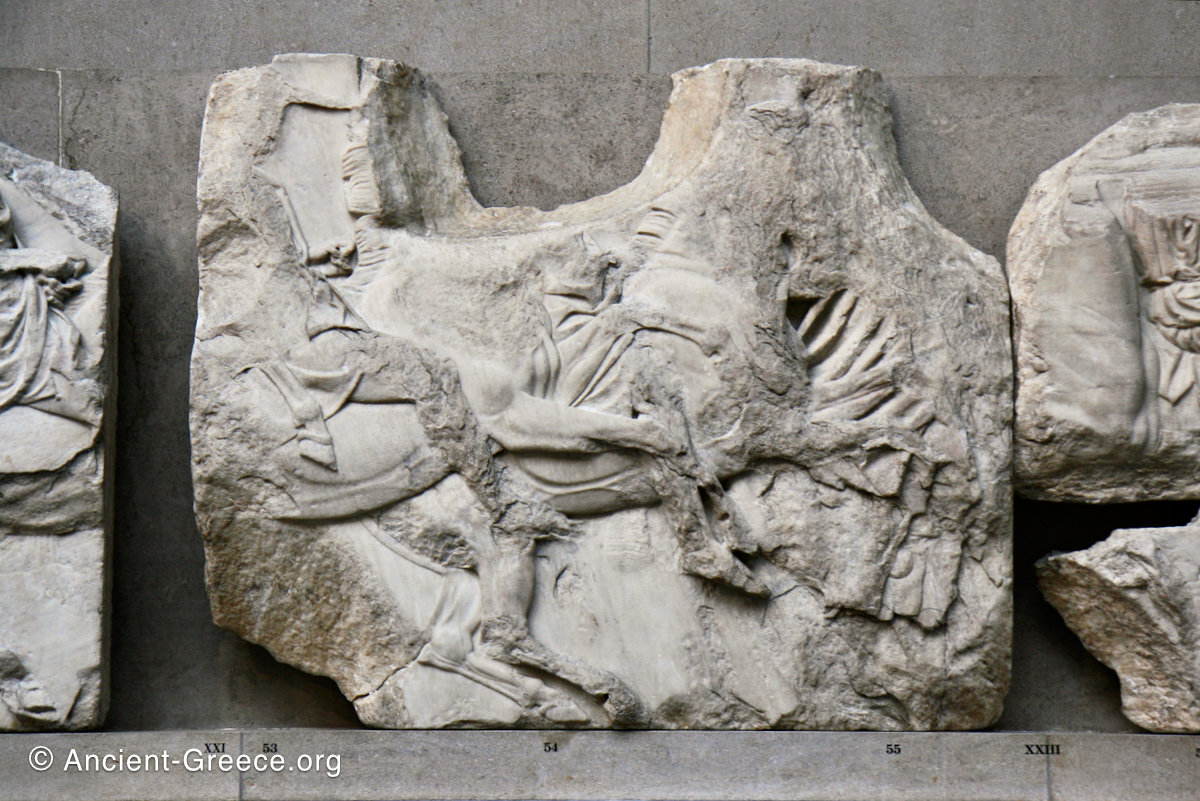
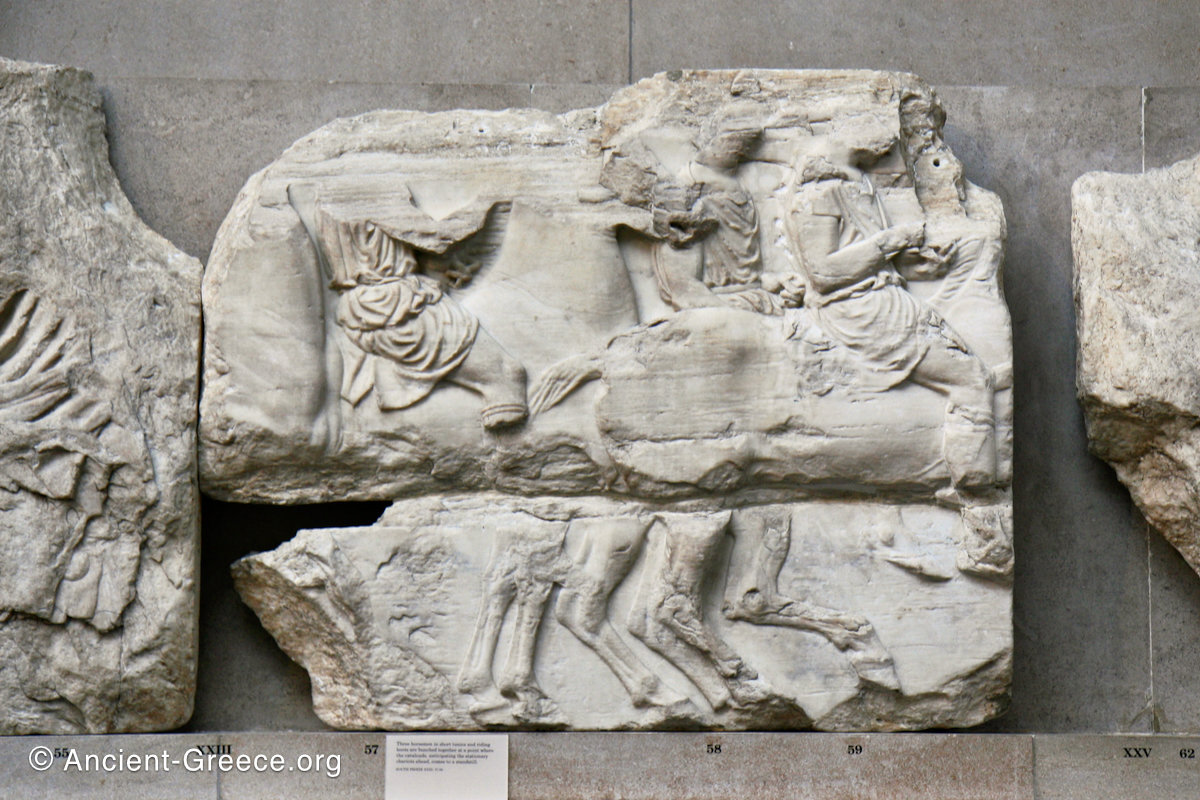
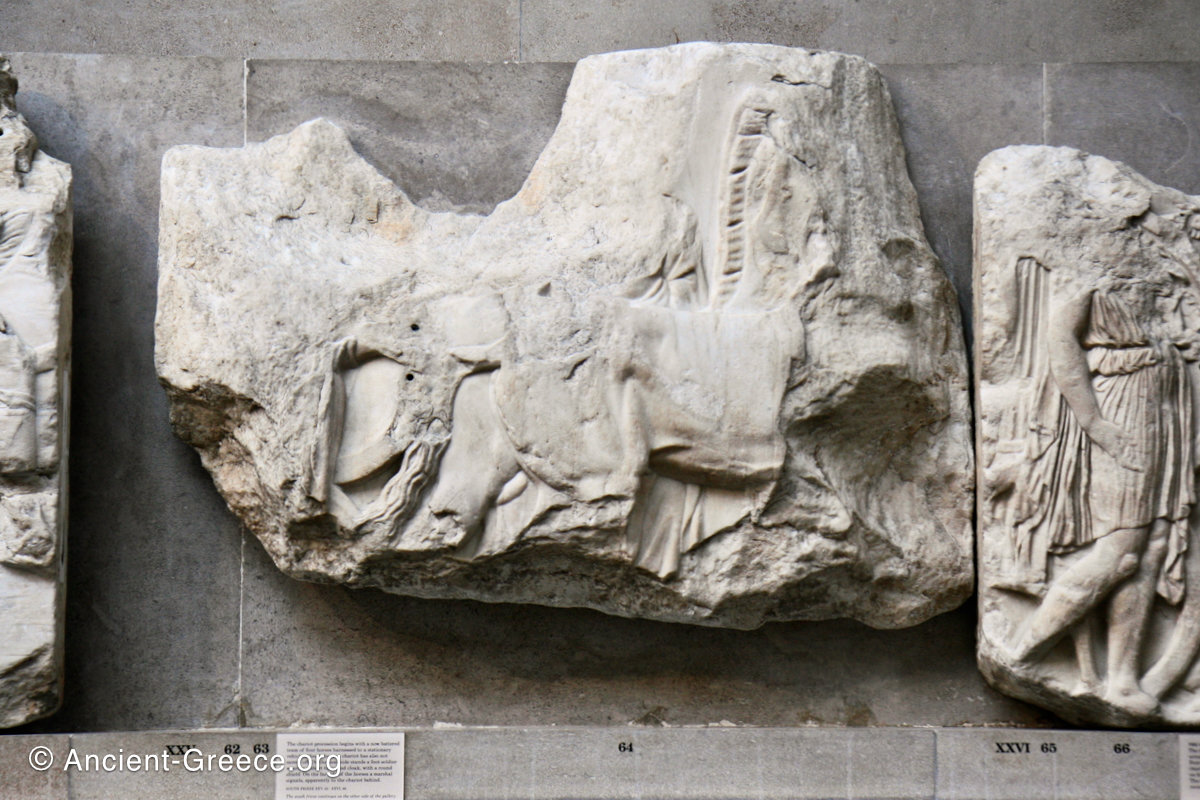
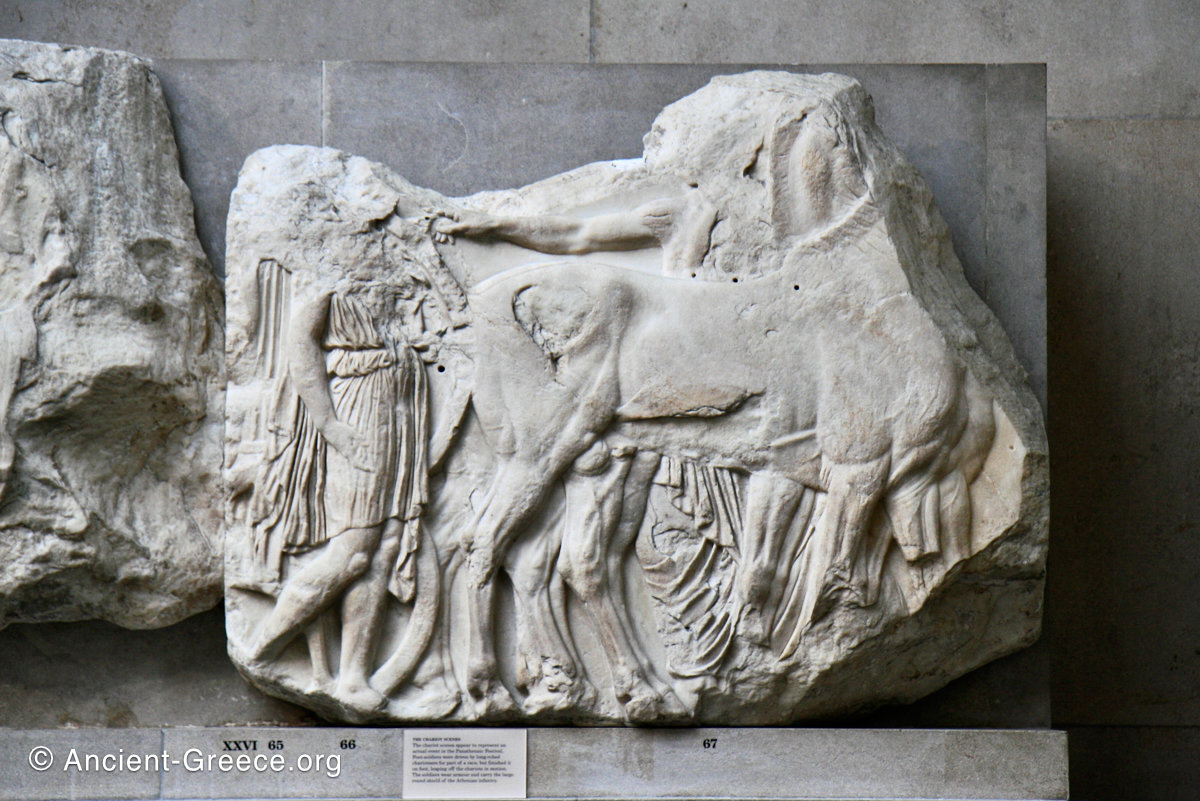
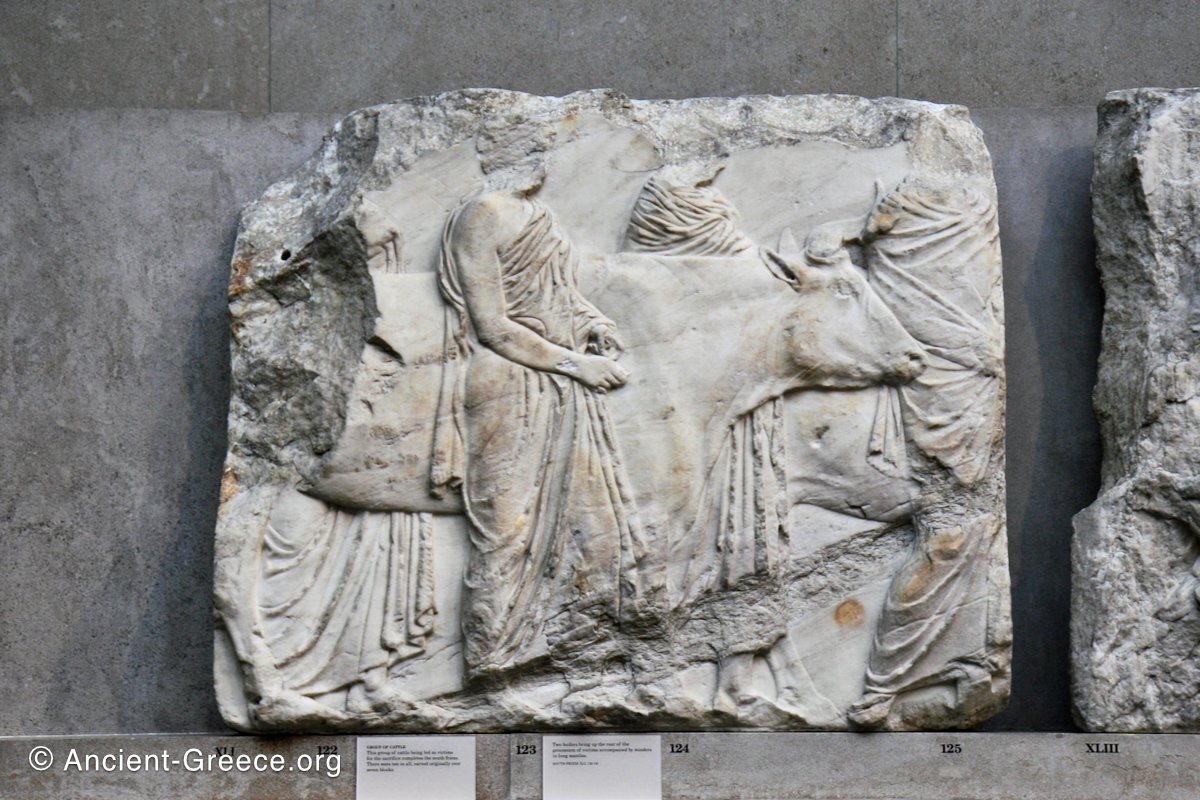
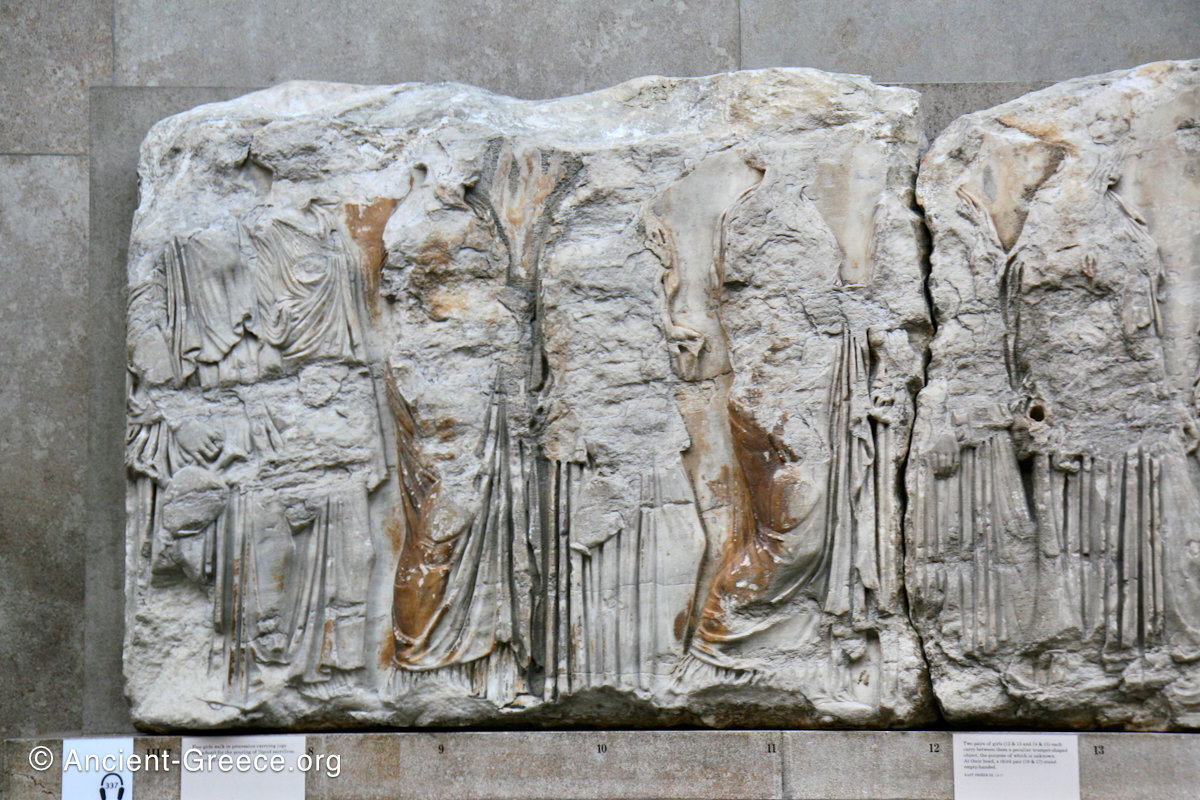
In the south frieze citizens of Athens move in procession through the south wall of the cella towards the east end and the peplos scene. The sculptures depict several calvary groups in different attires, chariots, and people leading sacrificial animals.
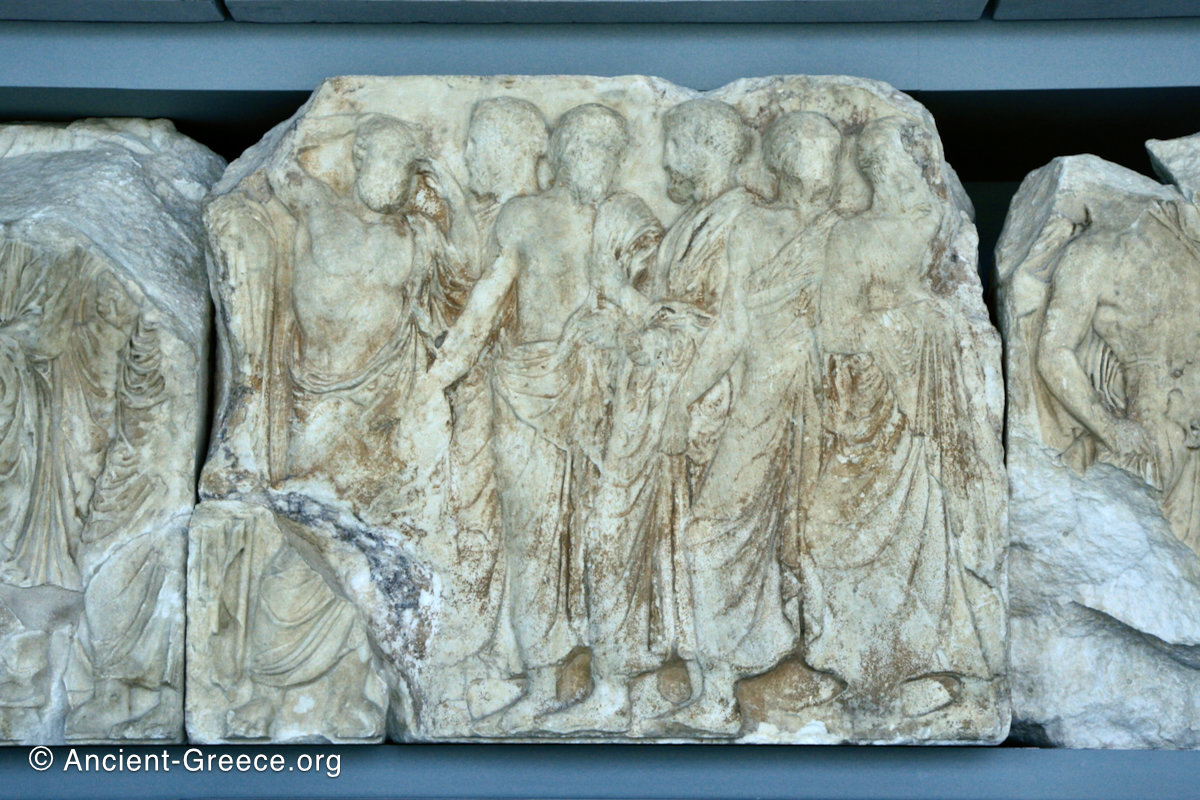
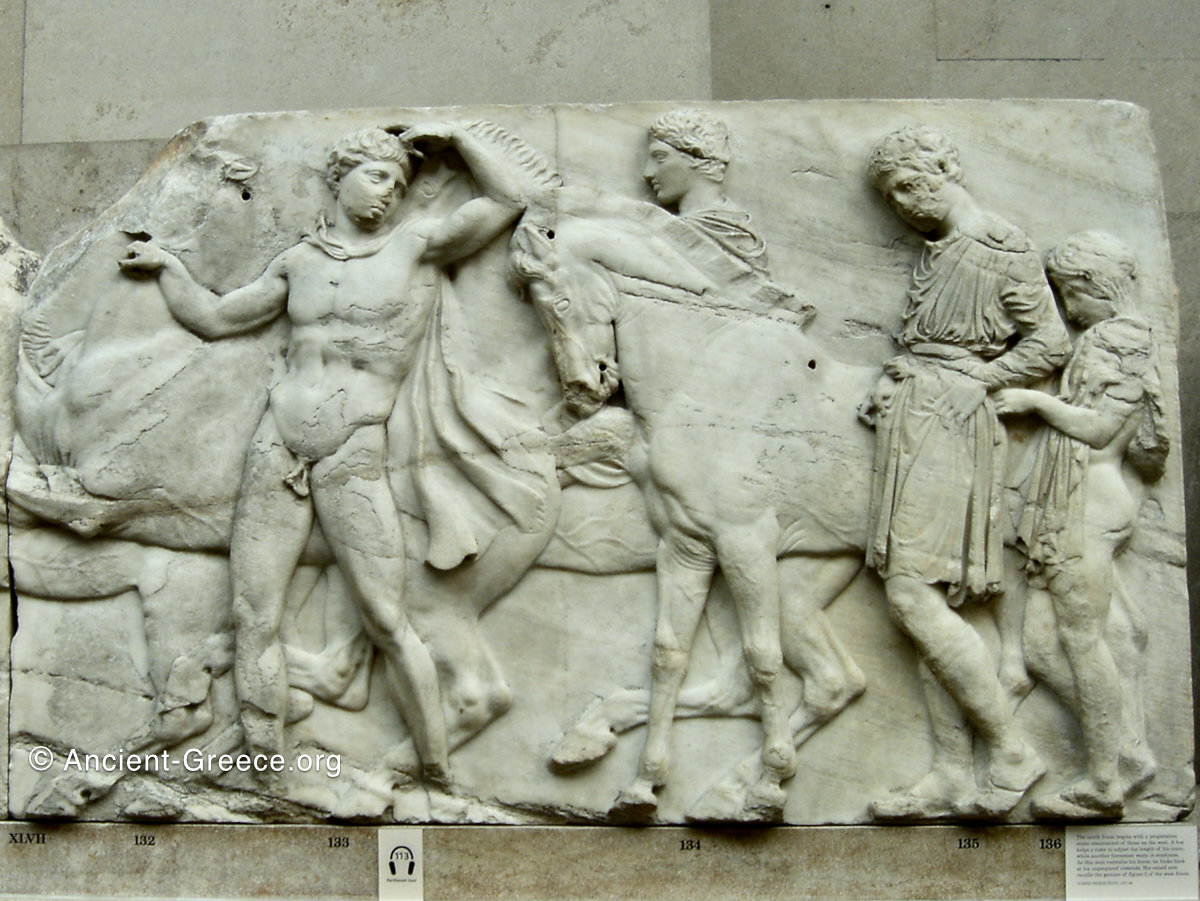
North Frieze











































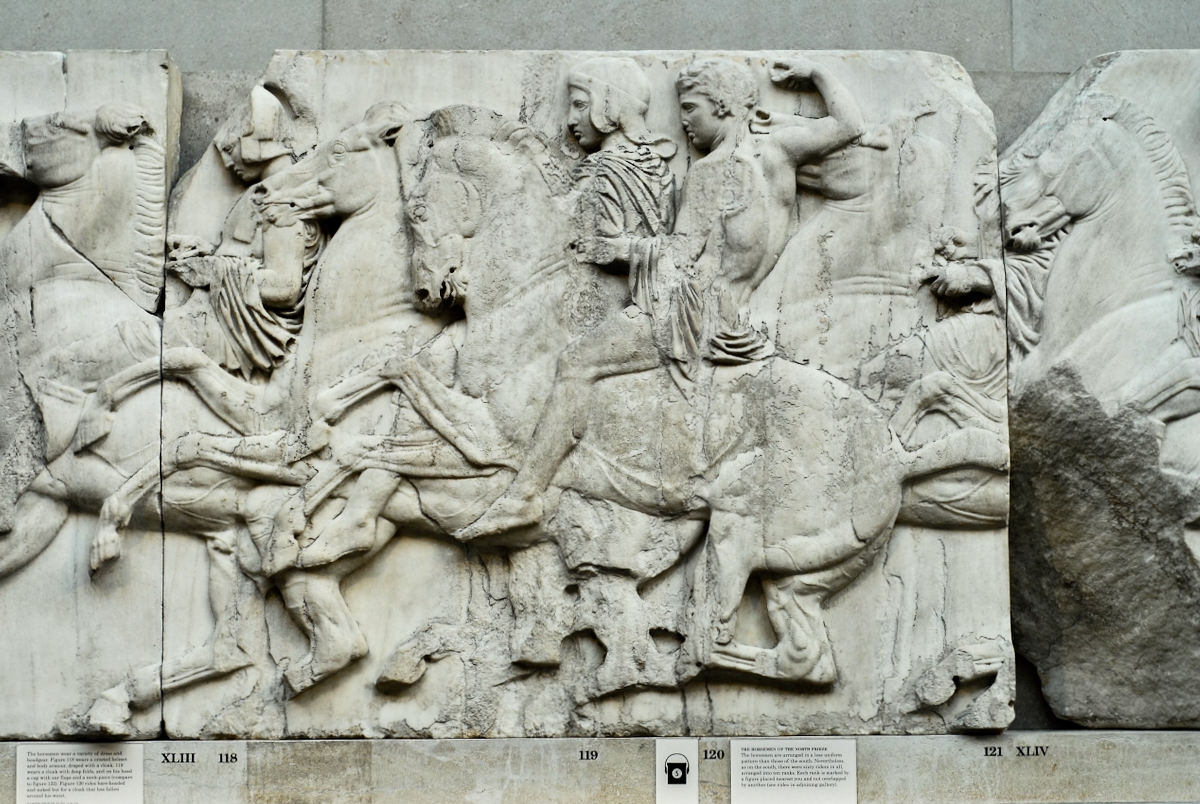
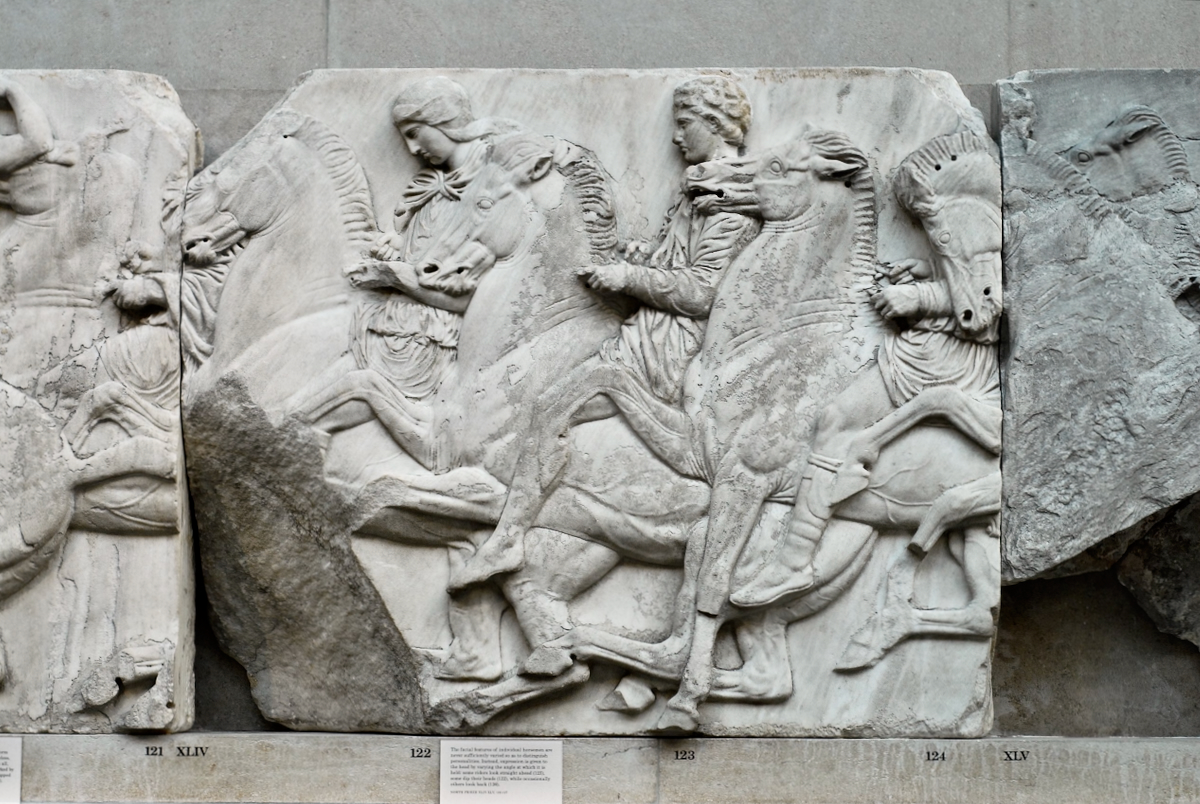
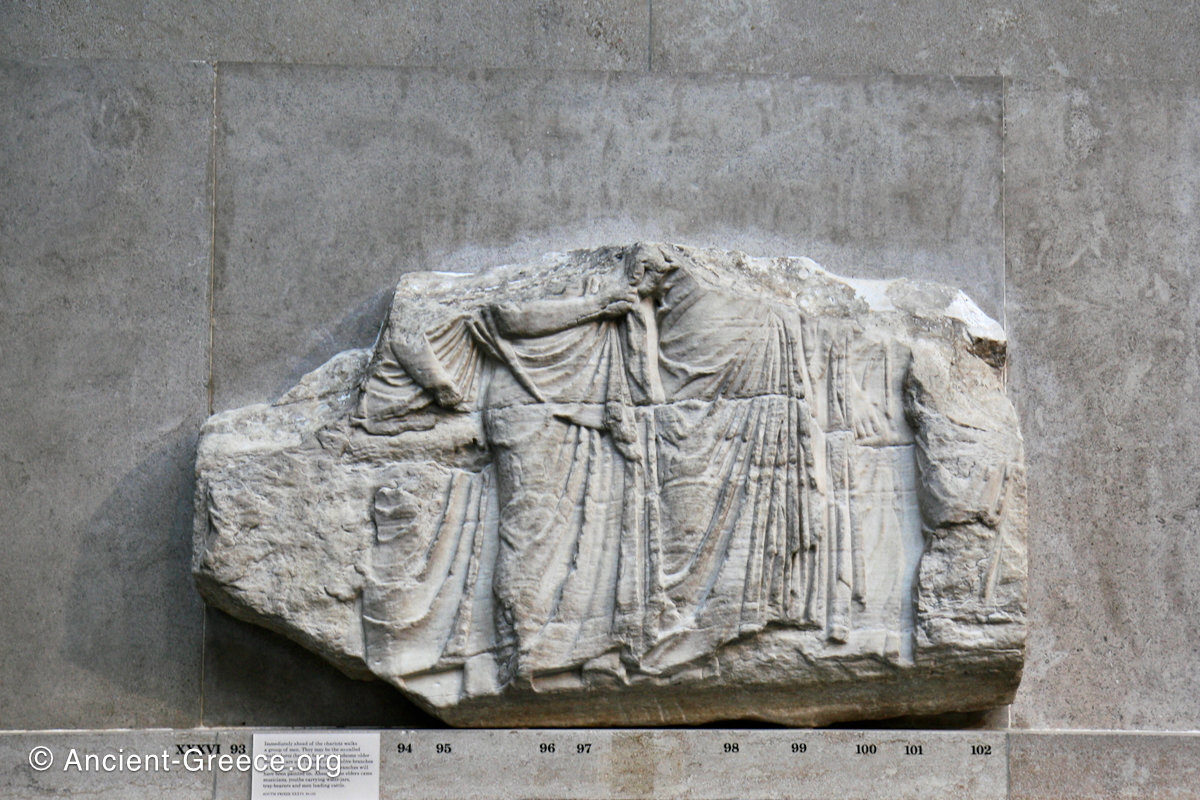
In the north frieze citizens of Athens move in procession towards the peplos scene on the east end of the temple. Horesemen, a host of elders, musicians, and people escorting sacrificial animals appear in the scenes towards the east end.
Parthenon Timeline
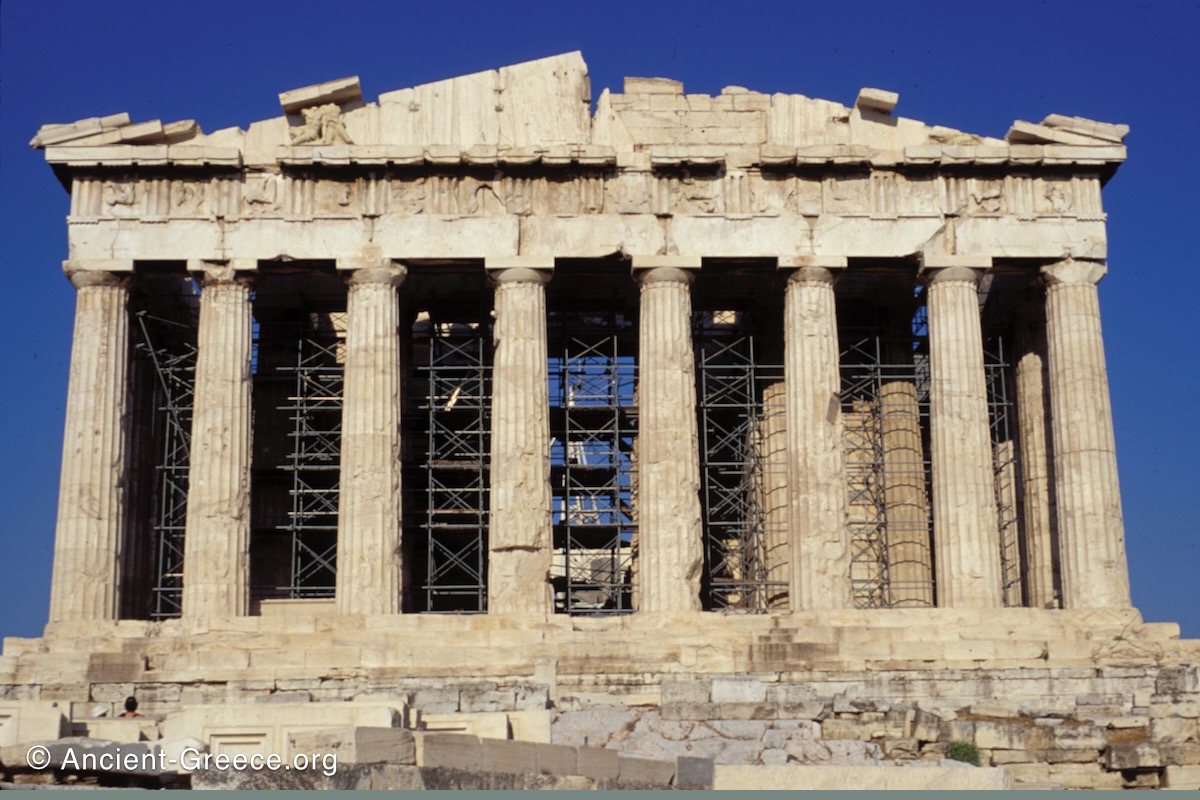
447-432 BCE: The current version of the Parthenon was built.
267 CE: Herulian Invasion: Destruction of Athenian Monuments, followed by more destruction from Vandals, and Visigoths shortly thereafter.
Circa 300 CE: The Parthenon underwent hasty repairs that redressed and refitted blocks of stone for different purposes.
6th Century: Converted into a Christian church. Sections of the frieze were removed to create windows for the church.
1180: Church renovations removed the central section of the entablature, including the central scene of the east frieze and pediment to create an enlarged apse.
1205: The Parthenon became a Latin Church.
1458: The Parthenon was converted into a Muslim mosque
1687: Explosion after bombardment in the Turkish-Venetian war left the Parthenon largely in the state we see it today.
1800-1805: The Italian painter, Lugeri, working for Lord Elgin, caused extensive destruction to the Parthenon by dislodging and sawing off parts of the ancient building as he removed the sculptures known as “The Elgin Marbles”.
1834: The Acropolis became an archaeological site.
1842-1844, 1900-1902, 1913, 1922-1933:Restoration of the Parthenon.
1940, 1954-60: Restoration of the Parthenon.
(Korres)
Related Pages